Abstract
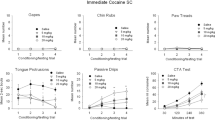
We systematically paired auditory, olfactory, and social stimuli with each injection of morphine in rats. We found that, when morphine was kept constant at a low dose, the external stimuli acquired the property of a conditional stimulus (CS) to cause hyperthermia which was antagonized by naloxone. In rats in which morphine doses were regularly increased to cause morphine dependence, the CS presented during withdrawal, caused reduction in withdrawal signs (wet shakes, hypothermia, aggression) and produced hyperglycemia as well as elevation of striatal homovanillic acid. CS-induced alleviation of withdrawal hypothermia was blocked by mecamylamine, phenoxybenzamine, haloperidol, benztropine or naloxone but not by cyproheptadine or propranolol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borison, H. L., Fishburn, B. R., Bhide, N. K., and McCarthy, L. E.: Morphine-induced hyperglycemia in cats.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 138:229–235, 1972.
Crisler, G.: Salivation is unnecessary for the establishment of the salivary conditioned reflex induced by morhpine.Physiology 84:553, 1930.
Drawbaugh, R., Miksic, S., Smith, N., and Lal, H.: Naloxone antagonism of conditional reversal of narcotic withdrawal signs and conditional morphine hyperthermia: An indirect evidence for release of endogenous opioid-like substance in the rat.Fed. Proc. 36:309, 1976.
Drawbaugh, R. and Lal, H.: Effect of pharmacological interference with various neuropathways on blockade of morphine withdrawal hypothermia by morphine and conditional stimulus.Neuropharmacol. 15:375–378, 1976.
Drawbaugh, R. and Lal, H.: Reversal by narcotic antagonist of a narcotic action elicited by a conditional stimulus.Nature 247:65–67, 1974.
Gianutsos, G., Hynes, M., Puri, S., Drawbaugh, R., and Lal, H.: Effects of apomorphine and nigrostriatal lesions on aggression and striatal dopamine turnover during morphine withdrawal: Evidence for dopaminergic supersensitivity in protracted abstinence.Psychoparmacologia (Berl.) 34: 37–44, 1974.
Gianutsos, G., Drawbaugh, R. B., Hynes, M.D., and Lal, H.: The narcotic withdrawal syndrome in the rat.In S. Ehrenpries and E. Neidel (Eds.): Methods in Narcotic Research. New York, Marcel Dekker, 1975; pp. 293–309.
Gianutsos, G., Hynes, M., Drawbaugh, R., and Lal, H.: Paradoxical absence of aggression during naloxone?precipitated morphine withdrawal.Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 43:43–46, 1975a.
Goldberg, S. and Schuster, C.: Conditioned morphine induced abstinence changes: Persistence in post-morphine dependent monkeys.J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 14:33–46, 1970.
Kleitman, N. and Crisler, G.: A quantitative study of a salivary conditioned reflex.Am. J. Physiol. 79:571, 1927.
Lal, H., O’Brien, J., and Puri, S.: Morphine withdrawal aggression sensitization by amphetamines.Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22:217–223.
Lal, H.: Morphine withdrawal aggression.In S. Ehrenpries and E. A. Neidel (Eds.): Methods in Narcotic Research. New York, Marcel Dekker, 1975; pp. 149–171.
Lal, H., Puri, S. K., and Volicer, L.: A comparison between narcotics and neuroleptics: Effects on striatal dopamine turnover, cyclic AMP, and adenylate cyclase.In D. Ford and D. Clouet (Eds.): Tissue Responses to Addictive Drugs. Spectrum Publication, 1976, in press.
Lal, H. and Numan, R.: Blockade of morphine-withdrawal body shakes by haloperidol.Life Sci. 18:163–168, 1976.
Lynch, J. L., Fertziger, A. P., Teitelbaum, H. A., Cullen, J. W., and Gantt, W. H.: Pavlovian conditioning of drug reactions: Some implications for problems of drug addiction.Cond. Reflex 8:211–223, 1973.
Martin, W. R., Wikler, A., Eades, C. G., and Pescor, F. T.: Tolerance to and physical dependence on morphine in rats.Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 4:247–260, 1963.
Miksic, S., Smith, N., Numan, R., and Lal, H.: Acquisition and extinction of a conditioned hyperthermic response to a tone paired with morphine administration.Neuropsychobiology 1:277–283, 1975.
Numan, R., Smith, N., and Lal, H.: Reduction of morphine-withdrawal body shakes by a conditional stimulus in the rat.Psychopharmacol. Comm. 1: 295–303, 1975.
Numan, R., Reddy, C., Drawbaugh, R., and Lal, H.: Effect of morphine on rectal temperature after acute and chronic treatment in the rat. Paper presented at New England Pharmacology Meeting, 1976.
Pavlov, I. P.:Conditional Reflexes, translated by G. Anrep. New York, Oxford University Press, 1927.
Roffman, M., Desjardin, P., and Lal, H.: Conditional tolerance to hexobarbital.In J. Singh and H. Lal (Eds.): Drug Addiction: Neurobiology and Influence on Behavior. New York, Stratton Intercontinental, 1974, pp. 251–258.
Roffman, M., Reddy, C., and Lal, H.: Control of morphine withdrawal hypothermia by conditional stimuli.Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 29:197–201, 1973.
Wikler, A. and Pescor, F.: Classical conditioning of a morphine abstinence phenomenon, reinforcement of opioid drinking behavior and “relapse” in morphine addicted rats.Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10:255–284, 1967.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lal, H., Miksic, S., Drawbaugh, R. et al. Alleviation of narcotic withdrawal syndrome by conditional stimuli. Pav. J. Biol. Sci. 11, 251–262 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000318
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000318