Abstract
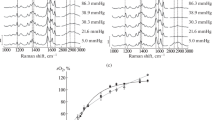
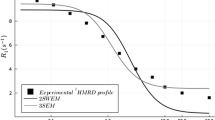
The microviscosity and the protein rotational correlation time are analyzed in samples of hemoglobin A and hemoglobin S with the intracellular concentration at 36°C and during spontaneous deoxygenation. With this purpose, we use glutathione and carbonmonoxy hemoglobin labeled with 4-maleimido-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) as probes and 4-maleimido TEMPO bound to the hemoglobin (A and S) as a spin label. The saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance experiment showed a sigmoidal behavior, and an increase (about twice) of the hemoglobin rotational correlation time and microviscosity during the polymerization process of hemoglobin S. The delay time determined by this method coincides with that obtained in proton magnetic resonance experiments. These results help to explain the temporal behavior of the proton relaxation times obtained in samples of hemoglobin A and S under the same experimental conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eaton W.A., Hofricter J.: Adv. Prot. Chem.40, 63–279 (1990)
Ferrone F.A., Manning J.M., Wei B., Josephs R., Bookchin R.M., Briehl R.W., Li X.: J. Biol. Chem.277, 13479–13487 (2002)
Cabal C., Fernández A., Lores M., Alvarez E., Losada J., Soler C., Pérez E. in: Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (Boesch Ch., Heshiki A., Grist T. M., eds.), p. 1705, Sixth Scientific Meeting and Exhibition, Sidney, Australia 1998. Berkeley: ISMRM 1998.
Lores M., Cabal C.: Appl. Magn. Reson.28, 79–84 (2005)
Van-Quynh A., Willson S., Bryant R.: Biophys. J.84, 558–563 (2003)
Herrmann A., Müller P.: Biochim. Biophys. Acta885, 80–87 (1986)
Gennaro A.M., Luquita A., Rasia M.: Biophys. J.71, 389–393 (1996)
Thiyagarajan P., Johnson M.E.: Biophys. J.42, 269–274 (1983)
Thomas D.D., Dalton L.R., Hyde J.S.: J. Chem. Phys.65, 3006–3024 (1976)
Bryant R.G., Shirley W.M.: Biophys. J.32, 3–16 (1980)
Daveloose D., Fabre G., Berleur F., Testylier G., Leterrier F.: Biochim. Biophys. Acta763, 41–49 (1983).
Fernández A.: Ph.D. thesis, University of Oriente, Santiago de Cuba, Cuba, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lores, M., Cabal, C., Nascimento, O. et al. EPR study of the hemoglobin rotational correlation time and microviscosity during the polymerization of hemoglobin S. Appl. Magn. Reson. 30, 121–128 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166986
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166986