Abstract
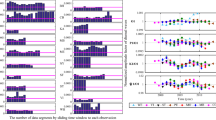
Based on the 28 series of the high precision and high minute sampling tidal gravity observations at 20 stations in Global Geodynamics Project (GGP) network, the resonant parameters of the Earth's nearly diurnal free wobble (including the eigenperiods, resonant strengths and quality factots) are precisely determined. The discrepancy of the eigenperiod between observed and theoretical values is studied, the important conclusion that the real dynamic ellipticity of the liquid core is about 5% larger than the one under the static equilibrium assumption is approved by using our gravity technique. The experimental Earth's tidal gravity models with considering the nearly diurnal free wobble of the Earth's liquid core are constructed in this study. The numerical results show that the difference among three experimental models is less than 0.1%, and the largest discrepancy compared to those widely used nowdays given by Dehant (1999) and Mathews (2001) is only about 0.4%. It can provide with the most recent real experimental tidal gravity models for the global study of the Earth's tides, geodesy and space techniques and so on.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herring, T. A, Gwinn, C. R, Shapiro, I. I., Geodesy by radio interferometry: studies of the forced nutations of the Earth 1. data analysis, Journal of Geophysical Research, 1986, 91(B5): 4745–4754.
Defraigne, P, Dehant, V, Hinderer, J., Staking gravity tide measurements and nutation observations in order to determine the complex eigenfrequency of nearly diurnal free wobble, Journal of Geophysical Research, 1994, 99(B5): 9203–9213.
Sato, T, Fluid core resonance measured by quartz tube extensometers at Esashi Earth tide station (ed. Kakkuri, J.), Proc. of 11th Int. Sympos. Earth Tides, Stuttgart: E. Schweizerbart'sche, 1991, 573–582.
Xu, J. Q, Sun, H. P, Luo, S. C., Study of the Earth's free core nutation by tidal gravity data recorded with international superconducting gravimeters, Science in China, Series D, 2002, 45(4): 337–347.
Wahr, J. M, Sasao, T., A diurnal resonance in the ocean tide and in the Earth's load response duo to the resonant free core nutation, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 1981, 64: 747–765.
Mathews, P. M., Love numbers and gravimetric factor for diurnal tides, Journal of the Geodetic Society of Japan, 2001, 47(1): 231–236.
Crossley, D. J, Hinderer, J, Global geodynamics project-GGP: status report 1994, Proc. of workshop on non-tidal gravity changes, Luxembourg: Conseil de L'Europe Cahiers du Centre Européen de Géodynamique et de Séismologie (ed. Poitevin, C.), 1995, 11: 244–269.
Wenzel, H. G., The nanogal software: data processing package Eterna 3.3, Bulletin D'informations de Marées Terrestres, 1996, 124: 9425–9439.
Ducarme, B, Sun, H. P, Xu, J. Q., New investigation of tidal gravity results from the GGP Network, Bulletin D'informations de Marées Terrestres, 2002, 136: 10761–10775.
Sun, H. P, Takemoto, S, Hsu, H. T. et al., Precise tidal gravity recorded with superconducting gravimeters at stations Wuhan/China and Kyoto/Japan, Journal of Geodesy, 2001, 74: 720–729.
Vauterin, P, Tsoft: graphical and interactive software for the analysis of earth tide data, Proc. of 13th Int. Sympos. Earth Tides (eds. Paquet, P, Ducarme, B.), Brussels: Observatoire Royal de Belgique, Série Géophysique, 1998, 481–486.
Chen, X. D, Sun, H. P., New method for pre-processing and analyzing tidal gravity observations, Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics (in Chinese), 2002, 22(3): 83–87.
Sun, H. P., Comprehensive researches for the effect of the ocean loading on gravity observations in the western Pacific area, Bulletin D'informations de Marées Terrestres, 1992, 113: 8271–8292.
Sun, H. P, Xu, H. T, Jentzsch, G. et al., Tidal gravity observations obtained with a superconducting gravimeter at Wuhan/China and its application to geodynamics, Journal of Geodynamics, 2002, 33(1–2): 187–198.
Agnew, D. C., A program for computing ocean-tide loading, Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(B3): 5109–5110.
Sun, H. P, Xu, J. Q, Ducarme, B., Experimental Earth tidal models of the core resonance obtained by stacking tidal gravity observations from GGP Stations, Bulletin D'informations de Marées Terrestres, 2002, 136: 10729–10733.
Dehant, Y, Defraigne, P, Wahr, J., Tides for a convective Earth, Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B1): 1035–1058.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Xu, J. & Ducarme, B. Experimental earth tidal models in considering nearly diurnal free wobble of the Earth's liquid core. Chin.Sci.Bull. 48, 935–940 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325679
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325679