Abstract
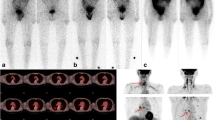
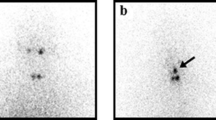
Objective: After initial treatment with total thyroidectomy and radioiodine ablation, most follow-up protocols for patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma contain cyclic diagnostic I–131 imaging and serum thyroglobulin measurements. The applied diagnostic I–131 doses vary between 37 and 370 MBq. The aim of this study was to determine the yield of a diagnostic scan with 370 MBq I-131 in patients with a negative diagnostic scan with 74 MBq I–131.Methods: Retrospective evaluation of 158 patients who received a high-dose diagnostic scan with 370 MBq I–131 because of a negative low-dose diagnostic scan with 74 MBq I–131. Special attention was paid to the patients with positive high-dose diagnostic scanning and undetectable serum thyroglobulin levels after thyroid hormone withdrawal.Results: In 127 (80%) of patients the 370 MBq I–131 scan was negative, just like the preceding low-dose scan. In 31 (20%) of patients abnormal uptake was present on the 370 MBq diagnostic scan. In 19 of these 31 patients serum thyroglobulin was undetectable. In 15/19 the high-dose diagnostic scan proved either false positive or demonstrated clinically irrelevant minor ablation rests. In only four patients (2.5%) did the high-dose diagnostic scans reveal possibly relevant uptake caused by residual differentiated thyroid cancer.Conclusion: In 98% of patients a 370 MBq dose of I–131 for diagnostic WBS had no additional value. The combination of a low-dose diagnostic I–131 scan using only 74 MBq combined with a serum Tg level measurement proved sufficient for correct clinical decision making regarding whether the patient requires additional I–131 therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlumberger MJ. Papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma.New Engl J Med 1998; 338: 297–306.
Mazzaferri EL, Kloos RT. Current approaches to primary therapy for papillary and follicular thyroid cancer.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1447–1463.
Nemac J, Rohling S, Zamrazil V, Pohunkova D. Comparison of the distribution of diagnostic and thyroablative I-131 in the evaluation of differentiated thyroid cancers.J Nucl Med 1979; 20: 92–97.
Waxman A, Ramanna L, Chapman N, Chapman D, Brachman M, Tanasescu D, et al. The significance of I-131 scan dose in patients with thyroid cancer: Determination of ablation: Concise communication.J Nucl Med 1981; 22: 861–865.
Ramanna L, Waxman AD, Brachman MB, Tanasescu DE, Chapman N, Braunstein G. Treatment rationale in thyroid carcinoma: effect of scan dose.Clin Nucl Med 1985; 10: 687–689.
Sherman SI, Tielens ET, Sostre S, Wharam MD, Ladenson PW. Clinical utility of post-treatment radioiodine scans in the management of patients with thyroid carcinoma.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994; 78: 629–634.
Greenler DP, Klein HA. The scope of false-positive iodine- 131 images in thyroid carcinoma.Clin Nucl Med 1989; 14: 111–117.
Park HM, Perkins OW, Edmondson JW, Shnute RB, Manatunga A. Influence of diagnostic radioiodines on the uptake of ablative dose of iodine-131.Thyroid 1994; 4: 49- 54.
Pacini F, Lippi F, Formica N, Elisei R, Anelli S, Ceccarelli C, et al. Therapeutic doses of iodine-131 reveal undiag- nosed metastases in thyroid cancer patients with detectable serum thyroglobulin levels.J Nucl Med 1987; 28: 1888- 1891.
Cholewinski SP, Yoo KS, Klieger PS, O’Mara RE. Absence of thyroid stunning after diagnostic whole-body scanning with 185 MBq131I.J Nucl Med 2000; 41: 1198–1202.
Jeevanram RK, Shah DH, Sharma SM, Ganatra RD. luence of initial large dose on subsequent uptake of therapeutic radioiodine in thyroid cancer patients.Nucl Med Biol 1986; 13: 277–279.
Muratet JP, Dacer A, Minier JF, Larra F. Influence of scanning doses of iodine-131 on subsequent first ablative treatment outcome in patients operated on for differentiated thyroid carcinoma.J Nucl Med 1998; 39: 1546–1550.
Legar FA, Izembart M, Dagousset F, Barritault L, Baillet G, Chevalier A, et al. Decreased uptake of thrapeutic doses of iodine-131 after 185-MBq iodine-131 diagnostic imaging for thyroid remnants in differentiated thyroid carcinoma.J Nucl Med 1998; 25: 242–246.
Morris LF, Waxman AD, Braunstein GD. The nonimpact of thyroid stunning: remnant ablation rates in131I-scanned and nonscanned individuals.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 3507–3511.
Cailleux AF, Baudin E, Travagli JP, Ricard M, Schlumberger M. Is diagnostic iodine-131 scanning useful after total thyroid ablation for differentiated thyroid cancer?J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 175–178.
Ozata M, Suzuki S, Miyamoto T, Liu RT, Fierro-Renoy F, DeGroot LJ. Serum thyroglobulin in the follow-up of patients with treated differentiated thyroid cancer.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994; 79: 98–105.
Pacini F, Agate L, Elisei R, Capezzone M, Ceccarelli C, Lippi F, et al. Outcome of differentiated thyroid cancer with detectable serum Tg and negative diagnostic131I whole body scan: Comparison of patients treated with high131I activities versus untreated patients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 4092–4097.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Grant: Supported by a grant from “De Vereniging voor Academische Ziekenhuizen”, The Netherlands.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phan, T.T.H., van Tol, K.M., Links, T.P. et al. Diagnostic I–131 scintigraphy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: No additional value of higher scan dose. Ann Nucl Med 18, 641–646 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02985956
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02985956