Abstract
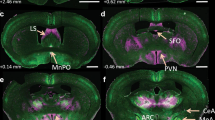
The brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is important in fluid balance and blood pressure regulation. In this study, we compared angiotensin (Ang) receptor density in the subfornical organ (SFO) and paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of a) brain angiotensinogen deficient rats (ASrAogen); b) those with high levels of brain Ang II [(mRen2)27]; c) Hannover Sprague Dawley (SD) rats at 48 and 68 wks of age. Since there was no difference between the two ages in any of the three strains, the data from the 48 and 68 wk time points were combined. There was a significantly higher level of AT1 receptors in the SFO and PVN of ASrAogen animals compared to both the SD and (mRen2)27 rats. This suggests that the brain RAS is important in regulating receptor density and that the differences may be explained by lower levels of the peptide locally. These higher levels of receptors suggest that the ASrAogen animals in adulthood and early aging would be more sensitive to either circulating or endogenous brain Ang II than the SD animals of similar age. In contrast, the similar receptor density in the (mRen2)27 and SD rats suggest that previous reports of reduced responses in the (mRen2)27 rats may result from differences in post receptor mechanisms such as intracellular signaling. Moreover, our data reveal that functional assessments are necessary in addition to receptor density levels to understand the consequences of long-term alterations in brain tissue peptides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allred AJ, MC Chappell, CM Ferrario and DI Diz (2000) Differential actions of renal ischemic injury on the intrarenal angiotensin system.Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol 279, F636-F645.
Bains JS, A Potyok and AV Ferguson (1992) Angiotensin II actions in paraventricular nucleus: functional evidence for neurotrans-mitter role in efferents originating in subfornical organ.Brain Res. 599, 223–229.
Brennan TJ, M Morris and JR Haywood (1984) GABA agonists inhibit central sodium-induced vasopressin-dependent increases in arterial pressure.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 103, 223–234.
Castren E and JM Saavedra (1989) Angiotensin II receptors in par-aventricular nucleus, subfornical organ, and pituitary gland of hypophysectomized, adrenalectomized, and vasopressin-defi-cient rats.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 725–729.
Culman J, A Blume, P Gohlke and T Unger (2004) The renin-angiotensin system in the brain: possible therapeutic implications for AT1-receptor blockers.J. Hum. Hypertens 16, S64-S70.
Deschepper CF, J Bouhnik and WF Ganong (1986) Colocalization of angiotensinogen and glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes of rat brain.Brain Res. 374, 195–198.
Diz DI and N Pirro (1992) Differential actions of angiotensin II and angiotensin-(1-7) on transmitter release.Hypertension 19 (Suppl II), II-41-II-48.
Diz DI, KL Barnes and CM Ferrario (1986) Contribution of the vagus nerve to angiotensin II binding in the canine medulla.Brain Res. Bull. 17, 497–505.
Diz DI, JA Jessup, BM Westwood, SM Bosch, S Vinsant, PE Gallagher and DB Averill (2001) Angiotensin peptides as neuro-transmitters/neuromodulators in the dorsomedial medulla.Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 29, 473–482.
Healy DP and MP Printz (1984) Distribution of immunoreactive angiotensin II, angiotensin I, angiotensinogen, and renin in the central nervous system of intact and nephrectomized rats.Hypertension 6, I-130-I-136.
Jackson L, A Sakima, SD Oden, EN Tommasi, D Ganten, CM Ferrario and DI Diz (2003) Angiotensin receptor density in dor-somedial medulla under varying local angiotensin levels during aging.Hypertension 44: 516 (Abstr.)
Kusaka I, G Kusaka, C Zhou, M Ishikawa, A Nanda, DN Granger, JH Zhang and J Tang (2004) Role of AT1 receptors and NAD(P)H oxidase in diabetes-aggravated ischemic brain injury.Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 286, H2442-H2451.
Lavoie JL and CD Sigmund (2003) Minireview: overview of the renin-angiotensin system--an endocrine and paracrine system.Endocrinology 144, 2179–2183.
Lavoie JL, MD Cassell, KW Gross and CD Sigmund (2004) Adjacent expression of renin and angiotensinogen in the rostral ventrolateral medulla using a dual-reporter transgenic model.Hypertension 43, 1116–1119.
Lee MA, M Bohm, M Paul, M Bader, U Ganten and D Ganten (1996) Physiological characterization of the hypertensive trans-genic rat TGR(MREN2)27.Am. J. Physiol 270, E919-E929.
Li P, M Morris, DI Diz, CM Ferrario, D Ganten and MF Callahan (1996) Role of paraventricular angiotensin AT-1 receptors in salt sensitive hypertension in MRen-2 transgenic rats.Am. J. Physiol 270, R1178-R1181.
