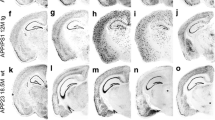
Abstract
Several reports indicate that Alzheimer disease (AD) brain contains elevated levels of heat shock 70 proteins. To determine the cellular localization of the heat shock 70mRNAs, specific oligonucleotide probes werein situ hybridized to AD and control brains. When oligonucleotides werein situ hybridized to brain sections with no AD neuropathology, hybridization was cell-specific and prior ribonuclease (RNase) treatment of adjacent sections resulted in no hybridization signal. However,in situ hybridization to AD hippocampus resulted in heavy grain deposition over senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Despite altering a number of experimental variables, we observed a similar pattern of grain deposition with most of the oligonucleotides tested, including one oligonucleotide specific for glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA.In situ hybridization with either an RNA probe for glutamic acid decarboxylase or an oligonucleotide probe specific for 18S rRNA did not show this pattern of grain deposition. In control studies a sense hsc70 oligonucleotide showed no grain deposition in either cerebellum or hippocampus. Sections from AD hippocampus pretreated with RNase prior toin situ hybridization demonstrated enhanced grain deposition with the majority of probes tested. Anomalousin situ hybridization to AD hippocampus was usually eliminated by removing formamide from the posthybridization weshes, although post-RNase sticking often remained intense. These findings indicate that artifactual probe binding to senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles may complicate the analysis ofin situ hybridization studies using oligonucleotide probes to determine mRNA distribution in AD brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., and Gajdusek D. C. (1987) Localization of amyloid β-protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer’s disease.Science 237, 77–80.
Barton A. J. L., Harrison P. J., Najlerahim A., Heffernan J., McDonald B., Robinson J. R., Davies D. C., Harrison W. J., Mitra P., Harday J. A., and Pearson R. C. A. (1990) Increased tau messenger RNA in Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus.Am. J. Pathol. 137, 497–502.
Chiang H.-L., Terlecky S. R., Plant C. P., and Dice J. F. (1989) A role for the 70-kilodalton heat shock protein in lysosomal degradation of intracellular proteins.Science 246, 382–385.
Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., and Blobel G. (1988) 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes.Nature 332, 805–810.
Collins M. L. and Hunsaker W. R. (1985) Improved hybridization assays employing tailed oligonucleotide probes: A direct comparison with 5′-end-labeled oligonucleotide probes and nick-translated plasmid probes.Anal. Biochem. 151, 211–224.
Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., and Schekman R. (1988) A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides.Nature 332, 800–805.
Dworniczak B. and Mirault M.-E. (1987) Structure and expression of a human gene coding for a 71 kd heat shock “cognate” protein.Nucl. Acid. Res. 15, 5181–5197.
Eberwine J., Yeh H., Miyashiro K., Cao Y., Nair S., Finnell R., Zettel M., and Coleman P. (1992) Analysis of gene expression in single live neurons.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 3010–3014.
Elghetany M. T., Saleem A., and Barr K. (1989) The congo red stain revisited.Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 19, 190–195.
Geck P. and Nasz I. (1983) Concentrated, digestible DNA after hydroxylapatite chromatography with cetylpyridinium bromide precipitation.Anal. Biochem. 135, 264–268.
Gething M. J. and Sambrook J. (1992) Protein folding in the cell.Nature 355, 33–45.
Goedert M. and Spillantini M. G. (1990) Molecular neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease:in situ hybridization studies.Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 10, 159–174.
Griffin W. S. T. and Morrison M. R. (1985)In situ hybridization—visualization and quantitation of genetic expression in mammalian brain.Peptides 6, 89–96.
Griffin W. S. T., Ling C., White C. L. III, and Morrison-Bogorad M. R. (1990) Polyadenylated messenger RNA in paired helical filament-immunoreactive neurons in Alzheimer disease.Alz. Dis. Assoc. Disord. 4, 69–78.
Guntern R., Bouras C., and Hof P. R. (1989) An improved staining method for senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease: quantitative comparison with other techniques.Soc. Neurosci. 15, 1033.
Harrison P. J., Barton A. J., Najlerahim A., McDonald B., and Pearson R. C. (1991a) Increased muscarinic receptor messenger RNA in Alzheimer’s disease temporal cortex demonstrated byin situ hybridization histochemistry.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 9, 15–21.
