Abstract
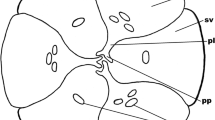
The embryogeny ofCommelina benghalensis L, from zygote to the globular proembryo, is presented. The terminal cell of the proembryo, after two vertical divisions, right angles to each other, becomes morphogenetically differentiated: one of the half-hemispheres is destined to develop into the cotyledon and the other into the epicotyl. The subjacent tier—derivatives of the basal cell—which is close to the terminal tier, show two ontogenetic norms of development. The root pole is differentiated from the derivatives of the basal cell which are opposite to the shoot pole.
The general outline of the proembryo as a whole becomes globular without any external morphological recognition into the cotyledon and epicotyl at the shoot pole. Nevertheless, the cotyledonary and epicotylary sectors of the terminal hemisphere lying adjacent to one another and occupying a truly terminal position on the embryonal axis, a position opposite to the root pole, can be recognised.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chikkanaiah P S 1961a The embryology ofRhoeo discolor Hance-A reinvestigation;J. Karnatak Univ. 6 57–60
Chikkanaiah P S 1961b Morphological and embryological studies in theCommelinaceae; Symp. Plant Embryology (CSIR New Delhi) 23–26
Chikkanaiah P S 1963 Embryology of some members of theCommelinaceae;Phytomorphology 13 174–183
Chikkanaiah P S 1964a An embryological study ofMurdania simplex (Vahl.) Brenar;J. Indian Bot. Soc. 43 238–248
Chikkanaiah P S 1964b Contribution to the life history ofFloscopa scandens Lour;J. Karnatak Univ. 9 11–122
Chikkanaiah P S 1964c Studies inTinantia fugax Scheidw;J. Karnatak Univ. 9 123–137
Chikkanaiah P S 1971 Post-fertilization studies inAneilema paniculata Wall;Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. B73 96–104
Davis G L 1966Systematic embryology of the Angiosperms (London: John Wiley & Sons)
Foster A S 1934 The use of tannic acid and iron chloride for staining cell walls in meristematic tissue;Stain Tech. 9 91–92
Guignard J L 1975 Du Cotyledon des Monocotylèdones;Phytomorphology 25 193–200
Haccius B and Lakshmanan K K 1966 Vergleichende Untersuchung der Entwicklung von Kotyledo und Sprobscheitel beiPistia stratiotes undLemna gibba, ein Beitrag zum Problem des sogennanten terminalen Blattorgane;Beitr. Biol. Pflanzen 42 425–443
Johansen D A 1940Plant Microtechnique (N.Y.: McGraw Hill)
Lakshmanan K K 1972 Monocot Embryo inVistas is Plant Science eds T M Varghese and Grover2 61–110
Lakshminarasimhamurthy 1934 Gametogenesis and embryogeny of someCommelinaceae;Curr. Sci. 4 528
Lakshminarasimhamurthy 1936 Gametogenesis and embryogeny of someCommelinaceae;J. Indian Bot. Soc. 17 101–116
Maheshwari S C and Baldev B 1958 A contribution to the morphology and embryology ofCommelina forskalaei Vahl;Phytomorphology 8 277–298
Murashige T and Skoog F 1962 A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures;Physiologia Pl. 15 473–497
Norstog K and Rhamstine E 1969 Isolation and culture of haploid and diploid cycad tissues;Phytomorphology 17 374–381
Philip V J and Gouri V 1975 Development of Cotyledon and epicotyl in Murdania semiteres (Dalz) Santapau (Aneilema paniculatum Wall);La Cellule 71 33–38
Schnarf K 1931Vergleichende Embryologie der Angiospermae (Berlin)
Solms-Laubauch 1878 Uber monokotyle Embryonen mit scheitelburtigen Vegetationspunkt;Bot. Zeit. 36 65–74
Souèges R 1958a Embryogenie des Commélinacèes. Dèveloppement de l’embryon chez leCommelina communis L;C R Acad. Sci. Paris 246 2082–2086
Souèges R 1958b Embryogenie des Commèlinaees. Dèveloppement de l’embryon chez leRhoeo discolor Hance;C R Acad. Sci. Paris 246 2436–2440
Yamashita T 1970 Eigenartige Wurzelanlage des Embryos beiLilaea subulata Humb. et Bonpl. undTriglochin maritimum L;J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo 10 181–205
Yamashita T 1972 Eigenartige Wurzelanlage des Embryos beiRuppia maritima;Beitr. Biol. Pfl. 48 157–170
Yamashita T 1973 Uber die Embryo-und Wurzelentwicklung beiZostera japonica;J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo 11 175–193
Yamashita T 1976 Uber die Embryo-und Wurzelentwicklung beiAponogeton madagascariensis (Mirbel) van Bruggen;J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo 12 37–64
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmanan, K.K. Studies on the development ofCommelina benghalensis L I. Zygote to globular proembryo. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 86, 167–174 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03050944
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03050944