Abstract
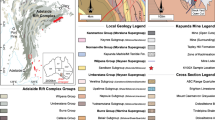
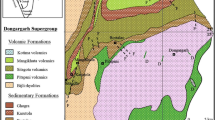
The present study was focused on red sandston beds occurring in the Chilgok Formation, lower Hayang Group of Cretaceous age. Red sandstones consist mainly of plagioclase, quartz, and volcanic rock fragment, with accessory minerals such as biotite, chlorite, pyroxene, hornblende, leucoxene, ilmenite, sphene, pyrite, and hematite. Volcanic rock fragments composed of pyroxene, plagioclase, and glass material are intensively altered. Reddening of sandstones was preferentially attributed to the presence of hematite, Fe- and Ti-bearing minerals. Hematite pigmentation was largely caused by post-depositional dissolution of Fe-silicates such as chlorite, biotite, and amphibole. Diagnostic alteration of mafic minerals as well as Ti-bearing minerals, together with clay minerals, indicates that pigmentary materials in the red beds inherited from diagenetic sources in the depositional basin, possibly during early diagenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berner, R.A., 1969, Goethite stability and the origin of red beds. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 33, 267–273.
Chang, K.H., 1966, Stratigrahy and sedimentation of Naktong Subgroup (Lower Cretaceous), Gyeongsang Proveince, southern Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 2, 17–51.
Chang, K.H., 1967, Sedimentary environments and stratifigraphic relations of the Silra conglomerate tongue, Gyeongsang province, southern Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 3, 101–112.
Chang, K.H., 1975, Cretaceous stratigraphy of southeast Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 11, 1–23.
Chang, K.H., Park, S.O. and Kim, H.S., 1997, Cretaceous stratigraphy and geologic history of medial Kyongsang Basin: tectonics and volcanism. Geosciences Journal, 1, 2–9.
Deer, W.A., Howie, R.A. and Zussman, J., 1980, An introduction to the rock-forming minerals. Longman, London, 528 p.
Frost, M.T., Grey, I.E., Harrowfield, I.R. and Mason, K., 1983, The dependence of alumina and silica contents on the extent of alteration of weathered ilmenites from Western Australia. Mineralogical Magazine, 47, 201–208.
Miki, T., 1992, Sedimentologic and paleoclimatic classification of Cretaceous red beds in East Asia: a general review. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 7, 179–184.
Miki, T. and Matsueda, H., 1985, Genesis of the paleogene purplered beds in western Kyushu, Japan. Memoir of Faculty Science, Kyushu University, 35, 399–415.
Miki, T., Matsueda, H. and Yim, W.-S., 1990, petrography and geochemistry of Cretaceous red beds in Hong Kong. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 4, 99–106.
Schwertmann, U. and Taylor, R.M., 1989, Iron Oxides. In: Dixon, J.B. and Weed, S.B. (eds.), Minerals in Soil Environments. Soil Science of America, Madison, Wisconsin, p. 379–438.
Shin, Y.S., 1998, Red beds of Cretaceous lower Hayang Group in the central part of Kyongsang basin Korea. Ph.D. thesis, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, 151 p. (in Korean)
Shin, Y.S., Lee, Y.T., Lee, Y.J. and Koh, I.S., 2001, Petrochemical characteristics of sandstones and mudstones from the Lower haying Group (Cretaceous), Taegu, Korea. Journal of the Geological Society of Korea, 37, 153–168. (in Korean with English abstract)
Turner, P., 1980, Continental Red Beds. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 562 p.
Um, S.H., Choi, H.I., Son, J.D., Oh, J.H., Kwak, Y.H., Shin, S.C. and Yun, S.H., 1983, Geological and geochemical studies on the Gyeongsang Supergroup in the Gyeongsang basin. Korea Institute of Energy and Resources Bulletin, 36, 124 p. (in Korean with English abstract)
Walker, T.R., 1967, Formation of red beds in modern and ancient deserts. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 78, 353–368.
Walker, T.R., 1974, Formation of red beds in moist tropical climates: a hypothesis. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 85, 633–638.
Yun, H., Moon, H.S., Lee, H.K., Kim, I.S. and Song, Y.S., 1993, The color of the sedimentary rocks in the Euiseong basin and its stratigraphical and paleoenvironmental implication. Journal of Paleontological Society of Korea, 9, 93–114. (in Korean with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choo, C.O., Shin, Y.S. & Koh, I.S. Mineralogical evidence for red coloration of sandstones at the Chilgok Formation of the Cretaceous Hayang Group, Southeastern Korea. Geosci J 6, 141–148 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03028285
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03028285