Abstract
The localization and elimination of35S-Thiazolidine carboxylic acid has been studied in rats following a single oral dose (100 mg/kg) and multiple oral doses (100 mg/kg/day) over 15 days.
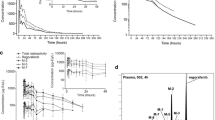
The compound was rapidly and completely absorbed as evaluated by the time of the maximum plasma35S-concentration (140 μg eq/ml at 30 min) and the amount of radioactivity in the feces (less than 1% of the dose over 48 h). Urinary excretion seems to be the unique route of elimination.
There was specific tissue accumulation of drug or metabolite, particularly in liver (29% of the dose at 3h), pancreas (7% of the dose at 3h), adrenals (320 μg eq/g at 3h), pituitary and thyroid (230 μg eq/g at 3h). Fixation of radioactivity appears significantly higher after chronic treatment than after acute treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Caroli J., Julien C. (1965). «Action thérapeutique de l’acide thiazolidine-carboxylique en hepatologie» Sem. Hop. Paris,41, 539–43.
Maitre P., Cier A. (1963). «Un nouvel hepatoprotecteur, l’acide thiazolidine-4-carboxylique. Etude pharmacologique et essais cliniques dans l’hépatite infectieuse». Sem. Hop. Paris,39, 2173–81.
Mac Kenzie C.G., Harris J. (1957). «N-Formylcysteine synthesis in mitochondria from formaldehyde and L-Cysteine via thiazolidine-carboxylic acid». J. Biol. Chem.,227, 393–406.
Cavallini D., De Marco C, Mondovi B., Trasarti F. (1956). «Studies of the metabolism of thiazolidine carboxylic acid by rat liver homogenate». Biochim. Biophys. Acta,22, 558–564.
Peres G., Zwingelstein G., Jouanneteau J. (1965). «L’absorption digestive et la fixation hépatique de l’acide L-thiazolidine 4-carboxylique». C.R. Soc. Biol.,157, 1592–1595.
Geelen G., Cier A. (1972). «Sur le métabolisme d’un médicament hépato-protecteur l’Acide Thiazolidine 4-carboxylique». Gazette Medica Italiana,131, 256–264.
Wepierre J., Laprand J., Garcet S. (1964). «Etude de la répartition et de l’élimination de l’esther méthylique de la cysteine35S chez la souris et le rat». Thérapie,19, 187–200.
Servin A., Garcet S., Huyen V.N., Cohen Y. (1976). «Pharmacocinetique compare de la L-cystéine et de l’un de ses dérivés S-substitués, la S-carboxymethyl cysteine». J. Pharmacol.,7, 275–286.
Harmand M.F., Blanquet P. «Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of35S-Thiazolidine Carboxylic acid in the rat. II. Identification of the metabolites.» in preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harmand, M.F., Blanquet, P. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of [35S]-Thiazolidine carboxylic acid in the rat. I Elimination and distribution. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 7, 323–327 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189636
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189636