Abstract
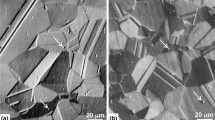
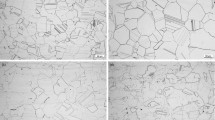
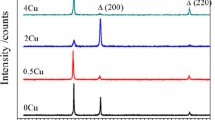
The effects of Cr, Mo and other minor additions (such as Cu and W) on corrosion resistance depends on the environment composition (eg. chloride, nitrate levels) and redox potential. These effects are first discussed in general terms and then specifically with respect to two new alloys, HASTELLOY® alloys C-22 and G-30. The beneficial effects of these elements on corrosion resistance must be balanced against the detrimental effects on thermal stability. High Cr, Mo and W levels can lead to the formation of embrittling intermetallic phases such as sigma and mu. Stability with respect to precipitation of intermetallic and carbide phases is also important from the perspective of fabricability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.Z. Friend, Corrosion of Nickel and Nickel-Base Alloys, John Wiley and Sons, N.Y. 1980.
H.J. Dundas and A.P. Bond, CORROSION/81, Paper No. 122, Presented at the Annual NACE Conference, Toronto, Canada, April 1981.
J.N. Wanklyn, Corrosion Science, v. 21, pp. 211–115, 1981.
R. Bandy, and D. Van Rooyen, Corrosion, V. 41, No. 4, pp. 228–233.
J. Kolts, J.B.C. Wu, and A.I. Asphahani, Metal Progress, September, 1983.
A. J. Sedriks, Corrosion of Stainless Steels, John Wiley & Sons, N.Y., 1979.
T.E. Evans, and A.C. Hart, Electrochemical Acta, V. 16, pp. 1955–1970, 1970.
H.H. Uhlig, P. Bond, and H. Feller, J. Electrochem. Soc, v. 110, p. 650, 1963.
H. Kita, J. of Electrochem. Soc, v. 113, No. 11, pp. 1095–1111, 1966.
M. Pourbaix, Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Acqueous Solutions, NACE Publication, 1974.
M. Raghavan et al., Met. Trpns., v. 17, pp. 1189–1194, 1983.
M. Raghavan et al., Met. Trans., v. 13A, pp. 979–984, June 1982.
R.B. Leonard, Corrosion, v. 25, pp. 222–228, 1969.
R.W. Kirchner, F.G. Hodge, Werkstoffe und Korrosion, v. 24, pp. 1042–1049, 1973.
H. Tawancy et al., J. of Metals, vol. 35, No. 6, pp. 37–43, 1983.
P.E. Manning et al, Paper No. 21, CORROSION/83, NACE Annual meeting in Anaheim, California, April, 1983.
P.E. Manning et al, Presented in ACHEMA 85 an International Meeting on Chemical Engineering, held at Frankfurt am Main, June 9–15, 1985.
Additional information
Narasi Sridhar received his Ph.D. in 1980 from the University of Notre Dame. He is currently an Engineering Associate in the Corrosion Group of Technology Department, Cabot Wrought Products Division. Dr. Sridhar is also a member of TMS.
James B.C. Wu received his Ph.D. in 1975 from University of Rochester. He is currently Manager of Asian Ventures for Cabot Stellite Division. Dr. Wu is also a member of TMS.
Paul E. Manning received his Ph.D. in 1978. He is currently a Market Development Engineer at Cabot Wrought Products Division.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sridhar, N., Wu, J.B.C. & Manning, P.E. Corrosion Resistant Ni-Cr-Mo Alloys. JOM 37, 51–53 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03258745
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03258745