Abstract
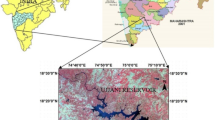
The reservoir surveys carried out using the conventional equipments like theodolite, plane table, sextant, range finders, sounding rods, echo-sounders and slow moving boats etc. are time consuming and sometime it takes up to three years to complete the survey of a major reservoir like Hirakud. During such longtime of survey, the siltation pattern and the bed levels also get changed. So, the need to update the sediment measurement techniques and to introduce latest technology available in the field was felt to overcome the difficulties faced in the conventional method especially in major reservoirs. With this objective, the present study of the assessment of the sedimentation in Linganmakki reservoir is carried out using remote sensing and GIS techniques. The revised capacities in the zone of reservoir levels (533.05 – 548.78 m) for the year 1989–1990 and 2001–2002 in the zone of 532.20 – 545.91 m of reservoir levels were determined, which is found 2837.84 M cum and 2207.95 M cum respectively. Based on these results, the sedimentation rates in the zone (533.05 – 548.78 m) come out to be 8.96 ham/100 km2/year and for the zone (532.20 – 545.91 m) is 8.57 ha-m/100 km2/year. It is found that the results are comparable during and the uniform sediment rate of 8.57 ha-m/100 km2/ year can be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhar, A.K. (1987). Remote sensing application to sedimentation studies. Technical report RN-45/87, National Institute of Hydrology, Roorkee.
Durbude, Dilip G and Varadarajan, N. (2002). Assessment of sedimentation in Tungabhadra reservoir using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Unpublished technical report, National Institute of Hydrology, Roorkee.
Garde, R.J. (1995). Reservoir sedimentation. State of art report no. INCOH/SAR-6/95, INCOH, National Institute of Hydrology, Roorkee.
Goel, M.K. and Jain, S.K. (1996). Evaluation of reservoir sedimentation using multi-temporal IRS-1A LISS II data.Asian Pacific Remote Sensing and GIS J.,8(2): 39–43.
Holeyer, R.J. (1978). Suspended sediment algorithms.Remote Sensing Environment,10(4): 323–338.
Khoram, S. (1981). Use of occean colour scanner data in water quality mapping.Photogramm. Engg. Remote Sensing,47(5): 667–676.
Mohanty, R.B., Mahapatra, G., Mishra, D. and Mahapatra, S.S. (1986). Report on application of remote sensing to sedimentation studies in Hirakund reservoir. Technical report of Orissa Remote Sensing Application Centre, Bhubaneswar and Hirakud Research Station, Hirakud, India.
Rajan, B.H. (1982). Sedimentation studies-Tungabhadra reservoir. Report on 1981 survey, Irrigation department, Govt. of Karnataka.
Shangale, A.K. (1991). Reservoir sedimentation status in India. Jalvigyan Sameeksha, INCOH, NIH Roorkee, VI (1&2).
Smith, S.E., Mancy, K.H. and Latif, A.F.A. (1980). Application of remote sensing technique towards the management of Aswan high dam reservoir. Proceeding of the International symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, pp.1297–1307.
Solomonson, V.V. (1973). Remote sensing applications in water resources. Proceeding of International Sym. on Earth Resources Technology, Washington D. C, USA during 10–14 December, 1973.
Varshney, R.S. (1997). Impact of siltation on the useful life of large reservoir. State of art report no. INCOH/ SAR-11/97, INCOH, National Institute of Hydrology, Roorkee.
Vibulsresth, S., Srisangthong, D., Thisayakorn, K., Suwanwerakamtom, R., Wongparn, S., Rodpram, C, Leelitham, S. and Jittanaon, W. (1988). The reservoir capacity of Ulbolratana dam between 173 and 180 meters above mean sea level.Asian Pacific Remote Sensing!,1(1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Durbude, D.G., Purandara, B.K. Assessment of sedimentation in the Linganmakki Reservoir using remote sensing. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 33, 503–509 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990735
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990735