Abstract
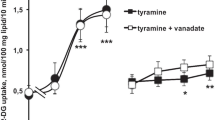
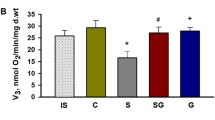
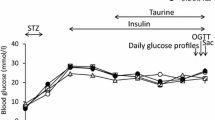
The biogenic amine tyramine has been reported to stimulatein vitro glucose transport in adipocytes, cardiomyocytes and skeletal muscle, and to improvein vivo glucose utilization in rats. These effects were dependent on amine oxidation, since they were blocked by inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (MAO) and semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO). We thus tested in this work whether a prolonged treatment with tyramine could improve glucose tolerance in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. First, tyramine content of standard rodent chow was determined by HPLC and daily tyramine intake of control rats was estimated to be around 26 μmol/kg body weight. Then, tyramine was administred during 3 weeks in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats at 29 μmol/kg by daily i.p. injection alone or together with vanadate 0.02 μmol/kg. In another group of diabetic rats, tyramine was subcutaneously delivered at 116 μmol/kg/day by osmotic minipumps. All tyramine treatments resulted in a decrease of the hyperglycemic responses to an i.p. glucose load. Adipocytes isolated from either untreated or treated diabetic rats were sensitive to the stimulation of glucose uptake by tyramine. However, diabetic animals receiving tyramine for three weeks did not recover from their hyperglycemia, hypoinsulinemia and glucosuria. These results show that the improvement of glucose tolerance induced by prolonged tyramine administration occurs in an insulin-depleted model and probably results from peripheral insulin-like actions of the oxidation of MAO/SSAO substrates, such as the stimulation of glucose uptake into adipocytes.
Resumen
Se ha descrito que la amina biogénica tiramina estimulain vitro el transporte de glucosa en adipocitos, cardiomiocitos y músculo esquelético y mejora la utilización de glucosa en la rata. Estos efectos son dependientes de la oxidación de la tiramina por la monoamino-oxidasa (MAO) y la amino-oxidasa sensible a semicarbazida (SSAO). En este trabajo, se estudia si un tratamiento crónico con tiramina aumenta la tolerancia a la glucosa en ratas diabéticas por estroptozotocina. El contenido en tiramina del alimento estándar para roedores se determinó por HPLC y se estimó que el consumo diario de tiramina en ratas control era de unos 26 μmol/kg de peso corporal. Por tanto, se administró diariamente durante 3 semanas tiramina por vía i.p. a la dosis de 29 μmol/kg, sola o con vanadato 0.02 μmol/kg a ratas diabéticas por estroptozotocina. Otro grupo recibió tiramina por vía subcutánea mediante minibombas osmóticas liberando 116 μmol/kg/día. Los tratamientos con tiramina han inducido disminución de las respuestas hiperglucemiantes a la sobrecarga de glucosa. En adipocitos aislados de ratas diabéticas, tratadas o no, la tiramina estimula el transporte de glucosa. Sin embargo, los animales diabéticos tratados con tiramina no se recuperaron de su hiperglucemia, hipoinsulinemia y glucosuria. Nuestros datos sugieren que la mejora de la tolerancia a la glucosa inducida por el tratamiento crónico con tiramina se observa en un modelo deficiente en insulina y probablemente se debe a acciones insulinomiméticas. Esto tambien indica que la administración de sustratos de MAO/SSAO podría constituir la base de nuevos tratamientos para mejorar la utilización de la glucosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abella, A., Marti, L., Camps, M., Claret, M., Fernandez-Alvarez, J., Gomis, R., Gumà, A., Viguerie, N., Carpéné, C., Palacin, M., Testar, X. and Zorzano, A. (2003):Diabetes,52, 1004–1013.
Enrique-Tarancon, G., Castan, I., Morin, N., Marti, L., Abella, A., Camps, M., Casamitjana, R., Palacin, M., Testar, X., Degerman, E., Carpéné, C. and Zorzano, A. (2000):Biochem. J.,350, 171–180.
Fankhauser, C., Charieras, T., Caille, D. and Rovei, V. (1994):J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Meth.,32, 219–224.
Faraj, B. A., Fulenwider, J. T. and Rypins, E. B. (1979):J. Clin. Invest.,64, 413–420.
Fontana, E., Boucher, J., Marti, L., Lizcano, J. M., Testar, X., Zorzano, A. and Carpéné, C. (2001):Biochem. J.,356, 769–777.
Lu, B., Ennis, D., Lai, R., Bogdanovic, E., Nikolov, R., Salamon, L., Fantus, C., Le-Tien, H. and Fantus, I. G. (2001):J. Biol. Chem. 276, 35589–35598.
Lyles, G. A. (1996):Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol.,28, 259–274.
Mercier, N., Moldes, M., El Hadri, K. and Fève, B. (2001):Biochem. J.,358, 335–342.
Morin, N., Lizcano, J. M., Fontana, E., Marti, L., Smih, F., Rouet, P., Prévot, D., Zorzano, A., Unzeta, M. and Carpéné, C. (2001):J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.,297, 563–572.
Morin, N., Visentin, V., Calise, D., Marti, L., Zorzano, A., Testar, X., Valet, P., Fischer, Y. and Carpéné, C. (2002):J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.,303, 1238–1247.
Panagiotidis, G., Strenström, A. and Lundquist, I. (1993):Eur. J. Pharmacol.,233, 285–290.
Pryme, I. F., Tiburcio, A. F., Flores, D. and Mattson, B. (1998): In COST 917—Biogenically active amines in food.Eds: S. Bardocz, A. White & A.F. Tiburcio, Office for publications of the european communities, Luxembourg, 1, 69–73.
Romero, R., Sanchez-Vinas, M., Gasquez, D. and Bagur, M. G. (2002):J. Agric. Food Chem.,50, 4713–4717.
Tamin, N. M., Bennett, L. W., Shellem, T. A. and Doerr, J. A. (2002):J. Agric. Food Chemistry,50, 5012–5015.
Visentin, V., Prevot, D., Marti, L. and Carpéné, C. (2003):Eur. J. Pharmacol.,466, 235–243.
Zorzano, A., Abella, A., Marti, L., Carpéné, C., Palacin, M. and Testar, X. (2003):Biochim. Biophys. Acta,1647, 3–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Visentin, V., Marq, P., Bour, S. et al. Effect of prolonged treatment with tyramine on glucose tolerance in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Physiol. Biochem. 59, 225–232 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179919
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179919