Summary
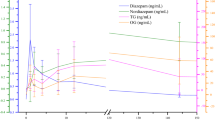
A bioavailability study of two lots of paracetamol tablets was carried out in 5 healthy volunteers, using a crossover aleatory design, and drug monitoring in urine and saliva by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Results were correlated with those obtained in an in vitro dissolution study. Statistical evaluation of bioavailability parameters indicates that the two formulations may be considered bioequivalent, in spite of differences found during early stages of the absorption process, which were preventable according to an in vitro dissolution study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameer B., Divoll M., Abemethy D.R., Greenblatt D. J., Shargel L. (1983). Absolute and relative bioavailability of oral acetaminophen preparations. J. Pharm. Sci., 72, 955–958.
Paulsen H., Kreilgard B. (1984): Bioavailability of paracetamol after single oral and rectal administration. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Sci. Ed., 12, 97–102.
Salvadó A., Cemeli J., del Pozo A. (1988): Puesta a punto de un método analítico para la determinación de paracetamol en plasma humano. C.I.F., 7 (2a.ép.), 206–209.
Van Bommel E.M.G., Raghoebar M., Tukker J.J. (1991): Kinetics of acetaminophen after single- and multiple-dose oral administration as a gradient matrix system to healthy male subjects. Biopharm. Drug Dispos., 12, 355–366.
Fagiolino P., Vázquez M. (1993): Bioequivalence study of paracetamol in saliva. Eur. J. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokinet. Special Issue 3, 164–168. Proceedings of the 5th Eur. Congr. Biopharm. Pharmacokinet. Brussels, Belgium (1993).
Sotiropoulus J.B., Deutsch T., Plakogiannis F.M. (1981): Comparative bioavailability of three commercial acetaminophen tablets. J. Pharm. Sci., 70, 422–425.
Wilson J.M., Slattery J.T., Forte A.J., Nelson S.D. (1982): Analysis of acetaminophen metabolites in urine by high performance liquid chromatography with UV and amperometric detection. J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Appl., 227, 453–462.
Hekimoglu S., Ayanoglu-Dülger G., Hincal A.A. (1987): Comparative bioavailability of three commercial acetaminophen tablets. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol., 25, 93–96.
Haile M.M., Pizzorno M.T., Volonté M.G. (1992): Efecto del aglutinante y del desintegrante sobre la disolución de comprimidos de paracetamol. Estudios de bioequivalencia in vitro. Acta Farm. Bonaerense, 11, 63–72.
Sokal R.R., Rohlf F.J. (1984): Introducción a la bioestadistica. Barcelona: Reverté, 170.
Steinijans V., Diletti E. (1983): Statistical analysis of bioavailability studies. Parametric and non parametric confidence interval. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 24, 127–136
Sokal R.R., Rohlf F.J. (1984): Introducción a la bioestadística. Barcelona: Reverté, 215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Retaco, P., González, M., Pizzorno, M.T. et al. Bioavailability study of paracetamol tablets in saliva and urine. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 21, 295–300 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189730
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189730