Abstract
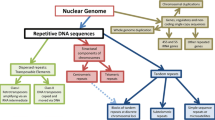
A high percentage ofDNA sequence noted in higher organisms is highly repetitive in nature. Such sequences may be highly homogeneous, moderate, minor and inverted. Those sequences are found in different loci including introns, spacers, transposons, in addition to their interspersion with unique sequences. Such sequences share the property of amplification, dispersion and possibly mobility. The term ‘DynamicDNA’ has been proposed to account for their varied property. Their presence may account for “C Value Paradox” in eukaryotes. Evolutionary advance is also associated with increase or decrease of repeated sequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angerur R C, Davidson E and Britten R J 1976 Single copyDNA and structural gene relationship among four sea urchin species;Chromosoma (Berl) 56 213
Appels R, Driscoll C and Peacock W J 1978 Heterochromatin and highly repeatedDNA sequences in Rye (Secale cereale);Chromosoma (Berl) 70 67
Artymiuk P J, Blake C C F and Dippel A E 1981 Genes pieced together—exons delineate homologous structures of diverged lysozymes;Nature (London) 290 287
Bachmann K, Goin O B and Goin C J 1972 NuclearDNA amounts in vertebrates;Brookhaven Symp. Biol. 23 419
Banerjee M and Sharma A K 1979 Variation inDNA content;Experientia 35 42
Barnett T and Rae P M M 1979 A 9·6 kg intervening sequence inD. viridis rDNA and sequence homology inDNA interruptions in diverse species ofDrosophila and other Diptera.Cell 16 763
Bassi P, Cremonini R and Cionini P G 1982 Cytological localization of inverted repeatedDNA sequences inVicia faba;Chromosoma (Berl.) 85 453
Beauchamp R S, Mitchell A R, Buckland R A and Bostock C J 1979 Specific arrangements of human satelliteIII DNA sequences in human chromosomes;Chromosoma 71 153
Bedbrook J R, Jones J, O’Dell M, Thompson R and Flavell R B 1980 A molecular description of telomeric heterochromatin inSecale species;Cell 19 545
Bennet M C 1972 NuclearDNA content and minimum generation time in herbaceous plants;Proc. R. Soc. (London) B181 109
Borschsenius S N, Merki Ina N A, Romanov G A and Vanvshin B F 1981 Palindromic and repetitive sequences in initiation sites ofDNA replication inTetrahymena;Mol. Biol. (Moscow) 15 816
Bostock C J 1980 The organisation ofDNA sequences in chromosomes, inCell biology (ed) R Goldstein and D M Prescott (New York: Academic Press)3 1
Bostock C J, Gosden J R and Mitchell A R 1978 Localization of a male-specificDNA fragment to a sub-region of human Y-chromosome;Nature (London) 272 324
Britten R J and Davidson E H 1971 Repetitive and non-repetitiveDNA sequences and a speculation on the origins of evolutionary novelty;Q. Rev. Biol. 46 111
Brown S D M and Dover G H 1979Nucleic Acid Res. 8 781
Bruttlag D and Peacock W J 1979 Sequences of the 1·672 g/cm 3 satelliteDNA ofDrosophila melanogaster;J. Molec. Biol. 135 565
Calabretta B, Robertson D L, Barrera-Saldona H A, Lambrou T P and Saunders G F 1983 Genome instability in a region of humanDNA enriched in Alu repeat sequences;Nature (London) 216 219
Calos M P and Millers J H 1980 Transposable elements;Cell 20 579
Cameron J R, Loh E Y and Davis R W 1979 Evidence of transposition of dispersed repetitiveDNA families in yeast;Cell 16 739
Cavalier-Smith T 1976 Long palindromes in eukaryoticDNA;Nature (London) 262 255
Cavalier-Smith T 1980 How selfish isDNA?;Nature (London) 285 617
Cohen E H and Kaplan G C 1982 Analysis ofDNAs from two species of the viridis group of Drosophila and implications on satelliteDNA evolution;Chromosoma (Berl.) 87 519
Cohn R H and Kedes L H 1979 Non-allelic histone gene clusters of individual sea urchins (Lytechinus pictus) polarity and gene organisation;Cell 18 843
Cooke H J and Hindley J 1979 Cloning of human satelliteIII: different components are on different chromosomes;Nucleic Acid Res. 6 3177
Cooke H J, Schmidtke J and Gosden R R 1982 Characterisation of human Y-chromosome repeated sequence and related sequences in higher primates;Chromosoma (Berl.) 87 491
Cremonini R, Ioro M L and Duranti M 1981 Differentiation of metaxylem cell line in the root ofAllium cepa II. Changes in nucleotide sequence redundancy;Protoplasma 108 1
Crick F 1979 Split genes andRNA splicing;Science 204 264
Darnell J E 1978 Implications ofRNA-RNA splicing in evolution of eukaryotic cells;Science 202 1257