Harrison P. J., Barton A. J., Najlerahim A., McDonald B., and Pearson R. C. (1991b) Regional and neuronal reductions of polyadenylated messenger RNA in Alzheimer’s disease.Psychol. Med. 21, 855–866.
Harrison P. J., Procter A. W., Barton A. J., Lowe S. L., Najlerahim A., Bertolucci P. H., Bowen D. M., and Pearson R. C. (1991c). Terminal coma affects messenger RNA detection in post mortem human temporal cortex.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 9, 161–164.
Higgins G. A. and Wilson M. C. (1987)In situ hybridization for mapping the neuroanatomical distribution of novel brain mRNAs, inIn Situ Hybridization. Applications to Neurobiology (Valentino K. L., Eberwine J. H., and Barchas J. D., eds.), pp. 146–162, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Higgins G. A., Lewis D. A., Bahmanyar S., Goldgaber D., Gajdusek D. C., Young W. G., Morrison J. H., and Wilson M. C. (1988) Differential regulation of amyloid-β-protein mRNA expression within hippocampal neuronal subpopulations in Alzheimer disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 1297–1301.
Hunt C. and Morimoto R. I. (1985) Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 6455–6459.
Johnson S. A., McNeill T., Cordell B., and Finch C. E. (1990) Relation of neuronal APP-751/APP-695 mRNA ratio and neuritic plaque density in Alzheimer’s disease.Science 248, 854–857.
Julien J.-F., Samama P., and Mallet J. (1990) Rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase sequence deduced from a cloned cDNA.J. Neurochem. 54, 703–705.
Khachaturian Z. S. (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.Arch. Neurol. 42, 1097–1104.
Kobayashi Y., Kaufman D. L., and Tobin A. J. (1987) Glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA: nucleotide sequence encoding an enzymatically active fusion protein.J. Neurosci. 7, 2768–2772.
Kosik K. S., Crandall J. E., Mufson E. J., and Neve R. L. (1989) Tauin situ hybridization in normal and Alzheimer brain: localization in the somatodendritic compartment.Ann. Neurol. 26, 352–361.
Lin S.-C. and Morrison-Bogorad M. (1990) Developmental expression of mRNAs encoding thymosinsβ 4 andβ 10 in rat brain and other tissues.J. Mol. Neurosci. 2, 34–44.
Mah V. H., Eskin T. A., Kazee A. M., Lapham L., and Higgins G. A. (1992)In situ hybridization of calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II and tau mRNAs; species differences and relative preservation in Alzheimer’s disease.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 12, 85–94.
Marotta C. A., Brown B. A., Strocchi P., Bird E. D., and Gilbert J. M. (1981) In vitro synthesis of human brain proteins including tubulin and actin by purified brain polysomes.J. Neurochem. 36, 966–975.
Miller E. K., Raese J. D., and Morrison-Bogorad M. (1991) The expression of heat shock protein 70 and heat shock cognate 70 messenger RNAs in rat cortex and cerebellum after heat shock or amphetamine treatment.J. Neurochem. 56, 2060–2071.
Milner C. M. and Campbell R. D. (1990) Structure and expression of the three MHC-linked HSP70 genes.Immunogenetics 32, 242–251.
Mirra S. S., Heyman A., McKeel D., Sumi S. M., Crain B. J., Brownlee L. M., Vogel F. S., Hughes J. P., van Belle G., and Berg L. (1991) The consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer’s disease (CERAD): Part II [2]. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease.Neurology 41, 479–486.
Morrison M. R. (1988) mRNA levels in neurological disease, inThe Molecular Biology of Neurological Disease (Rosenberg R. N. and Harding A., eds.), pp. 135–152, Butterworths, London.
Morrison M. R. and Griffin W. S. T. (1981) The isolation andin vitro translation of undegraded messenger RNAs from human postmortem brain.Anal. Biochem. 113, 318–324.
Morrison-Bogorad M. R., Groshan K., Miller E. K., and Raese J. D. (1989)In situ quantitation of heat shock 70 mRNAs in rat cerebellum after amphetamine-induced hyperthermia.Soc. Neurosci. Abs. 15, 1127.
