Summary and Conclusions
1. If frog’s stomach muscle is immersed in hypotonic sucrose solution, it maintains its excitability for about 24 hours, after a preliminary depression. The responses in the sucrose solutions may be several times bigger than in saline.
2. The spontaneous contractions of the muscle in sucrose solution are accompanied by action potentials.
3. When the muscle is contracting strongly in the sucrose solution, the sodium content (of the muscle) is negligible thus showing that sodium is not necessary for the production of mechanical and electrical changes.
4. When the muscle has acclimatised to sucrose, sodium has a depressant action, showing that the mechanical and electrical responses of the muscle are not due to any retention of sodium in the interspaces between the fibres.
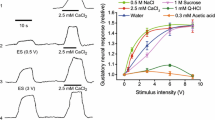
5. The muscle also responds as in sucrose solution, if all the sodium of the saline is replaced with ammonium, potassium, calcium, strontium and magnesium. This suggests that the membrane of this tissue is comparatively resistant and hence this muscle can be deprived of sodium, and still maintain its excitability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erlanger, J. and Blair, E. A...Amer. J. Physiol., 1938,124, 341.
Gokhale, S. K. and Singh, I...Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1945,21, 202.
Hawk, P. B., Oser, B. L. and Summerson, W. H.Practical Physiological Chemistry, 1949, 12th Edition, J. A. Churchil, London.
Hodgkin, A. L...Biol. Rev., 1951,26, 23.
—— and Katz, B...J. Physiol., 1949,108, 26.
Kato, G...Cold. Spr. Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol., 1936,4, 202. Quoted from A. L. Hodgkin.
Looney and Dyer..J. Lab. Clin. Med., 1944,28, 35. Quoted from Hawk, Oscr and Summerson.
McDowall, R. J. S., Munro, A. F. and Zayat, A. F.J. Physiol., 1955,130, 615.
Overton, E...Pflug. Arch. Gest. Physiol., 1902,92, 346. Quoted from Hodgkin, A. L.
Singh, I. ..J. Physiol., 1939.
—————..Curr. Sci., 1944,10, 251.
—————..Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1945,22, 76.
----- ..Presidential Address, Physiology Section, Indian Science Congress 44th Session, Calcutta 1957.
—— and Singh, S. I...Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1943,18, 58.
—————.. Ibid., 1947,26, 211.
Singh, I. and Singh, S. I...Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1948,28, 51.
—— and Bhatt, J. V...Curr. Sci., 1957,26, 17.
——, Sehra, K. B. and Singh, S. I.Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., 1945a,259, 21.
—————..Curr. Sci., 1945b,14, 152.
Weinbach..J. Biol. Chem., 1935,110, 35. Quoted from Hawk, Oser and Summerson.
Winton, F. R...J. Physiol., 1937,88, 492.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, I., Bhatt, J. Mechanical and electrical responses of unstriated muscle in sodium-free solutions. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 45, 64–76 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03051023
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03051023