Abstract
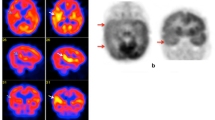
Accurate localization of epileptic foci is important for pre-surgical evaluation of patients with medically intractable epilepsy, and F-18 FDG PET has been proved to be a valuable method for this purpose. To examine the clinical value with interictal brain perfusion SPECT, we performed brain perfusion SPECT of Tc-99m HMPAO by means of a high resolution SPECT camera, and compared the results with F-18 FDG PET images and MRI in 10 patients with medically intractable epilepsy. In 9 of 10 patients (90%), FDG PET images showed focal hypo-metabolism in the area corresponding with the results of electroencephalography (EEG). SPECT images, however, demonstrated hypo-perfused lesions which corresponded with hypo-metabolic lesions on FDG PET images in only 6 cases (60%). Although MRI showed abnormal findings in 8 cases, the lesions were not directly related to epileptic foci in 2 cases. In conclusion, FDG PET is a valuable tool for accurate localization of epileptic foci. Brain perfusion SPECT, however, may not always be paralleled to metabolism visualized on FDG PET images.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Khalil BW, Sackellares JC, Latack JT, Vaderzant CW. Magnetic resonance imaging in refractory epilepsy.Epilepsia 25: 650, 1984.
Laster DW, Penry JK, Moody DM. Chronic seizure disorders: contribution of MR imaging when CT is normal.Am J Neuroradiol 6: 177–180, 1985.
Latack JT, Abou-Khalil BW, Siegel GJ, Sackellares JC, Gabrielson T, Aisen AM. Patients with partial seizures: evaluation by MR, CT and PET imaging.Radiology 159: 159–163, 1986.
Sussman NM, Scanlon M, Garfinkle W. Magnetic resonance imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy: comparison with EEG and computed tomography.Epilepsia 25: 650–651, 1984.
Sperling MR, Wilson G, Engel J Jr, Babb TL, Phelps M, Bradley W. Magnetic resonance imaging in intractable partial epilepsy: correlative studies.Ann Neurol 20: 57–62, 1986.
Ryding E, Rosen I, Elmqvist D, Ingvar DH. SPECT measurements with Tc-99m-HMPAO in focal epilepsy.J Cereb Bloob Flow Metab 8: 95–100, 1988.
Duncan R, Patterson J, Hadley DM, Wyper DJ, McGeorge AP, Bone I. Tc-99m-HMPAO single photon emission computed tomography in temporal lobe epilepsy.Acta Neurol Scand 81: 287–293, 1990.
Grasso E, Ambrrogio L, Cognazzo A, Gerbino-Promis PC, Zagnoni P, Camuzzini GF, et al. Single photon emission computed tomography with Tc-99m-HMPAO in the study of focal epilepsy.Ital J Neurol Sci 10: 175–179, 1989.
Bonte FJ, Devous MD, Stokely EM, Homan RW. Singlephoton tomographic determination of resional cerebral blood flow in epilepsy.AJNR 4: 544–546, 1983.
Neirinckx RD, Canning LR, Piper IM, Nowotnik DP, Pickett RD, Holmes RA, et al. Technetium-99m-d,1-HMPAO: A new radiopharmaceutical for SPECT imaging of regional cerebral blood perfusion.J Nucl Med 28: 191–202, 1987.
Theodore WH, Newmark ME, Sato S, Brooks R, Patronas N, Paz R De La, et al. F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in refractory complex partial seizures.Ann Neurol 14: 429–437, 1983.
Henry TR, Mazziotta JC, Engel Jr J, Christenson PD, Zhang JX, Phelps ME, et al. Quantifying interjctal metabolic activity in human temporallobe epilepsy.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10: 748–757, 1990.
Abou-Khalil BW, Siegel GJ, Sackellares JC, Gilman S, Hichwa R, Marshall R. Positron emission tomography studies of cerebral glucose matabolism in chronic partial epilepsy.Ann Neurol 22: 480–486, 1987.
Engel J Jr, Brown WJ, Kuhl DE, Phelps ME, Mazziotta JC, Crandall PH. Pathological findings underlying focal temporal lobe hypometabolism in partial epilepsy.Ann Neurol 12: 518–528, 1982.
Kuhl DE, Engel J Jr, Phelps ME, Selin C. Epileptic patterns of local cerebral metabolism and perfusion in humans determined by emission computed tomography of F-18 FDG and N-13 NH3.Ann Neurol 8: 348–360, 1980.
Engel J Jr, Kuhl DE, Phelps ME, Crandall PH. Comparative localization of epileptic foci in partial epilepsy by PCT and EEG.Ann Neurol 12: 529–537, 1982.
Stefan H, Pawlik G, Bocher-Schwarz HG, Biersack HJ, Burr W, Penin H, et al. Functinal and morphological abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy: a comparison of interictal and ictal EEG, CT, MRI, SPECT and PET.J Neurol 234: 377–384, 1987.
Ryvlin P, Philippon B, Cinotti L, Froment JC, Bars D Le, Mauguiere F. Functional neuro imaging strategy in temporal lobe epilepsy: a comparative study of F-18 FDG-PET and Tc-99m HMPAO-SPECT.Ann Neurol 31: 650–656, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagata, T., Tanaka, F., Yonekura, Y. et al. Limited value of interictal brain perfusion SPECT for detection of epileptic foci: High resolution SPECT studies in comparison with FDG-PET. Ann Nucl Med 9, 59–63 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164968
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164968