Abstract
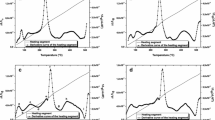
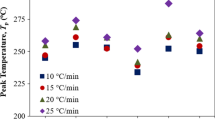
This study has been carried out by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to study the kinetics of precipitation and the dissolution of metastable and stable phases in Al-Mg-Si-(Cr,Be) alloys which were heat treated by T6, two-step aging and RRA (retrogression and reaging) treatment. The heat flow variations by phase transformation in the as-quenched specimen were calculated from DSC thermograms obtained from heating rates of 5, 10, 15 and 20°C/min. Four exothermic peaks may be attributed to the precipitation of G.P.I zone, G.P.II zone(β″), β′ and β (Mg2Si) phases, and three endothermic peaks may be attributed to the dissolution of G.P.I zone, β″ and the β′ phases, respectively. The kinetic equation (dY/dt)=f(Y)koexp(-Q*/RT) can be used to study the precipitation kinetics of Ai-Mg-Si-(Cr, Be) alloys, where Q*, ko, and f(Y)are the activation energy, frequency factors and the function of Y, respectively. The kinetic parameters measured from DSC curves can be used to interpret the transformation kinetics.The formation rate of β″ phase in the Al-Mg-Si alloy increased by the small addition of Be. This is because Be increases the nucleating rate of the β″ phase due to the decrease of the matrix/β″ interface energy. By the addition of Be or Cr and Be in Al-Mg-Si alloy, G.P. zone was easily decomposed during retrogression treatment at 225°C for 3 min. Therefore, maximum hardness can be obtained by RRA (150°C/20 min→225°C/3 min→ 180°C/3O min) in Al-0.8%Mg-1.0%Si-0.05% Be and Al-0.8% Mg-l.0% Si-0.l% Cr-0.05% Be alloys owing to the high density of β″ and β′ precipitates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Thomas,J. Inst. Metals 90, 57 (1961).
A. K. Jena, A. K. Gupta and M. C. Chaturved,Acta metall. 37, 885 (1989).
A. Luo, D. J. Lloyd, A.Gupta and W. V. Youdelis,Acta metall. 41, 769 (1993).
H. K. Cho, K. D. Woo and I. S. Eun, in2nd Int. Conf. on Al Alloys (eds., C. Q. Chen and E. A. Starke, Jr.), p. 83, Beijing, China (1990).
S. Fujikawa and K. Hirano,J. Nucl. Mater. 69–70, 564 (1978).
Sotak,Bull. Jpn. Inst. Met. 24, 797 (1985).
J. S. Lee, S. W. Kim and K. D. Woo,J. Kor. Inst. Met. & Mater. 36, 1355 (1998).
J. S. Lee,Ph. D Dissertation, p. 60, Chonbuk National University (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, K.D., Lee, J.S. & Kim, S.W. Calorimetric investigation of precipitation kinetics in Al-Mg-Si-X(Cr,Be) alloys. Metals and Materials 5, 363–368 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187759
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187759