Abstract
It is a well-known fact that theoretically the absorption of new quinolones in the intestinal tract is significantly inhibited as a result of their interaction with metal cations. In order to study the effects of S. M powder, which is frequently used in the department of dentistry, on the tissue transfer of new quinolones, we administered S. M powder in combination with levofloxacin (LVFX) to rabbits and made comparative studies of soft tissue transfer rates. Prior to the initiation of the present study, we confirmed that there is a significant difference in tissue transfer rates of ofloxacin (OFLX) and LVFX, based upon the fact that LVFX is an optical activator of the OFLX. We obtained the following results in this study:
-
1)
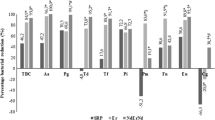
All the samples including the serum and tissue specimens collected from the LVFX single administration group reached Tmax 0.33–0.82 hours later than those collected from the OFLX single administration groups showed
-
2)
Although the serum samples collected from the LVFX and OFLX single administration groups showed nearly the equivalent Cmax, all tissue samples collected from the LVFX single administration group showed higher transfer rates than those collected from the OFLX single administration group.
-
3)
All the samples including the serum and tissue specimens collected from the S. M powder combination group showed lower values of Cmax and AUC than those collected from the LVFX single administration group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar JF and Francoual S: The clinical problems of bacterial resistance to the new quinolones. J anticrob Chemother,26(Suppl B): 270–213, 1990.
Crumplin GC: Mechanism of resistance to the 4-quinolone antibacterial agents, J Antimicrob Chemother,26(Suppl F): 131–144, 1990.
Wijands WJA, Herwaarden CL and Vree TB: Enoxacin raises plasma theophylline concentration. The Lancet,14(July): 108–109, 1984.
Maesen FP, Teengs JP, Baur C and Davies BI: Quinolones and raised plasma concentrations of theophylline, The Lancet,1(September): 530, 1984.
Wijnands WJA, Vree TB and Vanherwaarden: The influence of quinolone derivatives on theophylline clearance, Br J Clin Pharmacol,22: 677–683, 1986.
Wijnands WJA and Vree TB: Interaction between the fluoroquinolones and bronchodilator theophylline, J Antimicrob Chemother,22(Suppl C): 109–114, 1988.
Sano M, Kawakatu K, Yamamoto I, Yamasina H and Goto M: Inhibitory effect of enoxacin, ofloxacin and norfloxacin on renalexcretion of theophylline in humans. Eur J Clin Pharmacol,36: 323–324, 1989.
Barnett G, Segura J, Torre R and Carbo: Pharmacokinetic determination of relative potency of quinolone in hibition of caffeine disposition, Eer J Clin Pharmacol,39: 63–69, 1990.
Peloquin CA, Nix DE, Sedman AJ, Wilton JH, Toothaker RD, et al.: Pharmacokinetics and clinical effects of caffeine alone and in combination with oral enoxacin, Rev Infect Dis,11(Suppl 5S): 1095, 1989.
Healy DP, Polk RE, Kanawati L, Rock DT and Mooney ML: Interaction between oral ciproflozacin and caffeine in nomal volunteers, Antimicrob Agents Chemother.33: 474–478, 1989.
Staib AH, Stille W, Dietlein G, Shah PM, et al.: Interaction between quinolones and caffeine, Drugs,34 (Suppl 1): 170–174, 1987.
Stille W, Harder S, Mieke S, Beer C and Shah PM, et al.: Decrease of caffeine elimination in man during co-administraction of 4-quinolones, J Antimicrob Chemother,20: 729–734, 1987.
Simpon KJ and Brodie MJ: Low maternal serum AFP and down syndrome. The Lancet,20(July): 161, 1984.
Anatasio GD, Menscer D and Little JM: Norfloxacin and seizures, Ann Intern Med,15(July): 169–170, 1988.
Rippelmeyer DJ and Synhavsky A: Ciprofloxacin and allegic interstitial nephritis, Ann Intern Med,15 (July): 170, 1988.
Hootkins R, Fenves AZ, Brooks B, Farkas R, Stephens MK, et al.: Acute renal failure (ARF) secondary to oral ciprofloxacin (C), Kidneylnt,35: 227, 1989.
Murray KM and Wilson MG: Suspected ciprofloxacin induced interstitial nephritis, DICP,24(April): 379–380, 1990.
Davery PG: Overview of drug interactions with the quinolones, J Antimicrob Chemother,22(Suppl C): 97–107, 1988.
Janknegt R: Drug interaction with quinolones, J Antimicrob Chemother,26(Suppl D): 7–29, 1990.
Lode H: Drug interactions with quinolones, Rev Infect Dis,10(Supple 1): 132–136, 1988.
Davies BI and Maesen FPV: Drug interactions with quinolones, Rev Infect Dis,11(Suppl 5): 1083–1090, 1989.
Stahlmann R: Safety profile of the quinolones, J Antimicrob Chemother,26(Suppl D): 31–44, 1990.
Lennart KP, et al.: Variability in bioavailability Concentration versuseffect, Variability in Drug Therapy, lsted, 167–183, Raven Press, New York, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwashige, Y., Satoh, T. Studies on penetration of peroral new quinolone, levofloxacin to rabbit oral soft tissues with influence of stomachics sankyo magen mittel. Shigaku = Odontology 85, 408–418 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03039037
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03039037