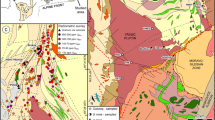
Abstract
Single zircon LAM-ICPMS U-Pb dating indicates that the Guidong granitic complex is a multistage batholith formed during Indosinian-Yanshanian time. The Luxi body (239 ±5 Ma) and the Xiazhuang body (235.8 ±7.6 Ma) intruded during Indosinian time, whereas the Aizi body (160.1 ±6.1 Ma) and the Siqian body (151 ±11 Ma) formed during Yanshanian time. Inherited zircons (1275–2137 Ma) in the Xiazhuang body imply that at least part of the source rocks of the Guidong complex are from the Proterozoic basement of southeast China. Detailed single zircon LAM-ICPMS U-Pb dating results provide important evidence for understanding the evolution, tectonic setting and mineralisation of the complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, P. R., Hua, R. M., Zhang, B. T. et al., Early Yanshanian post-orogenic granitoids in the Nanling region—Petrological constraints and geodynamic settings, Science in China, Ser. D, 2002, 8: 755–768.
Zhang, C. J., The features of uraninite in Guidong granite complex and its significance to search for uranium deposit, Journal of Chendu College of Geology (in Chinese), 1990, 17: 10–17.
Zhang, C. J., Discussion on the genetic type and metallogenetic specialization for Guidong granite massif, Uranium Geology (in Chinese), 1991, 7: 223–234.
Lin, J. R., On the difference of petrological characteristics and conditions for uranium metallogenesis between the eastern and western Guidong granite massif, Uranium Geolohy (in Chinese), 1992, 8: 93–99.
Wang, X. C., Rao, B., A geological study of basic dikes in Guidong granite of northern Guangdong province, Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences Edition) (in Chinese), 1989, 25: 120–435.
Machado, N., Gauthier, G., Determination of207Pb/206Pb ages on zircon and monazite by laser-ablation ICPMS and application to a study of sedimentary provenance and metamorphism in southeastern Brazil, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60: 5063–5073.
Poller, U., Liebetrau, V., Todt, W., U-Pb single-zircon dating under cathodoluminescence control (CLC-method): application to polymetamorphic orthogneisses, Chemical Geology, 1997, 139: 287–297.
Norman, M. D., Pearson, N. J., Sharma, A. et al., Quantitative analysis of trace elements in geological materials by laser ablation ICPMS: instrumental operating conditions and calibration values of NIST glasses, Geostandards Newsletter, 1996, 20: 247–261.
Belousova, E. A., Griffin, W. L., Shee, S. R. et al., Two age populations of zircons from the Timber Creek kimberlites, Northern Territory, as determined by laser-ablation ICP-MS analysis, Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2001, 48: 757–765.
Wang, X., Griffin, W. L., O’Reilly, S. Y. et al., Morphology and geochemistry of zircons from late Mesozoic igneous complexes in coastal SE China, Mineralogical Magazine, 2002, 66(2): 235–251.
Griffin, W. L., Belousova, E. A., Shee, S. R. et al., Crustal evolution in the northern Yilarn Craton: U-Pb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons, Precambrian Research, 2003, (in press).
Ludwig, K. R., Isoplot · a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Certer Special Publication la, 2000.
Hsü, K. J., Sun, S., Li, J. L., Huanan Alps, not South China platform, Science in China, Ser. B, 1988, 31(1): 109–119.
Carter, A., Roques, D., Bristow, C. et al., Understanding Mesozoic accretion in Southeast Asia: Significance of Triassic thermotectonism (Indosinian orogeny) in Vietnam, Geology, 2001, 29: 211–214.
Ren, J. S., Chen, T. Y., Niu, B. G. et al., Tectonic Evolution of the Continental Lithosphere and Metallogeny in Eastern China and Adjacent Areas (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1990, 26–27.
Meng, Q. R., Zhang, G. W., Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of Qinling orogen, central China, Tectonophysics, 2000, 323: 183–196.
Ren, J. S., Wang, Z. X., Chen, B. W. et al., The Tectonics of China from a Global View, Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999, 1–82.
Shen, W. Z., Ling, H. F., Li, W. X. et al., Study on the Nd-Sr isotopic compositions of granitoids in SE China, Geological Journal of China Universities (in Chinese), 1999, 5: 22–82.
Chen, J. F., Jahn, B. M., Crustal evolution of southeastern China: Nd and Sr isotopic evidence, Tectonophysics, 1998, 284: 101–133.
Hong, D. W., Xie, X. L., Zhang, J. S., An exploration on the composition, nature and evolution of mid-lower crust in south China based on the Sm-Nd isotopic data of granites, Geological Journal of China Universities (in Chinese), 1999, 5: 361–871.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Deng, P., O’Reilly, S.Y. et al. Single zircon LAM-ICPMS U-Pb dating of Guidong complex (SE China) and its petrogenetic significance. Chin.Sci.Bull. 48, 1892–1899 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184074
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184074