Abstract
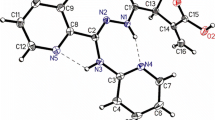
The molecular structure of acemetacin, 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic acid carboxymethyl ester, was determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The compound was recrystallized from a mixture of acetone and water in triclinic, space group P1, with a=7.796(1), b=10.245(2), c=13.542(3) Å, α=97.35(1), β=96.34(1), ψ=107.06(1)°, and Z=2. The calculated density is 1.422; the observed value is 1.42 g/cm3. The structure was solved by the direct method and refined by full matrix least-squares procedure to the final R value of 0.037 for 2960 independent reflections. There are water molecules, which are thought to be co-crystallized during the evaporation procedure, with the ratio of one water per compound molecule in the crystal. The conformation of the compound is found to be very similar to that of indomethacin. The molecules are stabilized by three O−H…O type intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the oxygen of water molecule and those of the compound.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Appleton, R. A. and Brown, K., Conformational Requirements at the Prostaglandin Cyclooxygenase Receptor Site: A Template for Designing 1. Non-steroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs.Prostaglandins, 18(1), 29–34 (1979).
Boltze, K. H., Brendler, O., Jacobi, H., Opitz, W., Raddatz, S., Seidel, P. R. and Vollbrecht, D., Chemische Struktur und antiphlogistische Wirkung in der Reihe der substitutierten Indol-3-essigsauren,Arzneim-Forsch., 30, 1314–1325 (1980).
Bray, M. A. and Gordon, D., Prostaglandin Production by Macrophages and the Effect of Antiinflammatory Drugs.,Br. J. Pharmac. 63, 635–642 (1978).
Fair, C. K., MoIEN,Structure Determination System, Delft Instruments, The Netherlands, 1990.
Flower, R. J., Moncada, S. and Vane, J. R., Drug therapy of inflammation, In Gilman A. G., Goodman, L. S., Rall, T. W. and Murad, F. (Eds.),The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 6th Edn., Macmillan Co., New York, 1980, pp. 638–728.
Foulon, M., Baert, F. and Fouret, R., Syncrystallization of Enantiomers or Diastereoisomers. I. Structure of (+)-(2R, αS)-2-Isopropyl-α-methyl-5-α-indanacetic acid (C15H20O2).Acta Cryst., B35, 2058–2062 (1979).
Gund, P. and Shen, T. Y., A Model for the Prostaglandin Synthetase Cyclooxygenation Site and Its Inhibition by Antiinflammatory Arylacetic acids.J. Med. Chem., 20(9), 1146–1152 (1977).
Hart, F. D., Huskisson, E. C. and Ansell, B. M., Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Analgesics, In Hart, F. D. (Ed.),Drug Treatment of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2nd End, ADIS Press, Sydney, 1982, pp. 9–60.
Johnson, C. K.,ORTEP, A FORTRAN Thermal-Ellipsoid Plot Program for Crystal Structure Illustrations (ORGN-3794). Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, 1975.
Kim, Y. B., Kim, S. J. and Koo, J. H., Refinement of the Structure of Alclofenac, 4-Allyloxy-3-Chlorophenylacetic acid (C11H11O3Cl).Arch. Pharm. Res., 9(4), 223–227 (1986).
Kim, Y. B., Song, H. J. and Park, I. Y., Refinement of the Structure of Naproxen, (+)-6-methoxy-α-methyl-2-naphthaleneacetic acid.Arch. Pharm. Res., 10(4), 232–238 (1987).
Kim, Y. B., Park, I. Y. and Park, Y. H., The Crystal Structure of Fe-______., 3-(4-bopreny _carbonyl)propionic acid (C16H14O15), A Non-steroidal Antiinflammatory Agent.Arch. Pharm. Res., 11(2), 127–133 (1988).
Kim, Y. B., Park, I. Y. and Park, Y. H.. The Crystal Structure of Cinmetacin (C21H19NO4), A Non-steroidal Antiinflammatory Agent.Arch. Pharm. Res., 12(1), 52–57 (1989).
Kim, Y. B., Park, I. Y. and Lah, W. R., The Crystal Structure of Naproxen Sodium, (C14H13O3Na), A Non-steroidal Antiinflammatory Agent.Arch. Pharm. Res., 13 (2), 166–173 (1990).
Kistenmacher, T. J. and Marsh, R. E., Crystal and Molecular Structure of an Antiinflammatory Agent, Indomethacin, 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methyoxy- 2-methylindole-3-acetic acid.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94(4), 1340–1345 (1972).
Koo, C. H., Kim, S. H. and Shin, W., Crystal Structure of Antiinflammatory Sulindac.Bull. of Korean Chem. Soc., 6(4), 222–224 (1985).
Nyburg, S. C., Some Uses of A Best Molecular Fit Routine,Acta Cryst., B30, 251–253 (1974).
The International Union of Crystallography,International Tables for X-ray Crystallography. Vol. III, Kynoch Press, Birmingham, England, 1974.
Tomlinson, R. V., Ringold, N. J., Qureshi, M. C. and Forchielli, E., Relationship between Inhibition of Prostaglandin Synthesis and Drug Efficacy: Support for Current Theory on Mode of Action of Asprin-Like Drugs.Biochem. Biophys. Res., 46(2), 552–559 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.B., Kim, J.A. & Park, I.Y. The crystal structure of acemetacin monohydrate (C21H18NO6Cl−H2O), A non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent. Arch. Pharm. Res. 16, 134–139 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036861
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036861