Abstract
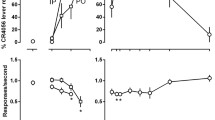
Rats were trained to discriminate 10 mg/kg chlordiazepoxide (CDAP) from saline in a two-lever drug discrimination procedure. Both CDAP and the nonsedative benzodiazepine partial agonist, bretazenil, dose-dependently substituted for the training dose of CDAP. Training was then suspended and half of the rats were placed on chronic CDAP, while the other half received water. Tolerance to the discriminative stimulus effects of CDAP developed after 1 mo and a final dose of approximately 110 mg/kg/d, as evidenced by the fact that the training dose of CDAP no longer produced drug-appropriate responding. An insurmountable tolerance also developed to bretazenil, as no rat responded on the drug-appropriate lever at doses as high as 56 mg/kg, whereas in the prechronic dose-effect curve, 1 mg/kg of bretazenil produced 100% drug-appropriate responding. One week after chronic CDAP was discontinued, the dose-effect curve for CDAP in the chronic CDAP group was comparable to that obtained in the prechronic phase, indicating that the rats were no longer tolerant to CDAP. In contrast to CDAP, the dose-effect curve for bretazenil did not return to its prechronic level, with higher doses being required for substitution. In the chronic water group, the dose-effect curves for CDAP and bretazenil were essentially the same before, during, and after the chronic regimen. Thus, suspension of training for 6 wk does not result in loss of the discriminative stimulus control. Chronic exposure to CDAP, however, does result in tolerance to the discriminative stimulus effects of CDAP, with an accompanying insurmountable cross-tolerance to the partial benzodiazepine agonist, bretazenil. These results support findings by other investigators who find tolerance to the discriminative stimulus properties of a wide range of psychoactive drugs (Young and Sannerud, 1989).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ator N. A. and Griffiths R. R. (1989) Differential generalization to pentobarbital in rats trained to discriminate lorazepam, chlordiazepoxide, diazepam, or triazolam.Psychopharmacology 98, 20–30.
Bennett D. A. (1983) The nonsedating potential anxiolytic, CGS 9896 (2-(p-chlorophenylpyrazolo [3,4-c]quinoline-3(tH)-one, in drug discrimination models.Pharmacologist 25, 155.
Emmett-Oglesby M. W., Shippenberg T. S., and Herz A. (1988) Tolerance and cross-tolerance to the discriminative stimulus properties of fentanyl and morphine.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 245, 17–23.
Foltin R. W. and Fischman M. W. (1991) Assessment of abuse liability of stimulant drugs in humans: a methodological survey.Drug. Alcohol Depend. 28, 3–48.
Haefely W., Martin J. R., and Schoch P. (1990) Novel anxiolytics that act as partial agonists at benzodiazepine receptors.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 11, 452–456.
Haigh J. R. M. and Feely M. (1988) Ro 16-6028, a benzodiazepine receptor partial agonist, does not exhibit anticonvulsant tolerance in mice.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 147, 282–285.
Martin I. L. (1988) The benzodiazepines and their receptors: 25 years of progress.Neuropharmacology 26, 957–970.
Martin J. R., Pieri L., Bonetti E. P., Schaffner R., Burkard W., Cumin R., and Haefely W. E. (1988) Ro 16-6028: a novel anxiolytic acting as a partial agonist at the benzodiazepine receptor.Pharmacopsychiatry 21, 360–362.
Martin J. R., Kuwahara A., Horii I., Moreau J. L., Jenck F., Sepinwall J., and Haefely W. (1990) Evidence that the benzodiazepine receptor partial agonist Ro 16-6028 has minimal abuse and physical dependence liability.Soc. Neurosci. Abstracts 16, 1104.
Miksic S. and Lal H. (1977) Tolerance to morphine-produced discriminative stimuli and analgesia.Psychopharmacology 54, 217–221.
Miller L. G., Galpern W. R., Greenblatt D. J., Lumpkin M., and Shader R. I. (1990) Chronic benzodiazepine administration. VI. A partial agonist produces behavioral effects without tolerance or receptor alterations.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 254, 33–38.
Moreau J. L., Jenck F., Pieri L, Schoch P., Martin J. R., and Haefely W. E. (1990) Physical dependence induced in DBA/2J mice by benzodiazepine receptor full agonists, but not by the partial agonist Ro 16-6028.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 190, 269–273.
Picker M. J., Doty P., Negus S. S., Mattox S. R., and Dykstra L. A. (1990) Discriminative stimulus properties of U50, 488 and morphine: effects of training dose on stimulus substitution patterns produced by mu and kappa opioid agonists.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 254, 13–22.
Preston K. L. and Jasinski D. R. (1991) Abuse liability studies of opioid agonist-antagonists in humans.Drug Alcohol Depend. 28, 49–82.
Sanger D. J. (1988) Discriminative stimulus properties of anxiolytic and sedative drugs: pharmacological specificity, inTransduction Mechanisms of Drug Stimuli (Colpaert F. and Balster R., eds.), pp. 73–84, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg.
Sanger D. J., Joly D., and Zivkovic B. (1985) Behavioral effects of nonbenzoediazepine anxiolytic drugs: a comparison of CGS 9896 and zopiclone with chlordiazepoxide.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 232, 831–837.
Schuster C. R. and Johanson C. E. (1988) Relationship between the discriminative stimulus properties and subjective effects of drugs, inTransduction Mechanisms of Drug Stimuli (Colpaert F. and Balster R., eds.), pp. 161–175, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Shannon H. E. and Holtzman S. G. (1976) Evaluation of the discriminative stimulus effects of morphine in the rat.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 198, 54–65.
Stephens D. N., Shearman G. T., and Kehr W. (1984) Discriminative stimulus properties of β-carbolines characterized as agonists and inverse agonists at central benzodiazepine receptors.Psychopharmacology 83, 233–239.
Wood D. M. and Emmett-Oglesby M. (1986) Characteristics of tolerance, recovery from tolerance and cross-tolerance for cocaine used as a discriminative stimulus.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 237, 120–125.
Wood D. M. and Emmett-Oglesby M. W. (1987) Evidence for dopaminergic involvement in tolerance to the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 138, 155–157.
Wood D. M., Lal H., and Emmett-Oglesby M. W. (1984) Acquisition and recovery of tolerance to the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine.Neuropharmacology 23, 1419–1423.
Young A. M. and Sannerud C. A. (1989) Tolerance to drug discriminative stimuli, inPsychoactive Drugs, (Goudie A. J. and Emmett-Oglesby M., eds.), pp. 221–278, Humana, Clifton, NJ.
Young A. M., Kapitsopoulos G., and Makhay M. M. (1991) Tolerance to morphine-like stimulus effects of mu opioid agonists.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 257, 795–805.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Author to whom all correspondence and reprint requests should be addressed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bronson, M.E. Tolerance/cross-tolerance to the discriminative stimulus effects of chlordiazepoxide and bretazenil. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 18, 85–98 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160023
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160023