Abstract
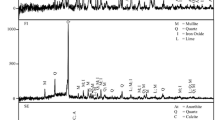
Acid mine drainage was reacted with coal fly ash over a 24 h reaction time and species removal trends evaluated. The evolving process water chemistry was modeled by the geochemical code PHREEQC using WATEQ4 database. Mineralogical analysis of the resulting solid residues was done by X-ray diffraction analysis. Selective sequential extraction was used to evaluate the transfer of species from both acid mine drainage and fly ash to less labile mineral phases that precipitated out. The quantity of fly ash, volume of acid mine drainage in the reaction mixture and reaction time dictated whether the final solution at a given contact time will have a dominant acidic or basic character. Inorganic species removal was dependent on the pH regime generated at a specific reaction time. Sulphate concentration was controlled by precipitation of gypsum, barite, celestite and adsorption on iron-oxy-hydroxides at pH > 5.5. Increase of pH in solution with contact time caused the removal of the metal ions mainly by precipitation, co-precipitation and adsorption. PHREEQC predicted precipitation of iron, aluminium, manganese-bearing phases at pH 5.53–9.12. An amorphous fraction was observed to be the most important in retention of the major and minor species at pH > 6.32. The carbonate fraction was observed to be an important retention pathway at pH 4–5 mainly due to initial local pockets of high alkalinity on surfaces of fly ash particles. Boron was observed to have a strong retention in the carbonate fraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, D. E.; Essington, M. E.; Mullen, M. D.; Ammons, J. T., (2001). Fly ash and lime-stabilized biosolid mixtures in mine spoil reclamation: Simulated weathering. J. Environ. Qual., 30(2), 608–616 (9 pages).
Abdel-Ghani, N. T.; Hegazy, A. K.; El-Chaghaby, G. A., (2009). Typha domingensis leaf powder for decontamination of aluminium, iron, zinc and lead: Biosorption kinetics and equilibrium modeling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(2), 243–248 (6 pages).
Adamo, P.; Dudka, S.; Wilson, M. J.; McHardy, W. J., (1996). Chemical and mineralogical forms of Cu and Ni in contaminated soils from the Sudbury mining and smelting region, Canada. Environ. Pollut., 91(1), 11–19 (9 pages).
Adriano, D. C.; Page, A. L.; Elseewi, A. A.; Chang, A. C.; Straughan, I., (1980). Utilization and disposal of fly ash and other coal residues in terrestrial ecosystems: A review. J. Environ. Qual., 9(3), 333–344 (12 pages).
Agyei, N. M.; Strydom, C. A.; Potgieter, J. H., (2002). The removal of phosphate ions from aqueous solution by fly ash, slag, ordinary Portland cement and related blends. Cement Concret. Res., 32(12), 1889–1897 (9 pages).
Akira, I.; Yuka, S.; Tsunenoni, N.; Hirokazu, T.; Akira, O.; Shinji, K., (2005). Leaching characteristics of boron and selenium for various coal fly ashes. Fuel., 84(5), 479–485 (7 pages).
Ball, J. W.; Nordstrom, D. K., ( 1991). WATEQ4F-user’s manual with revised thermodynamic data base and test cases for calculating speciation of major, trace and redox elements in natural waters. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File., Report 90-129 (40 pages).
Beckett, P. H. T., (1988). The use of extractants in studies on the trace metals in soils, sewage sludges and sludge-treated soils. Adv. Soil Sci., 9(5), 144–175 (32 pages).
Brittons, H. T. S., (1956). Hydrogen ions, 4th Ed. Chapman and Hall, London.
Campbell, A., (1999). Chemical, physical and mineralogical properties associated with the hardening of some South African fly ashes. M.Sc. Thesis University of CapeTown, South Africa.
Carlson, C. L.; Adriano, D. C., (1993). Environmental impacts of coal combustion residues. J. Environ. Qual., 22(2), 227–247 (21 pages).
Chao, T. T., (1972). Selective dissolution of manganese oxides from soils and sediments with acidified hydroxylamine hydrochloride. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 36(5), 764–768 (5 pages).
Cornell, R. M.; Schwertmann U., (1996). The iron oxides. VCH Verlagsgesellchaft, MBH.
Cravotta, C. A. I.; Mary, K. T., (1999). Limestone drains to increase pH and remove dissolved metals from acidic mine drainage. Appl. Geochem., 14(5), 581–606 (26 pages).
