Summary
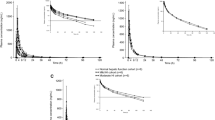
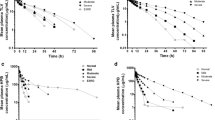
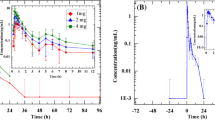
The single dose pharmacokinetics of temocapril, a novel prodrug type angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with preferential biliary excretion, were evaluated in 6 patients maintained on haemodialysis and in 1 patient on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). In a crossover design, each haemodialysis patient received a single oral dose of temocapril 1mg after breakfast on two occasions, on dialysis and nondialysis days, at an interval of 1 week. The CAPD patient received a single oral dose of temocapril 1mg. Plasma concentrations of temocapril and its active metabolite (diacid) and ACE activity were determined after drug administration. Area under the plasma concentration-time curves (AUC) in haemodialysis patients on the non-dialysis day were significantly greater than those in patients with normal renal function who were used as a reference (p < 0.01). Other pharmacokinetic parameters such as maximum plasma drug concentration (Cmax), biological half-life (t½) and time to reach Cmax (tmax) were not significantly different between the 2 groups. 24 hours after administration, the ACE inhibitions in haemodialysis patients were significantly higher than those in patients with normal renal function. There were no other significant differences between the 2 groups. The peak level of diacid (Cmax) in haemodialysis patients on the nondialysis day was significantly greater than that on the dialysis day (p < 0.05). Other pharmacokinetic parameters such as AUC, t½ and tmax were not significantly different between these 2 days. These parameters in the CAPD patient were similar to those in the haemodialysis patients on dialysis day. The results suggest that the elimination route of temocapril is mainly via the biliary route, but is partially a route permeated through a dialyser membrane or peritoneal membrane. It is suggested that temocapril is preferable to ACE inhibitors with renal elimination in the treatment of patients with hypertension undergoing dialysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duchin KL, Kripalani KJ, Kramer PK, Sica DA. Disposition and pharmacokinetics of fosinopril sodium (FS) and its diacid in hemodialysis (HD) patients. Abstract. Kidney International 35: 245, 1989
Fruncillo RJ, Rocci ML, Vlasses PH, Mojaverian P, Shepley K, et al. Deposition of enalapril and enalaprilate in renal insufficiency. Kidney International 31: S117–S122, 1987
Furuta S, Kiyosawa K, Higuchi M, Kasahara H, Saito H, et al. Pharmacokinetics of temocapril, an ACE inhibitor with preferential biliary excretion, in patients with impaired liver function. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 44: 383–385, 1993
Gavras H, Gavras I. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Hypertension 11 (Suppl. II): II37–II41, 1988
Hui KK, Duchin KL, Kripalani KJ, Chan D, Kramer PK, et al. Pharmacokinetics of fosinopril in patients with various degrees of renal function. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 49: 457–467, 1991
Jackson B, Cubela RB, Conway EL, Johnston CI. Lisinopril pharmacokinetics in chronic renal failure. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 719–724, 1988
Kawahara Y, Tokiwa H, Shimojo M. Determination of plasma angiotensin converting enzyme activity by high-performance liquid chromatography. Ann Rep Sankyo Res Lab 37: 107–112, 1985
Kelly JG, Doyle G, Donohue J, Laber M, Vandenburg MJ, et al. Pharmacokinetics of enalapril in normal subjects and patients with renal impairment. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 21: 63–69, 1986
Lowenthal DT, Irvin JD, Merrill D, Saris S, Ulm E, et al. The effect of renal function on enalapril kinetics. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 38: 661–666, 1985
Oguchi H, Miyasaka M, Koiwai T, et al. Plasma concentration and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition in patients with different renal functions after administration of temocapril, an ACE inhibitor with preferential biliary excretion. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 24: 421–427, 1993
Oizumi K, Koike H, Sada T, Miyamoto M, Nishino H, et al. Pharmacological profiles of CS-622, a novel angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. Japanese Journal of Pharmacology 48: 349–356, 1988
Ondetti MA, Rubin B, Cushman DW. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme, a new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science 196: 441–444, 1977
Onoyama K, Hirakawa H, Takishita S, Omae T, Fujishima M. Side effects of captopril in hypertensive patients with various grades of kidney dysfunction. Current Therapeutic Research 40: 333–336, 1986
Roccella EJ. The 1988 report of the joint national committee on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Archives of Internal Medicine 148: 1023–1038, 1988
Sada T, Koike H, Ikeda M. Cytosolic free calcium of aorta in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 16: 245–251, 1990
Sada T, Koike H, Miyamoto M. Long-term inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme suppresses calcium channel agonist induced contraction of aorta in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 14: 652–659, 1989a
Sada T, Koike H, Nishino H, et al. Chronic inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme decreases Ca2+-dependent tone of aorta in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 13: 582–588, 1989b
Shioya H, Shimojo M, Kawahara Y. Determination of a new angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (CS-622) and its active metabolite in plasma and urine by chromatography-mass spectrometry using negative chemical ionization. Journal of Chromatography 496: 129–135, 1989
Singhvi SM, Duchin KL, Morrison RA, Willard DA, Everett DW, et al. Disposition of fosinopril sodium in healthy subjects. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 9–15, 1988
Suzuki H, Kawaratani T, Shioya H, Uji Y, Saruta T. Study on pharmacokinetics and blood pressure lowering effect of a biliary excreted angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, CS-622, single dose study. Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicines 2: 263–270, 1992
Yamaoka K, Nakagawa T, Uno T. Statistical moment in pharmacokinetics. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 6: 547–558, 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokoo, M., Oguchi, H., Sato, K. et al. Single Dose Pharmacokinetics of Temocapril, an ACE Inhibitor with Preferential Biliary Excretion, in Dialysis Patients. Drug Invest 7, 254–261 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03257417
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03257417