Abstract
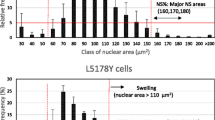
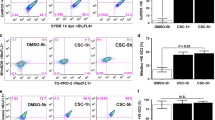
A series of bioassays such as sister chromatid exchange frequencies (SCEs), chromosomal aberration (CA), micronuclei rate (MN) and cell-cycle delay have been used to detecting the genotoxic effect of cigarette smoke condensate (CSC) on human diploid cell 2BS strain. The results suggested that a higher SCE, (17.0/cell) was observed in 2BS cells treated with CSC at 100 µg/ml, as compared with 6.9/cell of the background (P<0.001). CA rate was significantly increased from 4% to 36% in cells treated with 10 µg/ml CSC (P<0.001). MN rate varied from 9–26‰. in cells treated with CSC compared to that of control (6‰). Meanwhile, the cell-cycle of cells was markedly delayed by CSC. The survival rate of 2BS cells declined to 59.6% for treatment with CSC at 200 µg/ ml. There was a dose-effect response in SCEs, CA, MN rate. We proposed that active oxygen might responsible for genotoxicity of CSC on cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Raat WK. Comparison of the induction by cigarette smoke condensates of sister chromatid exchanges in Chinese hamster cells and mutation in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res 1979; 63:253.
Salomua et al. Genotoxic emissions of smoke emissions in mammalian cells. Environ Int 1985; 11:311.
Madle et al. Cytogenetic effects of cigarette smoke condensatein vitro andin vivo. Human Genet 1981; 59:349.
1986;8:39.
1989; 11(6):422.
Wu M, Wang X. Q. An improved method for differential staining of sister chromatids. Acad Sin 1980; 25:239.
1987;9(1):35.
Heddle JA, et al. The micronucleus assay I.In vitro. In: Stich HF and San RHC (eds). Short term tests for chemical carcinogens. New York: Springer-Verlay. 1980; 250.
1981;8:222.
1981; 15:284.
Hopkin JM, HJ Evans. Cigarette smoke condensate damage DNA in human lymphocytes. Nature (London) 1979; 279: 241.
Stich HF,. 1982; 16:132.
Venema G. The influence of substances extracted from cigarette-smoke on mitotic processes in Allium cepa. Chromosome 1959; 10: 679.
Leuchtenberger C, et al. Morphological and cytochemical effects of marijuana cigarette smoke on epithelioid cells of lung explants from mice. Nature (London) 1971; 234: 227.
Nakayama T, et al. Cigarette smoke induce DNA single- strand breaks in human cells. Nature 1985; 3144:462.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, M., Hu, G. & Luo, X. Genotoxic effect of cigarette smoke condensate (CSC) on human diploid cell 2BS strain. Chin J Cancer Res 4, 39–42 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02997508
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02997508