Abstract
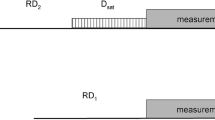
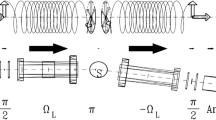
We measured87Rb nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and35Cl nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) Hahn spin-echo magnetization decays in the incommensurate (I) phase of Rb2ZnCl4 and, in each case, obtained a Hahn echo decay that was shorter than the Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill decay and one which decayed with a time constant proportional to the cube of the echo time. From these measurements we obtained from both the87Rb NMR and35Cl NQR measurements values for the diffusion coefficients that are comparable in magnitude, a fact that strongly supports the existence of slow modulation wave diffusionlike motions in the I phase, since such motions should affect both Rb and Cl ions similarly. In addition, we used87Rb two-dimensional exchange-difference NMR to study atomic motions in the incommensurate (I) and paraelectric (P) phases to elucidate the nature of the I-P transition. We measured as a function of the mixing time the frequency shifts of the cross peaks from the main diagonal and observed a gradual increase towards an asymptotic value in the I phase but a sudden jump to the final value in the P phase. We interpreted the motions observed in the P phase as normal modes arising from simultaneous reorientations of ZnCl4 tetrahedra and corresponding Rb ions displacements between two sites. These normal modes freeze out in the I phase and change to the diffusionlike motion of the modulation wave. We also performed35Cl NQR lineshape andT 1 measurements in K2ZnCl4 and obtained conclusive evidence for the presence of a narrow 1q (singly modulated) I phase between 146 and 149 K.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blinc R.: Phys. Rep.79, 331–398 (1981)
Ailion D.C., Norcross J.A.: Phys. Rev. Lett.74, 2383–2386 (1995)
Papavassiliou G., Leventis A., Milia F., Dolinsek J.: Phys. Rev. Lett.74, 2387–2390 (1995)
Papavassiliou G., Fardis M., Leventis A., Milia F., Dolinsek J., Apih T., Mikac M.U.: Phys. Rev. B55, 12161–12174 (1997)
Takigawa M., Saito G.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.55, 1233–1243 (1986)
Subramanian R.K., Muntean L., Norcross J.A., Ailion D.C.: Phys. Rev. B61, 996–1002 (2000)
Cummins H.Z.: Phys. Rep.185, 323–327 (1990)
Dolinsek J., Papavassiliou G.: Phys. Rev. B55, 8755–8765 (1997)
Ernst R.R., Bodenhausen G., Wokaunn A.: Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions. Oxford: Clarendon Press 1987.
Quilichini M., Pannetier J.: Acta Crystallogr. B39, 657–663 (1983)
Itoh K., Hinasada A., Natsunaga H., Nakamura E.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.52, 664–670 (1983)
Itoh K., Hinesada A., Daiki M., Ando A., Nakamkura E.: Ferroelectrics66, 287 (1986)
Gesi K.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.59, 416–419 (1990)
Grecu M.N., Cevc P., Blinc R.: Solid State Commun.105, 13–15 (1998)
Hasebe K., Asahi T., Kasano H., Mashiyama H., Kishimoto S.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.63, 3340–3343 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muntean, L., Subramanian, R.K. & Ailion, D.C. Magnetic resonance investigations of phase transitions and modulation wave motions in incommensurate solids. Appl. Magn. Reson. 19, 403–411 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03162383
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03162383