Abstract
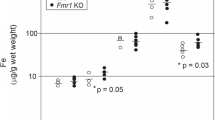
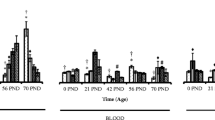
The changes in tissue Mn, Cu, Fe, Zn, and Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity were studied in control and Mn-deficient mice during postnatal development. Mn levels were lower in tissues from Mn-deficient mice than in controls throughout development. By day 60, Mn concentration in tissues from Mn-deficient mice was at least 70% lower than that of controls. Cu levels in the two groups did not differ appreciably. Liver Cu concentration was highest at day 5, then decreased. Heart and kidney Cu increased throughout development. Fe concentration in heart and liver was similar in both groups at 1, 5, and 20 days of age, but at day 60, kidney Fe in the Mn-deficient mice was 40% higher than in controls. The developmental pattern for MnSOD activity paralleled that of Mn concentration. At day 5, there were no differences in MnSOD activity between control and deficient mice. By day 60, MnSOD activity in most tissues was at least 50% lower than that of controls, possibly increasing the susceptibility of the Mn deficient animal to oxidative damage.
These developmental patterns should help investigators to determine the tissues and time periods in which to study trace element metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.L. Keen, B. Lönnerdal, and L. S. Hurley, inBiochemistry of the Essential Ultra-Trace Elements, E. Frieden, ed., Plenum, New York, 1984, pp.89–132.
L. S. Hurley,Physiol. Rev. 61, 249 (1981).
I. Fridovich,Ann. Rev. Biochem. 44, 147 (1975).
W. Bohnenkamp and U. Weser, inSuperoxide and Superoxide Dismutases, A. M. Michelson, J. M. McCord, and I. Fridovich, ed., Academic Press, New York, 1977, pp. 387–394.
D. L. Paynter,J. Nutr. 110, 437 (1980).
D. M. Williams, R. E. Lynch, G. R. Lee, and G. E. Cartwright,Proc. Soc. Exp. Med. 149, 534 (1975).
S. Zidenberg-Cherr, C. L. Keen, B. Lönnerdal, and L. S. Hurley,J. Nutr. 113, 2498 (1983).
G. de Rosa, C. L. Keen, R. M. Leach, and L. S. Hurley,J. Nutr. 110, 795 (1980).
D. I. Paynter,Biol. Trace. Element Res. 3, 121 (1980).
S. Zidenberg-Cherr, C. L. Keen, and L. S.Hurley,Biol. Trace Element Res. 7, 31 (1985)
O. Greengard,Assays Biochem. 7, 159 (1971).
S. Marklund and G. Marklund,Eur. J. Biochem. 41, 469 (1974).
M. S. Clegg, C. L. Keen, B. Lönnerdal, and L. S. Hurley,Biol. Trace Element Res. 3, 107 (1981).
M. S. Clegg, C. L. Keen, B. Lönnerdal, and L. S. Hurley,Biol. Trace Element Res. 4, 145 (1982).
A. R. Kemmerer, C. A. Elvehjem, and E. B. Hart,J. Biol. Chem. 92, 623 (1931).
L. T. Bell and L. S. Hurley,Lab. Invest. 29, 723 (1973).
C. L. Keen and L. S. Hurley,Mechanisms of Aging and Development 13, 161 (1980).
C. H. Hill and G. Matrone,Fed. Proc. 29, 1474 (1970).
H. W. Wilgus and A. R. Patton,J. Nutr. 18, 35 (1939).
C. J. Dillard, V. C. Gavino, and A. L. Tappel,J. Nutr. 113, 2266 (1983).
T. Yoshioka, K. Utsunio, and K. Sekiba,Biol. Neonate 32, 147 (1977).
V. Z. Lankin, A. K. Tikhaze, V. V. Lemeshko, K. Shermatov, L. A. Kaliman, and A. M. Vikhert,Translated from Byulleten Eksperimental noi Biologii i Meditsiny 92, 310 (1981).
I. Mavelli, A. Rigo, R. Federico, M. Ciriolo, and G. Rotilio,Biochem. J. 204, 535 (1982).
D. L. Baly, C. L. Keen, and L. S. Hurley,J. Nutr. (in press).
M. R. Bristow, M. E. Billingham, J. W. Mason, and J. R. Daniels,Cancer Treat. Rep. 62, 873 (1978).
R. Ogura, H. Toyama, T. Shimada, and M. Murakami,J. Appl. Biochem. 1, 325 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zidenberg-Cherr, S., Keen, C.L., Casey, S.M. et al. Developmental changes affected by Mn deficiency. Biol Trace Elem Res 7, 209–222 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02989247
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02989247
Index Entries
- Manganese deficiency, and development
- MnSOD, and development
- tissue Mn, and development
- development and Mn deficiency
- Superoxide dismutase, in Mn-deficient mouse tissues
- CuZn-SOD, and development
- manganese, in developing mouse tissues
- copper, in Mn-deficient mouse tissues
- iron, in Mn-deficient mouse tissues
- zinc, in Mn-deficient mouse tissues