Abstract
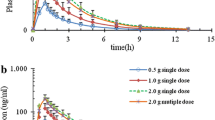
KR-984055 is a new oral cephalosporin antibiotic with activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Lipophilic ester-type prodrugs of KR-984055, i.e., KR-999001 and KR999002, have been synthesized in an attempt to increase the oral bioavailability of this broadspectrum antibiotic agent. In this study we determined the oral bioavailability of KR-984055 and its prodrugs in the rat, and evaluated the pharmacokinetic model that best describes the plasma concentration behavior following single intravenous (IV) and oral single dose. In addition, concentrations in plasma as well as biliary and urinary recovery of KR-984055 were determined. Also, protein binding of KR-984055 in plasma was examinedin vitro. The degree of protein binding of KR-984055was in the range of 92.09∼94.77%. KR-984055 exhibited poor oral bioavailability (7.02 ± 1.58%). The observed oral bioavailabilities of KR-984055 from KR999001 and KR-999002 were 38.77± 2.81% and 39.81 ± 5.25%, respectively. These data were calculated from the levels of free KR-984055 in plasma. Oral KR-999001 and KR-999002 were not recovered from plasma, suggesting that it was readily cleaved to free KR-984055. KR999001 and KR-999002 appear to be an efficient oral prodrug of KR-984055 that deserved further clinical evaluation in human.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell, J., Chantrell, L. J. and Eastmond, R., Purificationand partial characterization of rat intestinal cefuroxime axetil esterase.Biochem. Pharmacol., 36, 2317–2324 (1987).
Gabrielsson, J. and Weiner, D.,Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic data analysis: Concepts and applications. Swedich PharmaceuticalPress, Stockholm, (1997).
Li, W., Escarpe, P. A., Eisenberg, E. J., Cundy, K. C., Sweet, C., Jakeman, K. J., Merson, J., Lew, W., Williams, M., Zhang, L., Kim, C. U., Bischofberger, N., Chen, M. S. and Mendel, D. B., Identification of GS 4104 as an orally bioavailableprodurg of the influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitor GS 4071.Antimicrobia/ Agents and Chemotherapy, 42(3), 647–653 (1998).
Micropartition system MPS-1: For separation of free from protein-bound microsolute. Amicon Division, WR. Grace & Co, USA.
Naesens, L., Balzarini, J., Blschofberger, N. and De Clercq, E., Antiretroviral activity and pharmacokineticsin mice of oral bis (pivaloyloxymethyl)-9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine, the bis(povaloyloxymethyl) ester prodrug of 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) adenine.AntimicrobialAgents and Chemotherapy, 40, 22–28 (1996).
Ruiz-Carretero, P., Nacher, A., Merino-Sanjuan, M. and Casabo, V. G., Pharmacokinetics and absolute bioavailability of oral cefuroxime axetil in the rat.International Journal of pharmaceutics, 202, 89–96 (2000).
Okudaira, N., Tatebayashi, T., Speirs, G. C., Komiya, I.. and Sugiyama, Y., A study of the intestinal absorption of an estertype prodrug, ME3229, in rats: active efflux transport as a cause of poor bioavailability of the active drug.The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 294, 580–587 (2000).
Shargel, L. and Yu. A.,Applied Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics. Appleton & Lange, Stamford. (1999).
Stoeckel, K. Hofheinz, W., Laneury, J. P., Duchene, P., Shedlofsky. S. and Blouin, R. A., Stability of cephalosporin prod rug esters in human intestinal juice: Implications for oral bioavailability.Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 42, 2602–2606 (1998).
Umemura, K., Ikeda, Y., Kondo, K., Nakashima, M., Naganuma, H., Hisaoka, M., Nishino, H. and Tajima, M., Safety and pharmacokinetics of CS-834, a new oral carbapenem antibiotic, in healthy volunteers.Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 41, 2664–2669 (1997).
Wilkins, J., Ashofteh, A., Setoda, D., Wheatley, W. S., Huigen, H. and Ling, W., Ultrafiltration using the Amicon MPS-1 for assessing methadone plasma protein binding.Ther Drug Manit., 19(1), 83–87 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Y.S., Woo, S.K., Jung, M.H. et al. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of oral cephalosporins, KR-984055 and its prodrugs, KR-999001 and KR-999002, in the rat. Arch Pharm Res 26, 83–88 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179937
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179937