Mann JFE, MI Phillips, R Dietz, H Haebara and D Ganten (1978) Effects of central and peripheral angiotensin blockade in hypertensive rats.Am. J. Physiol. (Heart Circ. Physiol.) 234, H629-H637.
Mayorov DN and GA Head (2003) AT1 receptors in the RVLM mediate pressor responses to emotional stress in rabbits.Hypertension 41, 1168–1173.
McKinley MJ, AL Albiston, AM Allen, ML Mathai, CN May, RM McAllen, BJ Oldfield, FA Mendelsohn and SY Chai (2003) The brain renin-angiotensin system: location and physiological roles.Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 35, 901–918.
Monti J, M Schinke, M Bohm, D Ganten, M Bader and G Bricca (2001) Glial angiotensinogen regulates brain angiotensin II receptors in transgenic rats TGR(ASrAOGEN).Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol 280, R233-R240.
Moriguchi A, KB Brosnihan, H Kumagai, D Ganten and CM Ferrario (1994) Mechanisms of hypertension in transgenic rats expressing the mouse Ren-2 gene.Am. J. Physiol 266, R1273-R1279.
Moriguchi A, EA Tallant, K Matsumura, TM Reilly, H Walton, D Ganten and CM Ferrario (1995) Opposing actions of angiotensin-(1-7) and angiotensin II in the brain of transgenic hypertensive rats.Hypertension 25, 1260–1265.
Morimoto S, MD Cassell, TG Beltz, AK Johnson, RL Davisson and CD Sigmund (2001) Elevated blood pressure in transgenic mice with brain-specific expression of human angiotensinogen driven by the glial fibrillary acidic protein promoter.Circ. Res. 89, 365–372.
Morimoto S, MD Cassell and CD Sigmund (2002) Neuron-specific expression of human angiotensinogen in brain causes increased salt appetite.Physiol. Genomics 9, 113–120.
Mullins JJ, J Peters and D Ganten (1990) Fulminant hypertension in transgenic rats harbouring the mouse Ren-2 gene.Nature 344, 541–544.
Oden SD, CS Carter, CM Ferrario, D Ganten, L Ferder, N Basso, WE Sonntag and DI Diz (2002) Influence of the brain renin-angiotensin system on cognitive ability during aging.Hypertension 40, 381.
Phillips MI (1978) Angiotensin in the brain.Neuroendocrinol.25, 354–377.
Saavedra JM and C Chevillard (1982) Angiotensin-converting enzyme is present in the subfornical organ and other circumven-tricular organs.Neurosci. Lett. 29, 123–127.
Saavedra JM, J Fernandez-Pardal and C Chevillard (1982) Angiotensin-converting enzyme in discrete areas of the rat fore-brain and pituitary gland.Brain Res. 245, 317–325.
Sakima A, EN Tommasi, DB Averill, CM Ferrario and DI Diz (2003) Imbalance of endogenous brain angiotensin II and angiotensin-(1–7) contributes to diminished baroreceptor reflex function in aging rats. Proc. XVth Inter-American Soc.Hypertension 75.
Schinke M, O Baltatu, M Bohm, J Peters, W Rascher, G Bricca, A Lippoldt, D Ganten and M Bader (1999) Blood pressure reduction and diabetes insipidus in transgenic rats deficient in brain angiotensinogen.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 3975–3980.
Senanayake PD, A Moriguchi, H Kumagai, D Ganten, CM Ferrario and KB Brosnihan (1994) Increased expression of angiotensin peptides in the brain of transgenic hypertensive rats.Peptides 15, 919–926.
Tagawa T and RAL Dampney (1999) AT1 receptors mediate excitatory inputs to rostral ventrolateral medulla pressor neurons from hypothalamus.Hypertension 34, 1301–1307.
Tallant EA, D Ganten and CM Ferrario (1994) Attenuated responses to angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells from trans-genic (mREN2) 27 rats.Am. J. Hypertension 7 (4 Part II), 1359.
Thone-Reineke C, M Zimmermann, C Neumann, M Krikov, J Li, N Gerova and T Unger (2004) Are angiotensin receptor blockers neuroprotective?Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 6, 257–266.
Touyz RM (2004) Reactive oxygen species and angiotensin II signaling in vascular cells — implications in cardiovascular disease.Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 37, 1263–1273.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasper, S.O., Ferrario, C.M., Ganten, D. et al. Central depletion of angiotensinogen is associated with elevated AT1 receptors in the SFO and PVN. neurotox res 6, 259–265 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033436
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033436