Eary, L. E.; Rai, D.; Mattigod, S. V.; Ainsworth, C. C., (1990). Geochemical factors controlling the mobilization of inorganic constituents from fossil fuel combustion residues: II, Review of the Minor Elements. J. Environ. Qual., 19(2), 202–214 (13 pages).
Erol, M., KüÇükbayrak, S.; Ersoy-MeriÇboyu, A.; Uluba, T., (2005). Removal of Cu2+ and Pb2+ in aqueous solutions by fly ash. Energy Conver. Manage., 46(7–8), 1319–1331 (13 pages).
Feng, X. D.; Dang, Z.; Huang, W. L.; Yang, C., (2009). Chemical speciation of fine particle bound trace metals. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(3), 337–346 (10 pages).
Foner, H. A.; Thomas, L. R.; Hower, C. J.; Uschi, M. G., (1999). Characterization of fly ash from Israel with reference to its possible utilization. Fuel., 78(2), 215–223 (9 pages).
Furr, A. K.; Parkinson, T. F.; Hinrichs, R. A.; Van Campen, D. R.; Bache, C. A.; Gutenmann, W. H.; John J. L. E. S.; Pakkala, I. S.; Lisk, D. J., (1977). National survey of elements and radioactivity in fly ashes: Absorption of elements by cabbage grown in fly ash soil mixtures. Environ. Sci. Tech., 11(13), 1194–1201 (8 pages).
Gitari, M. W.; Petrik, L. F.; Etchebers, O.; Key, D. L.; Iwuoha, E.; Okujeni, C., (2006). Treatment of acid mine drainage with fly ash: Removal of major contaminants and trace elements. J. Environ. Sci. Health-Part A., A 41,(8), 1729–1747 (19 pages).
Gitari, M. W.; Petrik, L. F.; Etchebers, O.; Key, D. L.; Okujeni, C., (2008). Utilization of fly ash for treatment of coal mines wastewater: Solubility controls on major inorganic contaminants. Fuel., 87(12), 2450–2462 (13 pages).
Hullet, L. D.; Weinbeger, A. J., (1980). Some etching studies of the microstructure and composition of large aluminosilicate particles in fly ash from coal-burning power plants. Environ. Sci. Tech., 14(8), 965–970 (6 pages).
Jenke, R. D.; Gordon, K. P., (1983). Chemical changes in concentrated, acidic, metal-bearing waste waters when treated with lime. Environ. Sci. Tech., 17(4), 217–223 (7 pages).
Jenne, E. A., (1977). Trace element sorption by sediments and soils-site and processes. in: Chappell, W.; Peterson, S. K. (Eds.), Proc. Symp. Molybdenum in the Environment. MarcelDekker, New York, 425–552 (28 pages).
Karbassi, A. R.; Monavari, S. M.; Bidhendi, G. R. N.; Nouri, J., Nematpour, K., (2008). Metal pollution assessment of sediment and water in the Shur River. Environ. Monitor. Assess., 147(1–3), 107–116 (10 pages).
Kitano, Y.; Minoru, O.; Masatoshi, I., (1978). Co-precipitation of borate-boron with calcium carbonate. Geochem. J., 12(3), 183–189 (7 pages).
Krüger, J. E., (2003). South African fly ash: A cement extender. A South Coal Fly Ash Association publication.
Ma, L. Q.; Rao, G. N., (1997). Chemical fractionation of cadmium, copper, nickel and zinc contaminated soils. J. Environ. Qual., 26(1), 259–264 (6 pages).
Mahvi, A. H., (2008). Application of agricultural fibers in pollution removal from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(2), 275–285 (11 pages).
Maree, J. P.; Du Plessis, P.; Van der Walt, C. J., (1992). Treatment of acidic effluents with limestone instead of lime. Water Sci. Tech., 26(1–2) 345–355 (11 pages).
Maree, J. P.; Van Tonder, G. J.; Millard, P., (1996). Underground neutralization of mine water with limestone. Water Research Commission. Report No. 609/1/96.
Mattigod, S. V.; Dhanpat, R.; Eary, L. E.; Ainsworth, C. C., (1990). Geochemical factors controlling the mobilisation of inorganic constituents from fossil fuel combustion residues: 1. Review of the major elements. J. Environ. Qual., 19(2), 188–201 (14 pages).
Mohsenzadeh, F.; Nouri, J.; Ranjbar, A.; Mohammadian Fazli, M.; Babaie, A. A., (2006). Air pollution control through kiln recycling by-pass dust in a cement factory: Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng., 3(1), 5–8 (4 pages).
