Abstract
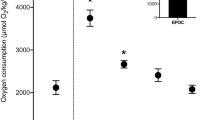
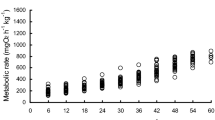
Oxygen consumption, ammonia excretion and ammonia quotient (AQ) (vol. NH3/vol.O2) in the catfish,Mystus armatus, acclimated to and tested in fresh water at 30°C, were obtained with special reference to swimming speed and ambient oxygen. At normoxia the fish maintained an AQ of about 0·12, while at low ambient oxygen (below 2 ppm) the AQ increased sharply to a value of 0·3 indicating an increase in protein metabolism of hypoxic conditions.Mystus armatus exercising continuously for 5 hr at various swimming speeds, utilized more proteins during the later phase of exercise. The increased protein utilization may be of advantage in maintaining acid-base balance and also in conserving sodium (Na+) in fish.
In the recovery metabolism ofMystus armatus after hypoxic asphyxiation, the oxygen consumption showed a clearcut rise over the prehypoxic level, indicating that an oxygen debt was accumulating inMystus armatus exposed to hypoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association 1965 Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. 12th ed. APHA Inc. New York
Basu S P 1959 Active respiration of fish in relation to ambient concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide;J. Fish Res. Bd. Can 16 175–212
Beamish F W H 1964 Respiration of fishes with special emphasis on standard oxygen consumption III. Influence of oxygen;Can. J. Zool. 42 355–366
Beamish F W H and Mookherjii 1964 Respiration of fishes with special emphasis on standard oxygen consumption I. Influence of weight and temperature on respiration of goldfish;Can. J. Zool. 42 161–175
Blazka P, Volf M and Capela M 1960 A new type of respirometer for the determination of the metabolism of fish in an active state;Physiol. Bohemoslov. 9 553–558
Brett J R 1962 Some consideration on the study of respiratory metabolism in fish, particularly salmon;J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 19 1025–1038
Brett J R 1964 The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of young sockeye salmon;J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 21 1183–1226
Brett J R and Sutherland D B 1965 Respiratory metabolism of pumpkin seed (Lepomis gibbosus) in relation to swimming speed;J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 22 405–409
Driedzic W R and Hochachka P W 1975 The unanswered question of high anaerobic capabilities of carp white muscle;Can. J. Zool. 53 706–712
Forster R P and Goldstein L 1969 Formation of excretory products inFish Physiology eds W S Hoar and D J Randall (New York and London: Academic Press) Vol. 1 Ch. 5, pp. 313–355
Fromm P O 1963 Studies on renal and extra-renal excretion in a freshwater teleost;Salmo gairdneri Comp. Biochem. Physiol 10 121–128
Fromm P O and Gillette J R 1968 Effect of ambient ammonia on rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri);Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 26 887–896
Garcia Romeu F and Motias R 1966 Mise on e’vi-dense de changes Na+/NH +4 /Chez languille deau douce;Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 17 1201–1204
Goldstein L, Forster R P and Fanelli G M Jr 1964 Gill blood flow and ammonia excretion in the marine teleostMyxocephalus scorpius;Comp. Biochem. Physiol 12 489–499
Job S V 1959 The metabolism ofPlotosus anguillaris (Bloch) in various concentrations of salt and oxygen in the medium;Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. B50 267–288
Karuppannan N V 1972 Studies on locomotory metabolism ofTilapia mossambica (Peters); Ph.D. Thesis, Madurai University, Madurai
Kutty M N 1968 Respiratory quotient in goldfish and rainbow trout;J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 25 1689–1728
Kutty M N 1972 Respiratory quotient and ammonia excretion inTilapia mossambica;Mar. Biol. 16 126–133
Kutty M N 1975 Energy metabolism in mullet-invited contribution: Chapter in IBP synthesis volume on grey mullets (in press)
Kutty M N and Peer Mohamed M 1975 Metabolic adaptations of mullet,Rhinomugil corsula (Hamilton) with special reference to energy utilization;Aquaculture 5 253–270
Maetz J and Garcia Romeu F 1964 In mechanism of sodium and chloride uptake by the gills of a fresh water fish,Carassius auratus II. Evidence for NH +4 /Na+ and HCO −3 /Cl− exchanges;J. Gen. Physiol. 47 1209–1227
Muir B S, Nelson G J and Bridges K W 1965 A method for measuring swimming speed in oxygen consumption studies;Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 94 378–382
Peer Mohamed M 1974 Influence of hypoxia on fish metabolism and activity; Ph.D. Thesis, Madurai University, Madurai
Rao G M M 1968 Oxygen consumption of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in relation to activity and salinity;Can. J. Zool. 46 781–786
Rector F C, Seldin D W and Copenhaver J H 1955 The mechanism of ammonia excretion during ammonium chloride acidosis;J. Clin. Invest. 34 20–26
Rosado A, Flores G, Mora J and Soberson G 1962 Distribution of and ammonia load in the normal rat;Am. J. Physiol. 203 37–42.
Saunders R L and Kutty M N 1974 Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion in Atlantic salmon smolts (Ms)
Smit H 1965 Some experiments on the oxygen consumption of gold fish (Carassium auratus L) in relation to swimming speed;Can. J. Zool. 43 623–633
Smit H, Amelink-koutstall J M, Vijverberg J and Von Vanpelklein 1971 Oxygen consumption and efficiency of swimming goldfish;Com. Biochem. Physiol. 39 1–28
Smith L S and Newcomb T W 1970 A modified version of the Blazka respirometer and exercise chamber for large fish;J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada 27 1321–1324
Spoor W A 1946 A quantitative study of the relationship between activity and oxygen consumption of the goldfish;Biol. Bull. Mar. Biol. Lab., Woods Hole 91 312–325
Stroganov N S 1962 Methods for ammonia determination used in studies on fish metabolism inThe techniques for the investigation of Fish Physiology ed. Pavlovski, pp. 106–111; 1964Izd. Akad. Nauk. S.S.S.R. Podossenrki per. Moscow, U.S.S.R. (Translated from Russian by Israel Programme for Sci. Transl. Jerusalem) 1130
Suyama M, Koike J and Suzuki K 1960 Studies on the glycolysis and the formation of ammonia in the muscle and blood of elasmobranchs;J. Tokyo Univ. Fish. 46 51–65
Webb P W 1971 The swimming energetics of trout. II. Oxygen consumption and swimming efficiency;J. Exp. Biol. 55 521–540
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukumaran, N., Kutty, M.N. Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion in the catfishMystus armatus, with special reference to swimming speed and ambient oxygen. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 86, 195–206 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03050948
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03050948