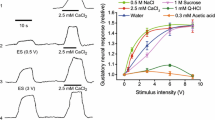
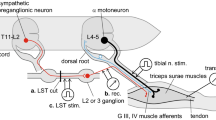
Abstract
Stimulation of the central stump of either vagosympathetic trunk in the dog, the contralateral nerve remaining intact, regularly provoked deep respiratory movements with forceful expiration, followed by a period of apnea, and a fall in blood pressure, systolic and diastolic, of 20–60 mm/Hg. Stimulation of the cephalad portion of the left nerve provoked brief acceleration of heart rate during the period of hyperventilation, followed by bradycardia; when the stimulus was applied to the central stump of the right nerve heart rate remained relatively unchanged. When a 12-second tone as a conditional stimulus (CS) was reinforced during its last six seconds with such stimulation of the vagosympathetic trunk as an unconditional stimulus (US), despite the striking visceromotor responses elicited by the US, no conditional reflex was established even after more than 3,400 trials in 16 dogs (34–781 trials per animal).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, E. D.: Afferent impulses in the vagus and their effect on respiration.J. Physiol.,79: 332, 1933.
Agostoni, E., Chinnock, J. E., Daly, M.deB., and Murray, J. G.: Functional and histological studies of the vagus nerve and its branches to the heart, lungs and abdominal viscera in the cat.J. Physiol.,135: 182, 1957.
Bailey, P., and Bremer, F.: A sensory cortical representation of the vagus nerve.J. Neurophysiol.,1: 404, 1938.
Bert, P.:Leçons sur la Physiologie Compareé de la Respiration. Balliere, Paris, 1879.
Bezold, A. von, and Hirt, L.: Untersuch.Physiol. Lab. Würzburg,1: 95, 1867.
Birykov, D. A., Komeva, E. A., Shlyafer, T. P., and Yakoleva, M. L:. Phylogenetic and ontogenetic patterns in development of reflex regulation of cardiac activity and respiration in animals.Fed. Proc,22: T-80, 1963.
Bonhoeffer, K., Kramer, K., and Muehl, N.: Ueber die Zuordnung pressorischer and depressorischer Kreislaufreflexe zu einzelnen Fasergruppen im Halsvagus des Hundes.Arch. Ges. Physiol.,267: 265, 1958.
Brick, I.: Circulatory responses to immersing the face in water.J. App. Physiol.,17: 33, 1966.
Bykov, K. M.: The Cerebral Cortex and Internal Organs. Translation by W. H. Gantt. New York, Chemical Publishing Co., 1957.
Bykov, K. M., and Alexijew-Berkman, I. A.: Die Ausbildung bedingter Reflexe auf die Harnausscheidung.Arch. Ges. Physiol,224: 710, 1930.
Caralesu, F. R., and Pearce, J. W.: Electrical activity of efferent vagal fibers and dorsal nucleus of the vagus during reflex bradycardia in the cat.J. Physiol,176: 228, 1964a.
Caralesu, F. R., and Pearce, J. W.: Effects on heart rate of electrical stimulation of medullary vagal structures in the cat.J. Physiol,176: 241, 1964b.
Cheringovskii, V. N.: Morphophysiologic architecture of subcortical and cortical projections of afferent vagus nerve fibers.Fed. Proc,24: (translation supplement) 668, 1965.
Corson, S. A.: Conditioning of water and electrolyte excretion.Res. Publ. Ass. Res. New. Ment. Dis.,43: 140, 1966.
Corson, S. A.: Endocrines and the central nervous system.Res. Publ. Ass. Res. Nerv. Ment. Dis.,43: 140, 1966.
Cottle, M. K.: Degeneration studies of the primary afferents of IXth and Xth cranial nerves.J. Comp. Neurol.,122: 329, 1964.
Daggett, W. M., Nugent, G. C., Carr, P. W., Powers, P. C., and Harada, Y.: Influence of vagal stimulation on ventricular contractility, O2 consumption and coronary flow.Am. J. Physiol.,212: 8, 1967.
Dawes, G. S.: Studies on veratrum alkaloids: Receptor areas in coronary arteries and elsewhere as revealed by the use of veratridine.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.,89: 325, 1947.