Morrison-Bogorad M., Pardue S., Groshan K., White C. L. III, Bigio E. H., Border B., Miller E. K., Gonzalez R., and Raese J. D. (1990) Anomalous reaction of oligo probes for 3 heat shock mRNAs in Alzheimer hippocampus.Neurosci. Abs. 16, 1628.
Morrison-Bogorad M., Groshan K., Pardue S., Border B., Miller E. K., and Raese J. D. (1991) Differential expression of members of the heat, shock gene family in brain of adult and aged rats, inAlzheimer’s Disease: Basic Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies (Iqbal K., McLachlan D. R. C., Winblad B., and Wisniewski H. M. (eds.), pp. 243–252, Wiley, Chichester, England.
Morrison-Bogorad M., Pardue S., Miller E. K., and Raese J. D. (1992a). The stress response, cell death and aging in rat and human brain.Neurochem. Int. 21(Supp. 1), A5.
Morrison-Bogorad M., Rosenberg R. N., Sparkman D., Weiner M., and White C. L. III (1992b) Alzheimer disease, inThe Molecular and Genetic Basis of Neurological Disease (Rosenberg R. N., Prusiner S. B., DiMauro S., Barchi R. L., and Kunkel R. M., eds.), pp. 767–780, Butterworths, London.
Najlerahim A., Harrison, P. J., Barton A. J. L., Heffernan J., and Pearson R. C. A. (1990) Distribution of messenger RNAs encoding the enzymes glutaminase, aspartase aminotransferase and glutamic acid decarboxylase in rat brain.Mol. Brain Res. 7, 317–333.
Neve R. L., Rogers J., and Higgins G. A. (1990) The Alzheimer amyloid precursor-related transcript lacking the β/A4 sequence is specifically increased in Alzheimer’s disease brain.Neuron 5, 329–338.
Pardue S., Groshan K., Raese J. D., and Morrison-Bogorad M. (1992) Hsp70 mRNA induction is reduced in neurons of aged rat hippocampus after thermal stress.Neurobiol. Aging 13, 661–672.
Shi Y. and Thomas J. O. (1992) The transport of proteins into the nucleus requires the 70-kilodalton heat shock protein or its cytosolic cognate.Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 2186–2192.
Somerville M. J., Percy M. E., Bergeron C., Yoong L. K., Grima E. A., and McLachlan D. R. (1991) Localization and quantitation of 68 kDa neurofilament and superoxide dismutase-1 mRNA in Alzheimer brains.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 9, 1–8.
Spillantini M. G., Hunt S. P., Ulrich J., and Goedert M. (1989) Expression and cellular localization of amyloid beta-protein precursor transcripts in normal human brain and in Alzheimer’s disease.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 6, 143–150.
Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., and Roses A. D. (1993) Apolipoprotein E: High-avidity binding to β-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer, disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 1977–1981.
Syrjänen S., Heinonen O., Miettinen R., Paljärvi L., Syrjänen K., and Riekkinen P. (1991) Short biotinylate oligonucleotides bind non-specifically to senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease.Neurosci. Lett. 130, 89–91.
Terlecky S. R., Chiang H.-L., Olson T. S., and Dice J. F. (1992) Protein and peptide binding and stimulation ofin vitro lysosomal proteolysis by the 73-kDa heat shock cognate protein.J. Biol. Chem. 267, 9202–9209.
Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., and Roth M. (1970) Observations on the brains of demented old people.J. Neurol. Sci. 11, 205–242.
Tomlinson B. E. and Corsellis J. A. N. (1984) Aging and the dementias, inGreenfield’s Neuropathology (Adams J. H., Corsellis J. A. N., and Duchen L. W., eds.), vol. 4, pp. 951–1025. Wiley, New York.
Voellmy R., Ahmed A., Schiller P., Bromley P., and Rungger D. (1985) Isolation and functional analysis of a human 70,000-dalton heat shock protein gene segment.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 4949–4953.
Willcutts M. D. and Morrison-Bogorad M. (1991) Quantitativein situ hybridization analysis of glutamic acid decarboxylase messenger RNA in developing rat cerebellum.Dev. Brain Res. 63, 253–264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pardue, S., White, C.L., Bigio, E.H. et al. Anomalous binding of radiolabeled oligonucleotide probes to plaques and tangles in Alzheimer disease hippocampus. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 22, 1–24 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160091
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160091