Summary
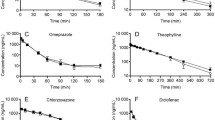
To investigate a newly developed quinolone antibiotics, the effect of antofloxacin hydrochloride on cytochrome P450 isoforms in rats was examined. A cocktail approach was adopted. Theophylline (CYP1A2), midazolam (CYP3A), chlorzoxazone (CYP2E1), dextromethorphan (CYP2D6), omeprazole (CYP2C19) and diclofenac (CYP2C9) were used as probes in the study, and own control was adopted. In Protocol 1, probes were given to rats simultaneously by co-administration with antofloxacin. The blood samples were obtained at designated time, and plasma concentrations of the six probes were determined by LC-MS. The pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated and compared in experimental groups in the absence and presence of antofloxacin. The result showed that the presence of antofloxacin resulted in a significant increase in theophylline values of AUC0-τ and t1/2 (P AUC0-τ =0.0004vs control,P t1/2 =0.005vs control), indicating that antofloxacin delayed the clearance of theophylline. In Protocol 2, the probes’ pharmacokinetic parameters were compared in rats that received six probes before and after 14.5 days of consecutive administration of antofloxacin (15 mg•kg−1, given orally, twice daily). The results suggested that the AUC0-τ of chlorzoxazone was significantly decreasedP=0.024), while that of dextromethorphan was significantly increased (P=0.027). In conclusion, these results indicated that antofloxacin may inhibit the activity of CYP1A2, thus delaying the clearance of its substrates, and may have a slight inhibitory effect on CYP2D6 as well as an inductive effect on CYP2E1 following chronic administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Ye H., Wu J.M., Yang Y.S., Chen K.X., Ji R.Y. (2002): Antibacterial activities of the derivatives -YH54 and YH57 of levofloxacin in vitro. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull., 18: 112–3.
Hong J.W., Hu C.Q. (2004): Determination of enantiomeric impurity of antofloxacin in hydrochloride by high performance liquid chromatography. Chin. J. Antibiot., 29: 349–353.
Mayer A. (1996): Overview of enzymes of drug metabolism. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharmacol., 24: 449.
Reginald F.F. (2004): Probing the world of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Mol. Interventions., 4: 157–162.
Siwaporn C., Anne N.N., Steven L. al. (2003): Combined phenotypic assessment of cytochrome P450 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A, iV-acetyltransferase-2, and xanthineoxidase activities with the ‘Cooperstown 5+1 cocktail’. Clin. Pharmacol Ther., 74: 437–447.
Magnus C., Katarina A., Per D., et al. (2003): The Karolinska cocktail for phenotyping of five human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 73: 517–528.
Zhou H.H., Zeen T., James F.M. (2004):‘Cocktail’ approaches and strategies in drug development: valuable tool or flawed science? J. Clin. Pharmacol., 44: 120–134.
Blakey G.E., Lockton J.A., Perrett J., et al. (2003): Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic assessment of a five-probe metabolic cocktail for CYPs 1A2,3A4,2C9,2D6 and 2E1. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 57: 162–169.
Tucker G.T., Houston J.B., Huang S.M. (2001): Optimizing drug development: strategies to assess drug metabolism/transporter interaction potential-toward a consensus. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 70: 103–114.
Yan S.L., Hu J.P., Xu Y.X., Zhang J.N. (2003): Simultaneous evaluation of the activity of hepatic CYP450 following administration of Fisch Fructus forsythiae by Cocktail probe drugs. Chin. Pharm. J., 38: 761–763.
Fan H.R., He F., Li Q.S., et al. (2004): Study on the influence of ginsenoside Re on cytochrome P450 isoforms by cocktail approach using probe drugs, caffeine, chlorzoxazone, omeprazole and dapsone in rats. Asian J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet., 4: 295–302.
Ashish S., Sylvie P., Pierre M., Bélanger Marie, A., Bettina A.H. (2004): A convenient five-drug cocktail for the assessment of major drug metabolizing enzymes: a pilot study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 58: 288–297.
Xu X., Xie L., Liu X.D. (2006): Simultaneous determination of midazolam, dextromethorphan and omeprazole in rat plasma. J. China Pharm. Univ., 37: 246–250.
Wijnands W.J.A., Van Herwaarden C.L.A., Vree T. (1984): Enoxacin raises plasma theophylline concentrations. Lancet, 5: 108–109.
Yoshihito N., Kohji H., Naoyuki M., Masamitsu N., Toshibaru M. (1999): Influence of gatifloxacin, a new quinolone antibacterial, on pharmacokinetics of theophyllline. J. Infect. Chemother., 5: 156–162.
Fuhr U., Anders E.M., Mahr G., Sorgel F., Sraib A.H. (1992): Inhibitory potency of quinolone antibacterial agents against cytochrome P450 1A2 activity in vivo and in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 36: 942–948.
Peterson T.C., Peterson M.R., Wornell P.A., Blanchard M.G., Gonsalez F.J. (2004): Role of CYP1A2 and CYP2E1 in the pentoxiphylline-ciprofloxacin drug interaction. Biochem. Pharmacol., 68: 395–402.
Hu J.H., Liu X.D., Xie L. (2006): An HPLC method for the determination of antofloxacin in rat plasma and bile and its pharmacokinetic study. J. China Pharm. Univ., 37: 153–156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, X., Hai-Yan, L., Li, L. et al. The influence of a newly developed quinolone: Antoflox-acin, on CYP activity in rats. Eur. J. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokinet. 33, 1–7 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191012
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191012