Abstract
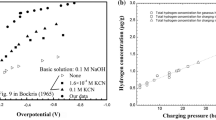
It is now apparent that Fe3Al and FeAl alloys with less than 40 at.% Al are intrinsically ductile. Brittleness is manifested only in environments providing ready access to hydrogen. Microstructure, alloy content and surface condition may alter somewhat the susceptibility to embrittlement by moisture or by hydrogen, but are key considerations in alloy design for toughness or ductility when aluminum content is within the Fe3Al-FeAl range. The susceptibility of iron aluminides to moisture and to hydrogen is a major factor hampering their development as structural alloys. Other properties which need to be improved include tensile strength and creep and impact resistance, but approaches to achieve improved strength properties must consider the susceptibility to the external environment. Development of alloys with less than 16% Al appears to be attractive for situations where reduced strength and oxidation resistance can be tolerated because of the insensitivity of these alloys to embrittlement. However, it must be realized that these alloys are not intermetallics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.S. Stoloff, Hydrogen Effects on Material Behavior(Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1990), pp. 483–497.
C.T. Liu, Intermetallic Compounds—Structure and Mechanical Properties, Proc. JIMlS-6 (Sendai, Japan: Japan Institute of Metals, 1991), pp. 703–712.
N.S. Stoloff, M. Shea, and A. Castagna, Environmental Effects on Advanced Materials, ed. R.H. Jones and R.E. Ricker (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1991), pp. 3–19.
C.T. Liu, Ordered lntermetallics—Physical Metallurgy and Mechanical Behavior, ed. C.T. Liu, R.W. Cahn, and G. Sauthoff (Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Kluwer Acad. Publ., 1992), pp. 321–334.
C.T. Liu, E.H. Lee, and C.G. McKamey, Scripta Metall., 23 (1989), pp. 875–880.
C.T. Liu, C.G. McKamey, and E.H. Lee, Scripta Metall., 24 (1990), pp. 385–390.
M. Shea, A. Castagna, and N.S. Stoloff, High Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys IV, ed. L.A. Johnson, D.P. Pope, and J.O. Stiegler (Pittsburgh, PA: MRS, 1992), pp. 609–616.
D.B. Kasul and L.A. Heldt, Environmental Effects on Advanced Materials, ed. R.H. Jones and R.E. Ricker (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1991), pp. 67–75.
A. Castagna and N.S. Stoloff, Scripta Metall., 26 (1992), pp. 673–678.
R.A. Buchanan and J.G. Kim, Dept. Of Energy, Fossil Energy Advanced Research and Development Materials Program, Report ORNL/Sub/88-07685CT92/02 (Springneld, VA: NTIS, August 1992).
D. Zhang et al., Scripta Metall., 27 (1992), pp. 297–301.
C.T. Liu, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, unpublished research (1992).
S.A. David, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, unpublished research (1993).
J. Scott, M.S. thesis, Rensselaer Polytechnic Inst. (May 1992).
A. Castagna, P.J. Maziasz, and N.S. Stoloff, High Temperature Ordered Intermetallics V, ed. I. Baker etal. (Pittsburgh, PA: MRS, 1993), pp. 1043–1048.
G.E. Fuchs and N.S. Stoloff, Acta Metall., 36 (1988), pp. 1381–1387.
J.P. Lin et al., Scripta Metall., 27 (1992), pp. 1295–1299.
C.G. McKamey, J.A. Horton, and C.T. Liu, J. Mater. Res., 4 (1989), pp. 1156–1193.
C.G. McKamey and D.H. Pierce, Scripta Metall., 28 (1993), pp. 1173–1176.
A. Castagna and N.S. Stoloff, unpublished work (1993).
A. Castagna and N.S. Stoloff, Proc. Fatigue 93, ed. J.P. Bailon and J.I. Dickson (Cradley Heath, U.K.: Engineering Materials Advisory Services, 1993).
C.T. Liu and E.P. George, High Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys IV, ed. L.A. Johnson, D.P. Pope, and J.O. Stiegler (Pittsburgh, PA: MRS, 1991), pp. 527–532.
D.J. Gaydosh and M.V. Nathal, Scripta Metall., 24 (1990), pp. 1281–1284.
P. Nagpal and I. Baker, Scripta Melall., 25 (1991), pp. 2577–2582.
O. Klein and I. Baker, Scripta Metall., 27 (1992) pp. 1823–1828.
J. Schneibel and M.G. Jenkins, Scripta Metall., 28 (1993), pp.389–393.
C.T. Liu and M. Takeyama, Scripta Metall., 24 (1990), pp. 1583–1588.
G.M. Camus, N.S. Stoloff, and D.J. Duquette, Acta Metall, 37 (1989), pp. 1497–1501.
I.M. Robertson and H.K. Birnbaum, Acta Metall., 34 (1986), pp. 363–366.
H.K. Birnbaum, Environment-Induced Cracking of Metals, ed. R.G. Gangloff and M.B. Ives (Houston, TX: NACE, 1990), pp. 21–29.
G.M. Bond, I.M. Robertson, and H.K. Birnbaum, Acta Metall., 37 (1989), pp. 1407–1213.
G.M. Bond, I.M. Robertson, and H.K. Birnbaum, Acta Metall., 36 (1988), pp. 2193–2198.
S.P. Lynch, Acta Metall., 36 (1988), p. 2639.
A.K. Kuruvilla and N.S. Stoloff, High Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys, ed. C.C. Koch, C.T. Liu, and N.S. Stoloff (Pittsburgh, PA: MRS, 1985), pp. 229–238.
C.L. Fu and G.S. Painter, J. Mater. Res., 6 (1991), pp. 719–723.
Y. Liu et al., Acta Metall., 37 (1989), pp. 507–517.
J.C.M. Li and C.T. Liu, Scripta Metall., 27 (1992), pp. 1701–1706.
D.S. Shih, G.K. Scarr, and G.E. Wasielewski, Scripta Metall., 23 (1989), pp. 973–978.
A.W. Thompson, Environmental Effects on Advanced Materials, ed. J.H. Jones and R.E. Ricker (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1991), pp. 21–23.
A.K. Kuruvilla and N.S. Stoloff, Scripta Metall., 19 (1985), pp. 83–87.
V.K. Sikka, S. Viswanathan, and S. Vyas, High Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys V, ed. I. Baker et al. (Pittsburgh, PA: MRS, 1993), pp. 971–976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoloff, N.S., Duquette, D.J. Moisture and hydrogen-induced embrittlement of iron aluminides. JOM 45, 30–35 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03222512
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03222512