Davidson E H and Britten R J 1979 Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences;Science 204 1052
Davidson E H, Jacobs H T and Britten R J 1983 Eukaryotic gene expression very short repeats and coordinate induction of genes;Nature (London) 301 468
Dawid I B and Botchun P 1977 Sequences homologous to ribosomal insertions occur in theDrosophila genome outside the nucleolar organiser;Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 74 4233
Dawid I B, Long E O, Di Novera P P and Pardue M L 1981 Ribosomal insertion like elements inDrosophila melanogaster are interspersed with mobile sequences;Cell 25 399
Deininger P L and Schmidt C W 1976 An electron microscope study of theDNA sequence organisation of the human genome;J. Molec. Biol. 106 773
Deumling B 1978 Localization of fold backDNA sequences in the nuclei and chromosomes ofScilla, Secale and Mouse;Nucleic Acid Res. 5 3589
Doolittle W F and Sapienza C 1980 Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution;Nature (London) 284 601
Dover G and Doolittle W F 1980 Modes of genome evolution;Nature (London) 288 646
Egel R 1981 Intergenic conversion and reiterated genes;Nature (London) 290 20
Ellison J R and Howard G C 1981 Nonrandom position of the A-T richDNA sequences in early embryos ofDrosophila viridis;Chromosoma (Berl.) 83 555
Evans G M and Rees H 1971 Mitotic cycles in dicotyledons and monocotyledons;Nature (London) 233 350
Evans L S and Van’t Hof J 1975 Is polyploidy necessary for tissue differentiation in higher plants;Am. J. Bot. 62 1060
Evans M B, Yeninolopov G N, Peunova N I and Ityin Y 1982 Transposition of mobile genetic elements in the interspecific hybrids inDrosophila;Chromosoma (Berl.) 85 375
Fedorof N V 1979 On spacers;Cell 16 697
Flavell R B 1980 Molecular changes in chromosomalDNA organisation and origins of phenotypic variation;Chromosomes Today 7 42 (London: Oliver and Boyd)
Friedman B E, Bouchard R A and Stern H 1982DNA sequences repaired at pachytene exhibit strong homology among distantly relation higher plants;Chromosoma (Berl.) 87 409
Gailit J O and Fredrickson D W 1981 Possible palindromicDNA;J. Theor. Biol. 88 241
Giraldez R, Cermemo M C and Orellana J 1979 Comparison of C-banding pattern in the chromosomes of inbred lines and open pollinated varieties of rye;Z. pflanzenzuecht. 83 40
Glover D M 1977 Cloned segment ofDrosophila melanogaster rDNA containing new types of sequence insertion;Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 74 4932
Gosden J R, Lowrie S S and Cooke H J 1981 A cloned repeatedDNA sequence in human chromosome heteromorphisms;Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 29 32
Gosden J R, Lawrie S S and Gosden C M 1981 SatelliteDNA sequences in human acrocentric chromosomes. Informations from translocations and heteromorphisms;Am. J. Human Genet. 33 243
Green M M 1980 Transposable elements inDrosophila and other Diptera;Annu. Rev. Genet. 14 104
Grosschedl R and Birnsteil M L 1980 Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutantsin vivo;Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 77 1432
Gupta V S and Ranjekar P K 1981DNA sequence organisation in finger millet;J. Biosci. 3 417
Hartman N, Bell A J and McLanchlan A 1979 Organisation of inverted repeat sequences in hamster cell nuclearDNA;Biochim. Biophys. Acta 564 372
Henstschel C H and Birnsteil M U 1981 The organisation and expression of histone gene families;Cell 25 301
Heumanns J M 1976 A model of replication of the ends of linear chromosomes;Nucleic Acids Res. 3 3167
Hinegardner R 1976 Evolution of genome size, inMolecular evolution (ed) F J Ayala (Sunderland (Mass): Sinauer Press)
Hutchinson J, Narayan R K J and Rees H 1980 Constraints upon the composition of supplementaryDNA;Chromosoma (Berl.) 78 127
Jacq B, Jourdan R and Jordan B R 1979 Structure and processing of precursor 55RNA inDrosophila melanogaster;J. Molec. Biol. 177 785
Jain H K 1980 IncidentalDNA;Nature (London) 288 647
Jelinek W 1977 Specific nucleotide sequences in Hela cell inverted repeatedDNA. Enrichment for sequences found in double stranded regions of heterogenous nuclearRNA;J. Molec. Biol. 115 591
John B 1983 The role of chromosome changes in the evolution of orthopteroid insects inChromosomes in evolution of eukaryotic groups (eds) A K Sharma and A Sharma1 1 (CRC Press)
John B and Miklos C L G 1979 Functional aspects of satelliteDNA and heterochromatin;Int. Rev. Cytol. 58 114
