Abstract
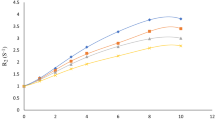
The oxidation of ferrous to ferric ions due to ionizing radiation has been used for chemical dosimetry since 1927. The introduction of metal indicator dye xylenol orange (XO) sensitises the measurement of ferric ion yield. A ferrous sulphate- agarose- xylenol orange (FAX) gel was prepared and the gel then exposed to dose ranging from 0.2 to 10 Gy using various high energy photon and electron beams from a linear accelerator. Some general characteristics of FAX such as energy dependence, optical density (OD)-dose relationship, reproducibility and auto-oxidation of ferrous ions were analysed. The radiation yield G of the gel was calculated for gels prepared in oxygen and in air and the values were 46.3±2.1 and 40.9±1.4 Fe3+ per 100 eV for photons respectively. However for stock gel which was kept for 5 days preirradiation the G value decreased to 36.6±1.1. The gel shows linearity in OD-dose relationship, energy independence and reproducibility over the dose range investigated. Auto-oxidation of ferrous ions resulted in optical density changes of less than 1.5% per day.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fricke, H. and Morse, S.,The chemical action of roentgen rays on dilute ferrous sulphate solutions as a measure of dose. Am. J. Roentgenol. Radium Therapy Nucl. Med. 18: 430–435, 1927.
Attix, F. H. and Roesch, W. C.,Radiation Dosimetry Vol II 2nd Ed. Academic Press, New York and London, 1966.
Appleby, A. and Leghrouz, A.,Imaging of radiation dose by visible color development in ferrous-agarose-xylenol orange gels. Med. Phys. 18: 309–312, 1991.
Tarte, B.J. and van Doorn, T.,Absorbance measurement with a helium-neon laser for chemical dosimetry. Aust. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 16: 75–78, 1993.
Brindha, S., Rose, J.V.R., Sathyan, S., Singh, R.R.I. and Ravindran, B.P.,Modified ferrous ammonium sulphate benzoic acid xylenol orange (MFBX) and thermoluminescent dosimeters— a comparative study. Phys. Med. Biol. 47: N153-N158, 2002.
Kron, T., Metcalfe, P. and Pope, J.,Investigation of the tissue equivalence of gels used for NMR dosimetry. Phys. Med. Biol. 38: 139–150, 1993.
Keall, P. and Baldock, C.,A theoretical study of the radiological properties and water equivalence of three types of gels used for radiation dosimetry. Aust. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 22: 85–91, 1999.
De Deene, Y., Venning, A., Hurley, C., Healy, B.J. and Baldock, C.,Dose-response stability and integrity of the dose distribution of various polymer gel dosimeters. Phys. Med. Biol. 47: 2459–2470, 2002.
Fong, P.M., Keil, D.C., Does, M.D. and Gore, J.C.,Polymer gels for magnetic resonance imaging of radiation dose distributions at normal room atmosphere. Phys. Med. Biol. 46: 3105–3113, 2001.
Rae, W.I.D., Willemse, C.A., Lotter, M.G., Engelbrecht, J.S. and Swarts, J.C.,Chelator effect on ion diffusion in ferroussulphate-doped gelatin gel dosimeters analysed by MRI. Med. Phys. 23: 15–23, 1996.
Baldock, C., Harris, P.J., Piercy, A.R. and Healy, B.J.,Experimental determination of the diffusion coefficient in twodimensions in ferrous sulphate gels using the finite element method. Aust. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 24: 19–30, 2001.
Gum, F., Scherer, J., Bogner, L., Solleder, M., Rhein, B. and Bock, M.,Preliminary study on the use of an inhomogeneous anthropomorphic Fricke gel phantom and 3D magnetic resonance dosimetry for verification of IMRT treatment plans. Phys. Med. Biol. 47: N67-N77, 2002.
Boudou, C., Biston, M., Corde, S., Adam, J., Ferrero, C., Esteve, F. and Elleaume, H.,Synchrotron stereotactic radiotherapy: dosimetry by Fricke gel and Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 49: 5135–5144, 2004.
Tarte, B.J., Jardine, P.A. and van Doorn, T.,Laser-scanned agarose gel sections for radiation field mapping. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 36: 175–179, 1996.
Healy, B.J., Zahmatkesh, M.H., Nitschke, K.N. and Baldock, C.,Effect of saccharide additives on response of ferrousagarose-xylenol orange radiotherapy gel dosimeters. Med. Phys. 30: 2282–2291, 2003.
Gupta, B.L. and Narayan, G.R.,G(Fe 3+)values in the FBX Dosimeter. Phys. Med. Biol. 30: 337–340, 1985.
Task Group 21, Radiation Therapy Committee, AAPM.Protocol for the determination of absorbed dose from high energy photon and electron beams. Med. Phys. 10: 741–771, 1983.
Gupta, B.L., Bhat, R.M., Gomathy, K.R. and Susheela, B.Radiation chemistry of the ferrous-sulphate-benzoic acid — xylenol orange system. Radiat. Res. 75: 269–277, 1978.
Schulz, R.J., deGuzman, A.F., Nguyen, D.B. and Gore, J.C.,Dose-response curves for Fricke infused agarose gels as obtained by nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys. Med. Biol. 35: 1611–1622, 1990.
Hill, B., Back, S.A.J., Lepage, M., Simpson, J., Healy, B. and Baldock, C.,Investigation and analysis of ferrous sulphate polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) gel dosimeter. Phys. Med. Biol. 47: 4233–4246, 2002.
Schreiner, L.J.,Fricke gel dosimetry. In Proceedings of DOSGEL 2001 2nd Int Conference on Radiotherapy Gel Dosimetry in Australia. Edited by Baldock C. and De Deene Y. p. 15–22, 2001.
Audet, C. and Schreiner, L.J.,Multiple-site fast exchange model for spin-lattice relaxation in the Fricke-gelatin dosimeter. Med. Phys. 24: 201–209, 1997.
Bero, M.A., Gilboy, W.B. and Doran, S.J.,Investigation into the radiochromic (FXG) gel dosimeter: stability and uncertainty in optical measurements. In Proceedings of DOSGEL 2001 2nd Int Conference on Radiotherapy Gel Dosimetry in Australia. Edited by Baldock C.and De Deene Y. p. 77–79, 2001.
Gupta, B.L., Narayan, G.R., Bhat, R.M., Kini, U.R., Ramaswamy, R S. and Suseela, B.,Use of the FBX dosimeter for the quality assurance of 60 Co and high energy teletherapy machines by mail. Phys. Med. Biol. 37: 2095–2102, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leong, L.H., Kandaiya, S. & Seng, N.B. Characterisation of a Ferrous Agarose Xylenol ( FAX ) gel for radiotherapy dose measurement. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 30, 135–140 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178418
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178418