Abstract
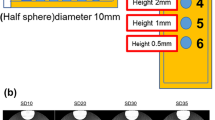
The aim of this study was to determine the thickest slice at the lowest radiation dose for detection of colon polyps larger than 5 mm in diameter at computed tomographic (CT) colonography. A colon phantom containing haustral folds, flexures, and straight segments was constructed of borosilicate. One hundred forty simulated polyps (5, 7, 10, and 12 mm) of various shapes (sessile, flat, and pedunculated) were attached at different colon locations (wall, base of fold, on the fold and fold tip). Polyps were positioned parallel, perpendicular, and oblique to the CT gantry. The air-filled phantom was scanned at different slice thicknesses (1.25-5 mm) and x-ray tube currents (5-308 mA). All polyps were identified in all data sets except one (1.25 mm slice thickness, 5 mA). In this acquisition, image noise reduced polyp visibility, and five of 140 (3%) polyps could not be identified. Unidentified polyps were 5 mm, flat or sessile in shape, located on the colon wall or base of the fold, and oblique or parallel to CT gantry. All tested CT techniques provided optimal polyp detection except settings at 1.25 mm and 5 mAs. Thin collimation ( < 5 mm) scans may not be necessary to detect clinically significant polyps.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cancer facts and figures 2002. American Cancer Society, 2002
Seeff L, Nadel M, Blackman D, Pollack L (2003) Colorectal cancer test use among persons aged > 50 years-United States, 2001. MMWR 52:193–196
Fenlon H, Nunes D, Schroy PI, et al. (1999) A comparison of virtual and conventional colonoscopy for the detection of colorectal polyps. N Engl J Med 341:1496–1503
Yee J, Akerkar GA, Hung RK, et al. (2001) Colorectal neoplasia: performance characteristics of CT colonography for detection in 300 patients. AJR 219:685–692
Fletcher JG, Johnson CD, Welch TJ, et al. (2000) Optimization of CT colonography technique: a prospective study trial in 180 patients. Radiology 216:704–711
McNitt-Gray MF (2002) Radiation dose in CT. Radiographics 22:1541–1553
McCollough CH (2002) Optimization of multidetector array CT acquisition parameters for CT colonography. Abdom Imaging 27:253–259
Bielen D, Thomeer M, Vanbeckevoort D, et al. (2003) Dry preparation for virtual CT colonography with fecal tagging using water-soluble contrast medium: initial results. Eur Radiol 13:453–458
Gryspeerdt S, Lefere P, Dewyspelaere J, et al. (2002) Optimisation of colon cleansing prior to computed tomographic colonography. JBR-BTR 85:289–296
Lefere PA, Gryspeerdt SS, Dewyspelaere J, et al. (2002) Dietary fecal tagging as a cleansing method before CT colonography: initial results-polyp detection and patient acceptance. Radiology 224: 393–403
Macari M, Lavelle M, Pedrosa I, et al. (2001) Radiology 218: 274–277
Morrin MM, Raptopoulos V (2001) Contrast-enhanced CT colonography. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI 22:420–424
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, K.T., Johnson, C.D., Anderson, S.M. et al. CT colonography: determination of optimal CT technique using a novel colon phantom. Abdom Imaging 29, 173–176 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03263754
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03263754