Jones J D G and Flavell R B 1982 The structure amount and chromosomal localization of definedDNA sequences in species of the genusSecale;Chromosoma (Berl.) 86 613
Jones R N 1975 B-chromosome system in flowering plant and animal species;Int. Rev. Cytol. 40 1
Kan N C and Gall J G 1982 The intervening sequence of the ribosomalRNA gene is highly conserved between twoTetrahymina species;Nucleic Acid Res. 10 2809
Kimura M 1968 Evolutionary rate at the molecular level;Nature (London) 217 624
Klein H L and Petes T D 1981 Intrachromosomal gene conversion in yeast;Nature (London) 289 144
Klein H L and Welch S K 1980 Inverted repeated sequences in yeast nuclearDNA;Nucleic Acid Res. 8 4641
Kuehn N and Arnheim N 1983 Nucleotide sequence of the genetically labile repeated elements 5 to the origin of mouse rDNA transcription;Nucleic Acid Res. 11 211
Kunz W, Grimm C and Frauz G 1982 Amplification and synthesis of rDNA The cell nucleus (eds) H Busch and L Rothblum (New York; Academic Press)C12 156
Kurnitt D M 1979 SatelliteDNA and heterochromatin variants: the case of unequal mitotic crossover;Human Genet. 47 169
Lelley T, Josifek K and Kaltsikes P J 1978 Polymorphism in the giemsa C-banding pattern of rye chromosomes;Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 20 307
Lewin B 1980Gene expression-eukaryotic chromosomes (New York: Wiley Interscience)2 1
Liebhader S A, Gossens M and Kan Y W 1981 Homology and concerted evolution at the 1 and 2 loci of human B-globin;Nature (London) 290 26
Lobov V P 1981 Repeated sequences in maizeDNA;Fiziol. Biochim. Kult. Rast. 13 477
Loomis W 1973Dev. Biol. 30 3
McClintock B 1952 Chromosome organisation and genic expression;Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 16 13
Miesfield R, Krystal M and Arnheim N 1981 A member of a new repeated sequence family which is conserved throughout eukaryotic evolution if found between the human sand B-globin genes;Nucleic Acid Res. 9 5931
Moyzis D K, Bonnet J, Li D W and Ts’o P O P 1981 An alternative view of mammalianDNA sequence organisation;J. Molec. Biol. 53 871
Muntzing A 1977 Accessory chromosomes;Ann. Rev. Genet. 8 243
Murray V and Holliday R 1979FEBS Lett. 106 5
Nagl W 1972 Molecular and structural aspects of the endomitotic chromosome cycle in angiosperms inChromosome today (eds) C D Darlington and K R Lewis (London: Oliver and Boyd)3 17
Ogden R C, Beckmann J S, Abelson J, Kang H S, Soll D and Schmidt O 1979In vitro transcription and processing of a yeast t-RNA gene containing an intervening sequence;Cell 17 399
Olmo E 1981 Evolution of genome size andDNA base composition in reptiles;Genetica 57 39
Orgel L E and Crick F H C 1980 SelfishDNA — the ultimate parasite;Nature (London) 284 604
Patton J L and Sherwood S W 1982 Genome evolution in pocket gophers (genusThomomyces)II;Chromosoma (Berl.),85 163
Potter S S, Brorein W J, Dunsmuir P and Rubin G M 1979 Transposition of elements of the 412, copea and 297 dispersed repeated gene families inDrosophila;Cell 17 415
Price H J 1976 Evolution ofDNA contents in higher plants;Bot. Rev. 42 27
Probst E, Kressmann A and Birnsteil M L 1979 Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte ofXenopus laevis;J. Molec. Biol. 135 705
Proudfoot N 1980 Pseudogenes;Nature (London) 286 840
Rhoades M M, Peacock W J, Dennis E S and Prior A J 1981 Highly repeatedDNA sequence limited to knob heterochromatin in maize;Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 78 4490
Robertson H, Dickson E and Jelinek W 1977 Determination of nucleotide sequences from double stranded regions of HeLa cell nuclearRNA;J. Molec. Biol. 115 571
Sau H, Sharma A K and Choudhuri R K 1980DNA, RNA and protein content of isolated nuclei from different plant organs;Indian J. Exp. Biol. 18 1519
Sekerka V 1981 Changes inDNA content of interkinetic nuclei of epicotyl cells ofVicia faba L. during the process of differentiation;Biologia 36 741
Sharma A K 1976 A new look at chromosome and its evolution;Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. (Anim. Sci.) (Silver Jubilee Medal Mem. Lecture)42 12
Sharma A K 1978a Change in chromosome concept;Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Anim. Sci.) 87 161
Sharma A K 1978b Additional genetic elements in chromosomes;Nucleus 21 113
Sharma A K 1980 Chromosomes and distribution of monocotyledons in the Eastern Himalayas, inTropical botany (eds) K Larsen and L B Holm-Nilsen (New York: Academic Press).