Dedashev, Ya. P.: Exteroceptive and interoceptive conditioned reflex influences on the motor activity of the reticulum and rumen in sheep.Fiziol. Zh. SSSR Sechenov,45: 1259, 1962. (Quoted by Razran, R. L.:Psychol. Rev., 68:81.)
DeGeest, H., Levy, M. N., Zeeske, H., and Lipman, R. I.: Depression of ventricular contractility by stimulation of the vagus nerves.Circ. Res.,17: 222, 1965.
Dell, P., and Olson, R.: Projections thalamiques, corticales et cerebelleuses des afferences viscerales vagales.Compt. Rend. Soc. Biol.,145: 1084, 1951.
Dell, P., and Olson, R.: Idem. Projections “secondaires” mesencephaliques, diencephaliques et amygdaliennes des afference viscerales vagales,Compt. Rend. Soc. Biol,145: 1088, 1951.
Feley, J. O., and DuBois, F. S.: Quantitative studies of the vagus nerve in the cat: (1) Ratio of sensory to motor fibers.J. Comp. Neurol. 67: 49, 1937.
Gantt, W. H.: Pharmacological agents in study of higher nervous activity.Dis. Nerv. Syst.,18: 1, 1957.
Getz, B., and Sernes, T.: The localization within the dorsal motor vagal nucleus. An experimental investigation.J. Comp. Neurol.,90: 95, 1949.
Gssell, R. A.: Cardiodynamics in heart block as affected by auricular systole, auricular fibrillation and stimulation of the vagus nerve.Am. J. Physiol.,40: 267, 1916.
Gunn, C. G., Sevelius, G., Puiggar, M. J., and Myers, F. K.: Vagal cardiomotor mechanisms in the hindbrain of the dog and cat.Am. J. Physiol.,214: 258, 1968.
Heinbecker, P., and O’Leary, J.: The mammalian vagus nerve-a functional and histological study.Am. J. Physiol.,106: 623, 1933.
Hering, E., and Breuer, J.: Die Selbststeuerung der Atmung durch den Vagus.Setzungsb. d.k. Akad. d. Wissenschaft (Wien),57: 672; 58:909, 1868.
Hering, H. E.: Der Karotisdruckversuch.Munchnen Med. Wschr.,70: 1287, 1923.
Heymans, C., Bouckaert, J. F., and Regniers, P.: Le sinus carotidien et la zone homologue cardio-aortique. Paris, Doin & Cie, 1933.
Heymans, C., and Neil, E.: Reflexogenic areas of the cardiovascular system. London, Churchill, 1958.
Hoffman, H. H., and Kuntz, A.: Vagus nerve components.Anat. Rec,127: 551, 1957.
James, A. H.: Cardiac syncope after swallowing.Lancet,1: 771, 1958.
Jarisch, A., and Zotterman, Y.: Depressor reflexes from the heart.Acta Physiol Scand.,16: 31, 1948.
Jones, J. V.: The afferent pathway of the Bezold reflex: The right vagal branches in cats.Brit. J. Pharmacol,8: 352, 1953.
Jones, R. L.: Cell fiber ratios in the vagus nerve.J. Comp. Neurol,67: 469, 1937.
Kerr, F. W. L.: Function of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.Science,157: 451, 1967.
Komendantova: Quoted by Bykov, 1957, p. 47.
Kopald, H. H., Roth, H. P., Flesher, B., and Pritchard, W. H.: Vagovagal syncope.New Eng. J. Med.,271: 1238, 1964.
Kosupkin, J. M., and Olmsted, J. M. D.: Slowing of the heart as a conditional reflex in the rabbit.Am. J. Physiol,139: 550, 1943.
Lamb, L. E., Dermksian, G., and Samoff, C. A.: Significant cardiac arrhythmias induced by common respiratory maneuvers.Am. J. Cardiol.,2: 563, 1958.
Levine, S. A.: Oculocardiac reflex.Arch. Int. Med.,15: 758, 1915.
Mitchell, G. A. G., and Warwick, R.: The dorsal vagal nucleus.Acta Anat.,25: 31, 1955.
Napolitano, L. M., Willman, V. T., Hanlon, C. R., and Cooper, T.: Intrinsic innervation of the heart.Am. J. Physiol,208: 455, 1965.
Nonindez, J. F.: Studies on the innervation of the heart. I. Distribution of the cardiac nerves with special reference to the identification of the sympathetic and parasympathetic postganglionics.Am. J. Anat.,65: 361, 1939.
