Summary
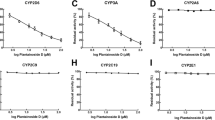
The potential interactions between rabeprazole, a widely used proton pump inhibitor, and anticancer drugs (5-fluorouracil, docetaxel, cyclophosphamide, gemcitabine, methotrexate, doxorubicin, etoposide) or drugs commonly present in the therapy of oncological patients (fluoxetine and ondansetron), were studied using in vitro human liver microsomes. The interactions between rabeprazole and the anticancer drugs were evaluated by measuring their concentrations in test and control incubations with HPLC-DAD-UV methods. To achieve this aim, nine HPLC-DAD-UV methods were developed using different stationary and mobile phases. The methods were then validated for the following parameters: selectivity, linearity, precision, and accuracy. As expected rabeprazole did not significantly inhibit the metabolism of the evaluated drugs in human liver microsomal preparations at the selected concentrations. These results shows that rabeprazole probably could be devoid of pharmacokinetic interactions with common drugs used during chemotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishizaki T., Horai Y. (1999). Cytochrome P450 and the metabolism of proton pump inhibitors-emphasis on rabeprazole. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther., 13, 27–36.
Yasuda S., Horai Y., Tomono Y., Nokai H., Yamato C., Manabe K., Kobayashi K., Chiba K., Ishizaki T. (1995). Comparison of the kinetic disposition and metabolism of E3810, a new proton pump inhibitor, and omeprazole in relation toS-mephenytoin 4′-hydroxylation status. Clin. Pharmacol. Therapy, 58, 143–154.
VandenBranden M., Ring B.J., Binkley S.N., Wrighton S.A. (1996). Interaction of human liver cytochromes P450 in vitro with LY307640, a gastric proton pump inhibitor. Pharmacogenetics, 6, 81–91.
Klotz U. (2000). Pharmacokinetic considerations in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Clin. Pharmacokinet, 38, 243–270.
Royer I., Monsarrat B., Sonnier M., Wright M., Crested T. (1996). Metabolism of docetaxel by human cytochromes P450: interactions with paclitaxel and other antineoplastic drugs. Cancer Res., 56, 58–65.
Vaclavikova R., Soucek P., Svobodova L., Anzenbacher P., Simek P., Guengerich F.P., Gut I. (2004). Different in vitro metabolism of paclitaxel and docetaxel in humans, rats, pigs, and minipigs. Drug Metab. Dispos., 32, 666–74.
Relling M.V., Nemec J., Schuetz E.G. Schuetz J.D., Gonzalez F.J., Korzekwa K.R. (1994).O-demethylation of epipodophyllotoxins is catalyzed by human cytochrome P450 3A4. Mol. Pharmacol., 45, 352–358.
Kawashiro T., Yamashita K., Zhao X.J., Koyama E., Tani M., Chiba K., Ishizaki T. (1998). A study on the metabolism of etoposide and possible interactions with antitumor or sup porting agents by human liver microsomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 286, 1294–1300.
Chang T.K.H., Weber C.F., Crespi C.L., Waxman D.J. (1993). Differential activation of cyclophosphamide and ifosphamide by cytochromes P-450 2B and 3A in human liver microsomes. Cancer Res., 53, 5629–5637
Ren S., Yang J.S., Kalhorn T.F., Slattery J.T. (1997). Oxidation of cyclophosphamide to 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide in human liver microsomes. Cancer Res., 57, 4229–4235.
Huang Z., Roy P., Waxman D.J. (2000). Role of human liver microsomal CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 in catalyzingN-de-chloroethylation of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide. Biochem. Pharmacol., 59, 961–972.
Mandrioli R., Cantelli Forti G., Raggi M.A., (2006). Fluoxetine Metabolism and Pharmacological Interactions: The Role of Cytochrome P450. Curr. Drug Metab., 7, 127–133 and references cited herein.
Dixon C.M., Colthup P.V., Serabjit-Singh C.J., Kerr B.M., Boehlert C.C., Park G.R., Tarbit M.H. (1995). Multiple forms of cytochrome P450 are involved in metabolism of ondansetron in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos., 23, 1225–1230.
Chladek J., Martinkova J., Sispera L. (1997). Anin vitro study on methotrexate hydroxylation in rat and human liver. Physiol. Res., 46, 371–379.
Diasio R.B., Harris B.E. (1989). Clinical pharmacology of 5-fluorouracil. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 16, 215–37.
Giovannetti E., Mey V., Loni L., Nannizzi S., Barsanti G., Savarino G., Ricciardi S., Del Tacca M., Danesi R. (2007). Cytotoxic activity of gemcitabine and correlation with expression profile of drug-related genes in human lymphoid cells. Pharmacol. Res., 55, 343–349.
17. De Jong J., Geijssen G.J., Munniksma C.N., Vermorken J.B., Van der Vijgh W.J. (1992): Plasma pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a new prodrugN-1-leucyldoxorubicin and its metabolites in a phase I clinical trial. J. Clin. Oncol., 10, 1897–1906.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamaro, I., Genazzani, A., Canonico, P. et al. Lack ofin vitro interactions using human liver micro-somes between rabeprazole and anticancer drugs. Eur. J. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokinet. 34, 19–26 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191379
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191379