Muller, J.; Seiler, K. P., (1999). Relevance of self-sealing processes in pyrite sinters for heavy metal mobility. Armanson, A. H. (Ed.), 5th. Symposium in Geochemistry of the Earth’s Surface. Balkema, Rotterdam, 211–214 (4 pages).
Nameni, M.; Alavi Moghadam, M. R.; Arami, M., (2008). Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by wheat bran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(2), 161–168 (8 pages).
Nordstrom, D. K.; Alpers, C. N., (1999). Geochemistry of acid mine waters. in: Plumlee, G. S.; Logsdon, M.J. (Eds.), The environmental geochemistry of mineral deposits part A. processes, techniques and health issues, Reviews in Economic Geology., 6A, 133–160, SEG Inc, Michigan.
Okafor, E. Ch.; Opuene, K., (2007). Preliminary assessment of trace metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(2), 233–240 (8 pages).
Page, A. L.; Elseewi, A. A.; Straughan, I., (1979). Physical and chemical properties of fly ash from coal-fired power plants with reference to environmental impacts. Resid. Rev., 71, 83–120 (38 pages).
Parkhurst, D. L., (1995). User’s guide to PHREEQC—A computer program for speciation, reaction-path, advective-transport, and inverse geochemical calculations: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report No 95-4227.
Pérez-López, R.; Nieto, J. M.; Almodovar, G. R., (2007a). Utilization of fly ash to improve the quality of the acid mine drainage generated by oxidation of a sulphide-rich mining waste: Column experiements. Chemosphere, 67(8), 1637–1646 (28 pages).
Pérez-López, R.; Cama, J.; Nieto, J. M.; Ayora, C., (2007b). The iron-coating role on the oxidation kinetics of a pyritic sludge doped with fly ash. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 71(7), 1921–1934 (14 pages).
Pérez-López, R.; Álvarez-Valero, A. M.; Nieto, J. M.; Almodóvar, G. R., (2007c). Mineralogy of the hardpan formation processes in the interface between sulphide-rich sludge and fly ash: Applications for acid mine drainage mitigation. Am. Mineralog., 92(11–12), 1966–1977 (12 pages).
Plank, C. O.; Martens, D. C., (1974). Boron availability as influenced by application of fly ash to soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc., 38(6), 974–977 (4 pages).
Reardon, E. J.; Czank, C. A.; Warren, C. J.; Dayal, R., Johnson, H. M., (1995). Determining controls on element concentrations in fly ash leachate. Waste Manage. Res., 13(5), 435–450 (16 pages).
Seth, R.; Elliot, W. C., (2000). The effects of pH regulation upon the release of sulfate from ferric precipitates formed in acid mine drainage. Appl. Geochem., 15(1), 27–34 (8 pages).
Shuman, L. M., (1985). Fractionation method for soil micronutrients. Soil Sci., 140(1), 11–22 (12 pages).
Spears, D. A.; Lee, S., (2004). Geochemistry of leachates from coal ash, Geological Society, London. Special publications. 236, 619–639 (21 pages).
Sposito, G., (1983). The chemical forms of trace metals in soils. Thornton, I. (Ed.). Applied Environmental Geochemistry. Academic press, London, 123–170 (49 pages).
Stumm, W.; Lee, G. F., (1961). Oxygenation of Ferrous iron. Ind. Eng. Chem., 53(2), 143–146 (4 pages).
Tessier, A.; Campell, P. G. C.; Bison, M., (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem., 51(7), 844–850 (7 pages).
Uhlmann, W. H.; Buttcher, O. T.; Steinberg, C. E. W., (2004). Buffering of acidic mine lakes: The relevance of surface exchange and solid bound sulphate. Mine. Water Environ., 23(1), 20–27 (8 pages).
Ure, A.; Quevaullier, P. H.; Muntau, H.; Griepink, B., (1993). Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the CEC. Int. J. Environ. Analyt. Chem., 51(1–4), 135–151 (17 pages).
Xenidis, A.; Evangelia, M.; Ioannis P., (2002). Potential use of lignite fly ash for the control of acid generation from sulphidic wastes. Waste Manage., 22(6), 631–641 (11 pages).
Younger, P. L.; Banwart, S. A.; Hedin, R. S., (2002). Mine water, hydrology, pollution, remediation. Kluwer academic Publishers Dordrecht. Chapter Two: Mine water chemistry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gitari, W.M., Petrik, L.F., Key, D.L. et al. Partitioning of major and trace inorganic contaminants in fly ash acid mine drainage derived solid residues. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 519–534 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326161
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326161