Oberholzer, R. J. H.: Afferent fibers of cardiovascular and pulmonary origins and their intrabrellar connections.Tohoku J. Exp. Med.,80: 288, 1962.
Paintal, A. S.: Conduction velocities of respiratory and cardiovascular afferent fibers in the vagus nerve.J. Physiol.,121: 341, 1953.
Paintal, A. S.: Vagal afferent fibers.Ergebn. Physiol,52: 74, 1963.
Perez-Cruet, J., Jude, J. R., and Gantt, W. H.: An attempt to condition extrasystoles using direct myocardial electrical stimulation as an unconditional stimulus.Conditional Reflex,1: 104, 1966.
Plumlee, L. A.: Personal communication.
Pogrebkova, A. V.: Conditioned reflexes to hypercapnia.Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR,73: 225, 1950. (Quoted by Razran, R. L.:Psychol. Rev., 68:81, 1961.)
Pogrebkova, A. V.: Respiratory interoand exteroceptive conditioned reflexes and their interrelationship.Trud. Inst. Fiziol. Pavlova,1: 103, 1952.
Richet, C.: De la resistance des canards a l’asphyxie.J. Physiol. Pathol. Gen.,1: 641, 1899.
Rudiger, W., and Lindeman, M.: Gallbladder distention and the effects of several drugs on heart rate, respiratory movements and cortical potentials in cats with hypothalamic lesions.Conditional Reflex,2: 113, 1967.
Samonina, G. E., and Udel’nov, M. G.: Electrophysiological analysis of activity in cardiac branches of vagus nerves in the course of viscero-cardiac reflexes.Fed. Proc,24: T567, 1965.
Sarokhtin, J., Turgel, K. U., and Minut-Sarokhtina, O.:Zh. Fiseol. USSR,17: 207, 1934. Quoted by Kosupkin, J. M. and Olmsted, J. M. D.: Slowing of the heart as a conditioned reflex in the rabbit.Am. J. Physiol., 139:550, 1943.
Tcheng, K. T.: Innervation du myocarde et du faisceau de His chez deux mammiferes, le mouton et le chat.Cardiologia,15: 227, 1949.
Tcheng, K. T.: Innervation of the dog’s heart.Am. Heart J.,41: 512, 1951.
Teitelbaum, H. A., Gantt, W. H., and Stone, A.: Cardiac conditional reflexes can be formed to pain not to acetylcholine.J. Nerv. Ment. Dis.,123: 484, 1956.
Uvnas, B.: Central cardiovascular control. InHandbook of Physiology. Sec. I, vol. 11, 1146. Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, 1960.
Wang, H. H., Blumenthal, M. R., and Wang, S. C.: Effect of efferent vagal stimulation on coronary sinus outflow and cardiac work in the anesthetized dog.Circ. Res.,8: 271, 1960.
Wang, S. C., and Borson, H. L.: An analysis of the carotid sinus cardiovascular reflex mechanism.Am. J. Physiol,150: 712, 1947.
Weiss, S., and Ferris, E. B.: Adams-Stokes syndrome with complete heart block of vagovagal reflex origin.Arch. Int. Med.,54: 931, 1934.
Whitteridge, D.: Afferent nerve fibers from heart and lungs in the cervical. vagus.J. Physiol,107: 496, 1948.
Widdecombe, J. G.: Respiratory reflexes from the trachea and bronchi of the cat.J. Physiol,123: 57; 71, 1954.
Wolf, S., Schneider, R. A., and Groover, M. E.: Further studies on the circulatory and metabolic alterations of the oyxgen-conserving (diving) reflex in man.Trans. Ass. Amer. Physicians,78: 242, 1965.
Wolf, S.: The bradycardia of the dive reflex-a possible mechanism of sudden death.Trans. Amer. Clin. Climat. Ass.,76: 192, 1964.
Wyss, D. A. M.: Respiratory effects from stimulation of the afferent vagus nerve.J. Neurophysiol,10: 315, 1947.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Grant HE-06945 from the National Heart Institute.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrus, E.C., Gantt, W.H., Plumlee, L.A. et al. Failure to develop a conditional reflex by stimulation of the cephalad portion of the severed vagosympathetic trunk: Its significance in terms of the central connections of the vagus. Conditional Reflex 4, 6–19 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000073
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000073