Sharma A K 1981DNA repeats and their terminology;Nucleus 24 87
Sharma A K 1982 Genetic diversity of some monocotyledonous crops and their wild relatives in the Eastern Himalayan Region;Workshop Conf. Trop. Pl. Res. SE Asia, New Delhi
Sharma A K 1983 Additional genetic materials in chromosomesProc. Second. Chrom. Conf. Kew (eds) P E Brandham and M D Bennett (London: George Allen and Unwin)35
Sharma A K and Aiyangar H R 1961 Occurrence of B-chromosome in, diploidAllium strachevii and their elimination;Chromosoma 12 310
Sharma A K and Mookerjea A 1954 Induction of division in cells—a study of the causal factors involved;Bull. Bot. Soc. G. C. Bose Mem. Vol. 824
Sharma A K and Sharma A 1980Chromosome techniques—theory and practice, 3rd edn (London: Butterworths)
Sherwood S W and Patton J L 1982 Genome evolution in pocket gophers (genusThomomyces)II.Chromosoma (Berl.) 85 163
Singh R J and Robbelen G 1979 Identification by giemsa technique of the translocations separating cultivated rye from the three wild species ofSecale;Chromosoma (Berl.) 59 217
Slighton J L, Blechl A E and Smithies O 1980 Human fetal Gr and Ar globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest thatDNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes;Cell 21 627
Smith G P 1976 Evolution of repeatedDNA sequences by unequal crossing over;Science 191 528
Sogin H L, Pace B and Pace N R 1977 Partial purification and properties of a ribosomalRNA maturation endonuclease fromBacillus subtilis;J. Biol. Chem. 252 1350
Stack S M and Comings D E 1979 The chromosomes andDNA ofAllium cepa;Chromosoma (Berl.) 70 161
Stebbins G L 1972 InTaxonomy, cytogenetics and evolution (ed) D H J Valentine (New York: Academic Press)
Strobel S W, Dunsmuir P and Rubin G M 1979 Polymorphism in the chromosomal location elements of the 412, copea 297 dispersed repeated gene families inDrosophila;Cell 17 429
Tchurikov N A, Ilyin Y V, Ananiev E V and Georgiev G P 1978 The properties of gene Dm 225, a representative of dispersed repetitive genes inD. melanogaster;Nucleic Acid Res. 5 2169
Vanderlyn L 1949 The heterochromatin problem is cytogenetics as related to other branches of investigation;Bot. Rev. 15 507
Waldron J, Dansmuir P and Bedbrook J 1983 Characterization of rDNA repeat unit in MitchellPetunia genome;Plant Molec. Biol. 2 57
Wall L V M and Bryant J A 1981 Isolation and preliminary characterization of cryptic satelliteDNA in peaPhytochemistry 20 1767
Wallace B and Kass T L 1974 On the structure of gene control regions;Genetics 77 541
Wallaver P K and Dawid I B 1978 RibosomalDNA inDrosophila melanogaster II. Heteroduplex mapping of cloned and uncloned rDNA;J. Molec. Biol. 126 769
Young M W 1979 Middle repetitiveDNA: a fluid component of the Drosophila genome;Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 76 6274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A.K. Additional DNA sequences—Topography, property, role and evolutionary significance. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 94, 487–504 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03053162
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03053162