Abstract
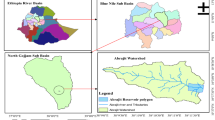
This specific study was conducted on the Abrajit reservoir in east Gojjam, Amhara region, Ethiopia. The general objective of the study was to investigate reservoir siltation and determination of the remaining valuable life span of the reservoir using ArcGIS 10.5 version and Golden surfer 16 latest version. A bathymetric survey using echo-sounding equipment (Garmin GPSMAP421s) was conducted and a topo map of reservoir data was used for assessment of the sediment volume. The accumulated sediment volume was estimated by subtracting the triangular interconnected network (TIN) map of the initial bed level from the currently measured bed level. The result of the research revealed that to date, 343,700.1 m3 bulk of sediment was accumulated in the reservoir that reduces 20% of the total reservoir capacity. In the results from the bathymetric investigation and software analysis, annually 28,641.675 m3 year−1 amount of sediment is coming from the catchments to the reservoir that contributed 1.66% of annual reservoir volume reduction. The measured recent storing capacity for the Abrajit Dam was 1,388,870 m3. From a comparison of remaining reservoir storage and annual sediment load, the reservoir will not serve more than 12 years. The estimated specific sediment yield (SSy) was found to be 4733.387 ton km−2 year−1. Therefore, to improve the estimated life span of the reservoir, watershed management is very important and further study is required to identify the area where watershed conservation will focus in the future. Upon the findings, the reservoir volume is running to reduce and it cannot serve all the demand what it designed for during the dry season. As a result, operation curves should be mandatory to give water service for the critical water needs, and regular monitoring of sediment accumulation in the reservoir is recommended.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown CB (1943) Discussion of “Sedimentation in reservoirs”. Proc ASCE 69(6)
Chomba IC, Sichingabula HM (2015) Sedimentation and its effects on selected small Dams East of Lusaka. Zambia. Modern Environmental Science and Engineering 1(6):325–340
Dagnew DC et al. (2015) Impact of conservation practices on runoff and soil loss in the sub-humid Ethiopian Highlands : The Debre Mawi watershed, (1998), pp. 210–219. https://doi.org/10.1515/johh-2015-0021
Dumanski J, Pieri C (2000) Land quality indicators: research plan. Agric Ecosyst Environ 81(2):93–102
Gill MA (1979) Sedimentation and useful life of reservoirs. J Hydrol 44(1–2):89–95
Haregeweyn N (2012) Reservoir sedimentation and its mitigating strategies: a case study of Angereb reservoir (NW Ethiopia). Journal of Soils and Sediments 12(2):291–305
Ilci V, Ozulu IM, Alkan RM, Erol S, Uysal M, Kalkan Y, Bilgi S, Seker DZ (2019) Determination of reservoir sedimentation with bathymetric survey: a case study of Obruk Dam Lake. Journal of Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 28(3):2305–2313
Jauhari VP (2000) The operation, monitoring, and decommissioning of large dams in India. Prepared for Thematic Review IV. 5: Operation, Monitoring, and Decommissioning of Dams. Water Policy 172
Javier F et al (2008) Variability of NSSDA estimations. 134(2):39–44. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9453(2008)134
Lal R (1994) Soil erosion research methods. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Lawrence P (2004) Sedimentation in small dams. Development of a catchment characterization and sediment yield prediction procedure
Li J, Heap AD (2011) Ecological Informatics. A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in environmental sciences: performance and impact factors. Ecological Informatics. Elsevier B.V. 6(3–4):228–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2010.12.003
Minear JT, Kondolf GM (2009) Estimating reservoir sedimentation rates at large spatial and temporal scales: a case study of California. Water Resour Res 45. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007WR006703
Mitiku H, Herweg K, Brigitta S (2006) Sustainable land management: A new approach to soil and water conservation in Ethiopia
Moges MM, Abay D, Engidayehu H (2018) Investigating reservoir sedimentation and its implications to watershed sediment yield : the case of two small dams in data- scarce upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia, (November 2017), pp. 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/lre.12234
NDEP (2004) Guidelines for digital elevation data (Version 1.0)
Rakhmatullaev S et al (2012) Sedimentation of reservoirs in Uzbekistan : a case study of the Akdarya Reservoir, Zerafshan River Basin To cite this version : HAL Id : insu-00617806 Sedimentation of reservoirs in Uzbekistan : a case study of the Akdarya Reservoir, Zerafshan River Bas
Sekellick AJ, Banks WS (2010) Water volume and sediment accumulation in Lake Linganore, Frederick County, Maryland, 2009. US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey
Verstraeten G, Poesen J (2000) Estimating trap efficiency of small reservoirs and ponds : methods and implications for the assessment of sediment yield. 2, pp. 219–251
Verstraeten G, Poesen J (2001) Factors controlling sediment yield from small intensively cultivated catchments in a temperate humid climate
Zandbergen PA (2008) Positional accuracy of spatial data : non-normal distributions and a critique of the national standard for spatial data accuracy. 12(1):103–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiferaw, M., Abebe, R. Reservoir sedimentation and estimating dam storage capacity using bathymetry survey: a case study of Abrajit Dam, Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Appl Geomat 13, 277–286 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-020-00348-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-020-00348-x