Abstract
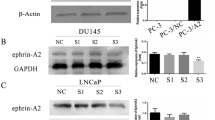
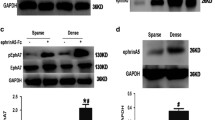
Epidermal growth faxtor receptor (EGFR)-vIII mutant has been demonstrated to over-express as prostatic neoplasms progressed from intraepithelial changes to metastatic disease. In this study, we transfected the EGFR-vIII expression vector into an immortalized normal prostate epithelium cell line RWPE-1 and established stable trans-fectants. The cell growth, glandular morphogenesis, cell motility, and soft-agar colony formation efficiency were then studied. The results showed that EGFR-vIII mutation increased the RWPE1 cell motility and clone formation efficiency, while it had no significant effect on the cell growth when compared to non-transfected as well as mock transfected RWPE-1 cells. Moreover, EGFR-vIII changed the RWPE1 acinar morphogenesis. Further study showed that these effects of EGFR-vIII mutation may be related to down-regulation of E-cadherin and up-regulation of β-catenin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilbert JA, Goetz MP, Reynolds CA, et al. Molecular analysis of metaplastic breast carcinoma: high EGFR copy number via aneusomy. Mol Cancer Ther 2008, 7: 944–51.
Li AR, Chitale D, Riely GJ, et al. EGFR Mutations in lung adenocarcinomas. Clinical testing experience and relationship to EGFR gene copy number and immunohistochemical expression. J Mol Diagn 2008, 10: 242–8.
Yatabe Y, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene amplification is acquired in association with tumor progression of EGFR-mutated lung cancer. Cancer Res 2008, 68: 2106–11.
Cho KS, Lee JS, Cho NH, Park K, Ham WS, Choi YD. Gene amplification and mutation analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor in hormone refractory prostate cancer. Prostate 2008, 68: 803–8.
Schlomm T, Kirstein P, Iwers L, et al. Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor protein overexpression and gene copy number gains in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13: 6579–84.
Cai CQ, Peng Y, Buckley MT, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor activation in prostate cancer by three novel missense mutations. Oncogene 2008, 27: 3201–10.
Olapade-Olaopa EO, Moscatello DK, MacKay EH, et al. Evidence for the differential expression of a variant EGF receptor protein in human prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 2000, 82: 186–94.
Moscatello DK, Holgado-Madruga M, Emlet DR, Montgomery RB, Wong AJ. Constitutive activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by a naturally occurring mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 1998, 273: 200–6.
Ekstrand AJ, Longo N, Hamid ML, et al. Functional characterization of an EGF receptor with a truncated extracellular domain expressed in glioblastomas with EGFR gene amplification. Oncogene 1994, 9: 2313–20.
Tang CK, Gong XQ, Moscatello DK, Wong AJ, Lippman ME. Epidermal growth factor receptor vIII enhances tumorigenicity in human breast cancer Cancer Res 2000, 60: 3081–7.
Nishikawa R, Ji XD, Harmon RC, et al. A mutant epidermal growth factor receptor common in human glioma confers enhanced tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994, 91: 7727–31.
Bello D, Webber MM, Kleinman HK, Wartinger DD, Rhim JS. Androgen responsive adult human prostatic epithelial cell lines immortalized by human papillomavirus 18. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18: 1215–23.
Webber MM, Bello D, Kleinman HK, Hoffman MP. Acinar differentiation by non-malignant immortalized human prostatic epithelial cells and its loss by malignant cells. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18: 1225–31.
Achanzar WE, Diwan BA, Liu J, Quader ST, Webber MM, Waalkes MP. Cadmium-induced malignant transformation of human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res 2001, 61: 455–8.
Okamoto M, Webber MM, Quader S, Oyasu R. Interleukin-6 and epidermal growth factor promote anchorage-independent growth of immortalized human prostatic epithelial cells treated with N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Prostate 1998, 35: 255–62.
Hsu YM, Chen YF, Chou CY, et al. KCI cotransporter-3 down-regulates E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 2007, 67: 11064–73.
Nishikawa R, Ji XD, Harmon RC, et al. A mutant epidermal growth factor receptor common in human glioma confers enhanced tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994, 91: 7727–31.
Moscatello DK, Montgomery RB, Sundareshan P, McDanel H, Wong MY, Wong AJ. Transformational and altered signal transduction by a naturally occurring mutant EGF receptor. Oncogene, 1996, 13: 85–96.
Ekstrand AJ, Sugawa N, James CD, Collins VP. Amplified and rearranged epidermal growth factor receptor genes in human glioblastomas reveal deletions of sequences encoding portions of the N- and/or C-terminal tails. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992, 89: 4309–13.
Bello-DeOcampo D, Kleinman HK, Deocampo ND, Webber MM. Laminin-1 and alpha6beta1 integrin regulate acinar morphogenesis of normal and malignant human prostate epithelial cells. Prostate 2001, 46: 142–53.
Montgomery RB, Moscatello DK, Wong AJ, Cooper JA, Stahl WL. Differential modulation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/extracellular signal-related kinase kinase and MAP kinase activities by a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 1995, 270: 30562–6.
Moscatello DK, Ramirez G, Wong AJ. A naturally occurring mutant human epidermal growth factor receptor as a target for peptide vaccine immunotherapy of tumors. Cancer Res 1997, 57: 1419–24.
Antonyak MA, Moscatello DK, Wong AJ. Constitutive activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase by a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 1998, 273: 2817–22.
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol 2006, 172: 973–81.
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J Cell Physiol 2007, 213: 374–83.
Whitaker HC, Girling J, Warren AY, Leung H, Mills IG, Neal DE. Alterations in beta-catenin expression and localization in prostate cancer. Prostate 2008, 68: 1196–205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, M., Young, C.Y.F. Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor vIII increases cell motility and clonogenecity in a prostate cell line RWPE1. J Endocrinol Invest 32, 272–278 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346466
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346466