Abstract
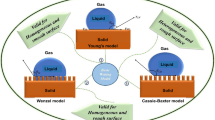
Superhydrophobicity is referred to the wettability of a solid surface which has a water apparent contact angle greater than 150°. It has attracted great interest in both fundamental researches and practical applications. This paper discusses two models: Wenzel model and Cassie model, to describe the superhydrophobic states of surface. The effects of surface morphology and microstructure on superhydrophobicity are discussed, and the internal relationship between Wenzel and Cassie states is presented. These two superhydrophobic states can coexist and they present different properties on contact angle hysteresis. It is reported that the irreversible transition can be realized from Cassie state to Wenzel state under some certain conditions. This paper also gives a review of recent progresses in the strategies of fabricating superhydrophobic surfaces by designing microstructured or microtextured surfaces. Finally, the fundamental research and applications of superhydrophobic surfaces are prospected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lafuma, A., Quere, D., Superhydrophobic states, Nature materials, 2003, 2: 457–460.
Feng, L., Li, S., Li, Y. et al., Super-hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial, Adv. Mater., 2002, 14: 1857–1860.
Blossey, R., Self-cleaning surfaces-virtual realities, Nature materials, 2003, 2: 301–306.
Wang, R., Hashimoto, K., Fujishima, A. et al., Light-induced amphiphilic surfaces, Nature, 1997, 388: 431–432.
Benedix, R., Dehn, F., Quaas, J. et al., Application of titanium dioxide photocatalysis to create self-cleaning building materials, Lacer, 2000, 5: 157–166.
Neinhuis, C., Barthlott, W., Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces, Annals of Botany, 1997, 79: 667–677.
Barthlott, W., Neinhuis, C., Purity of the sacred lotus or escape from contamination in biological surfaces, Planta, 1997, 202: 1–8.
Gu, Z.-Z., Uetsuka, H., Takahashi, K. et al., Structure color and the lotus effect, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2003, 42(8): 894–897.
Wenzel, R. N., Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water, Ind. Eng. Chem., 1936, 28: 988–994.
Cassie, A., Baxter, S., Wettability of porous surfaces, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1944, 40: 546–551.
Shibuichi, S., Onda, T., Satoh, N. et al., Super water-repellent surfaces resulting from fractal structure, J. Phys. Chem., 1996, 100: 19512–19517.
Cottin-Bizonne, C., Barrat, J.-L., Bocquet, L. et al., Low-friction flows of liquid at nanopatterned interfaces, Nature materials, 2003, 2: 237–240.
McHale, G., Newton, M. I., Frenkel’s method and the dynamic wetting of heterogeneous planar surfaces, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2002, 206: 193–201.
Taylor, G. I., Michael, D. H., On making holes in a sheet of fluid, J. Fluid Mech., 1973, 58: 625–639.
Onda, T., Shibuichi, S., Satoh, N. et al., Super water-repellent fractal surfaces, Langmuir, 1996, 12: 2125–2127.
Bico, J., Tordeux, C., Quere, D., Rough wetting, Europhys. Lett., 2001, 55(2): 214–220.
Bico, J., Thiele, U., Quere, D., Wetting of textured surfaces, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2002, 206: 41–46.
Patankar, N. A., On the modeling of hydrophobic contact angels on rough surfaces, Langmuir, 2003, 19: 1249–1253.
Oner, D., McCarthy, T. J., Ultrahydrophobic surfaces, Effects of topography length scales on wettability, Langmuir, 2000, 16: 7777–7782.
Yoshimitsu, Z., Nakajima, A., Watanable, T. et al., Effects of surface structure on the hydrophobicity and sliding behavior of water droplets, Langmuir, 2002, 18: 5818–5822.
Ramos, S. M. M., Charlaix, E., Benyagoub, A., Contact angle hysteresis on nano-structured surfaces, Surface Science, 2003, 540: 355–362.
Furmidge, C. G. L., Studies at phase interfaces, I. The sliding of liquid drops on solid surfaces and a theory for spray retention, J. Colloid Sci. 1962, 17, 309–324.
Chen, W., Fadeev, A. Y., Hsieh, M. C. et al., Ultrahydrophobic and ultralyophobic surfaces: Some comments and examples, Langmuir, 1999, 15: 3395–3399.
Huppert, H. E., Flow and instability of a viscous current running down a slope, Nature, 1982, 300: 427–429.
Aussillous, P., Quere, D., Liquid marbles, Nature, 2001, 411: 924–927.
Richard, D., Clanet, C., Quere, D., Surface phenomena: Contact time of a bouncing drop, Nature, 2002, 417: 811.
Richard, D., Quere, D., Viscous drops rolling on a tilted non-wettable solid, Europhys. Lett., 1999, 48: 286–291.
Mahadevan, L., Pomeau, Y., Rolling droplets, Phys. Fluids, 1999, 11: 2449–2453.
Kijlstra, J., Reihs, K., Klamt, A., Roughness and topology of ultra-hydrophobic surfaces, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2002, 206: 521–529.
Zhang, X., Shi, F., Yu, X. et al., Polyelectrolyte multilayer as matrix for electrochemical deposition of gold clusters: Toward super-hydrophobic surface, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126: 3064–3065.
Buzio, R., Boragno, C., Biscarini, F. et al., The contact mechanics of fractal surfaces, Nature materials, 2003, 2: 233–236.
Feng, L., Song, Y., Zhai, J. et al., Creation of a superhydrophobic surface from an amphiphilic polymer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2003, 42(7): 800–802.
Jiang, L., Super-hydrophobic surfaces from natural to artificial, Modern Scientific Instruments (in Chinese), 2003, 3: 6–10.
He, B., Patankar, N. A., Lee, J., Multiple equilibrium droplet shapes and design criterion for rough hydrophobic surfaces, Langmuir, 2003, 19: 4999–5003.
Rascon, C., Parry, A. O., Geometry-dominated fluid adsorption on sculpted solid substrates, Nature, 2000, 407: 986–989.
Terray, A., Oakey, J., Marr, D. W. M., Microfluidic control using colloidal devices, Science, 2002, 296: 1841–1844.
Seto, M., Westra, K., Brett, M., Arrays of self-sealed microchambers and channels, J. Mater. Chem., 2002, 12: 2348–2351.
Zhao, B., Moore, J. S., Beebe, D., Principles of surface-directed liquid flow in microfluidic channels, J. Anal. Chem., 2002, 74(16): 4259–4268.
Feng, X., Feng, L., Jin, M. et al., Reversible super-hydrophobicity to super-hydrophilicity transition of aligned ZnO nanorod films, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126: 62–63.
Blossey, R., Bosio, A., Contact line deposits and cDNA microar-rays: a “twin spot effect”, Langmuir, 2002, 18: 2952–2954.
Herminghaus, S., Roughness-induced non-wetting, Europhys. Lett., 2000, 52(2): 165–170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Wu, X., Lou, Z. et al. Superhydrophobicity from microstructured surface. Chin.Sci.Bull. 49, 1779–1787 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183400
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183400