Summary
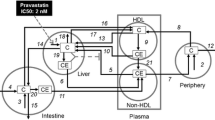
The pharmacokinetics of pravastatin, a serum-cholesterol-lowering drug, were studied in 20 middle-aged (46–59 years old,n=8) and elderly subjects (60–81 years old,n=12). Pravastatin serum levels were determined by HPLC and solid phase extraction. Cmax was 48.9±7.1 ng/ml (mean ± SEM,n=20), and the mean AUC0−4.5h was 104.4 ng·h/ml (n=5) for a 20 mg daily oral dose. A great interindividual variability was found for Cmax, which varied from 6.2 ng/ml to 117.8 ng/ml on the 20 mg dose. As could be expected, Cmax and AUC0−4.5h were dose-related, but Tmax and t1/2 were not. In six cases, the elimination of the drug in serum could be described by a single phase but in four cases with two phases. No significant difference was found in Cmax between the middle-aged and the elderly or between males and females.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Endo A., Kuroda M., Tsyhuta Y. (1976): ML-236A, ML-236B and ML-236C, new inhibitors of cholesterogenesis produced byPenicillium citrinum. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo), 29, 1346–1348.
Alberts A.W. (1988): Discovery, biochemistry and biology of lovastatin. Am. J. Cardiol., 62, 10J-15J.
Everett D.W., Chando T.J., Didonato G.C., Singhvi S.M., Pan H.Y., Weinstein S.H. (1991): Biotransformation of pravastatin sodium in humans. Drug. Metab. Dispos., 19, 740–748.
Pan H.Y., Funke P.T., Willard D.A., McKinstry D.N. (1989): Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of pravastatin sodium, a potent inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, in healthy volunteers. International. Congress Symposium Series no 162. London: Royal Society of Medicine, 9–21.
Pan H.Y. (1991): Clinical pharmacology of pravastatin, a selective inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 40(Suppl. 1), S15-S18.
Pan H.Y., Waclawski A.P., Funke P.T., Whigan D. (1993): Pharmacokinetics of pravastatin in elderly versus young men and women. Ann. Pharmacother., 27, 1029–1033.
Kjartansdóttir T., Kristinsson J., Kristjansson, S. (1992): Determination of pravastatin in serum by high-performance liquid chromatography and solid-phase extraction. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest., suppl. 211, 52, 101.
Funke P.T., Ivashkiv E., Arnold M.E., Cohen A.I. (1989): Determination of pravastatin sodium and its major metabolites in human serum/plasma by capillary gas chromatography/negative ion chemical ionisation mass spectrometry. Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom., 18, 904–909.
Morris M.J., Gilbert J.D., Hsie J.Y., Matuszewski B.K., Ramjit H.G., Bayne W.F. (1993): Determination of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors simvastatin, lovastatin and pravastatin in plasma by gas chromatography/chemical ionisation mass spectrometry. Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom., 22, 1–8.
Pan H.Y., DeVault A.R., Swites B.J. et al. (1990): Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pravastatin alone and with cholestyramine in hypercholesterolemia. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 48, 201–207.
Pan H.Y., Willard, D.A., Funke P.T., McKinstry D.N. (1987): The clinical pharmacology of SQ 3100 (CS 514) in healthy subjects. Paoletti R. et al. (Eds). Drugs Affecting Lipid Metabolism. Heidelberg: Springer.
Vega G.L., Krauss R.M., Grundy S.M. (1990): Pravastatin therapy in primary moderate hypercholesterolaemia: changes in metabolism of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. J. Intern. Med., 227, 81–94.
Franceschini G., Sirtori M., Vaccarino V., Gianfranceschi G., Chiesa G., Sirtori C.R. (1989). Plasma lipoprotein changes after treatment with pravastatin and gemfibrozil in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Lab. Clin. Med., 114, 250–259.
Johnson B.F., LaBelle P., Wilson J., Allan J., Zupkis R.V., Ronca P.D. (1990): Effects of lovastatin in diabetic patients treated with chlorpropamide. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 48, 467–472.
Saito Y., Goto Y., Nakaya N. et al. (1988): Dose-dependent hypolipidemic effect of an inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, pravastatin (CS-514), in hypercholesterolemic subjects. A double blind test. Atherosclerosis, 72, 205–211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sigurbjörnsson, S., Kjartansdóttir, T., Jóhannsson, M. et al. A pharmacokinetic evaluation of pravastatin in middle-aged and elderly volunteers. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 23, 13–18 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189821
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189821