Abstract
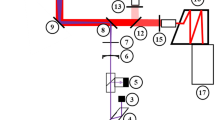
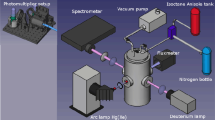
The exciplex fluorescence technique with the TMPD (tetamethyl-p-phenylene-diamine) / naphthalene dopant system was applied in a combustion-type constant-volume spray chamber. A detailed set of calibration experiments has been performed in order to quantify the TMPD fluorescence signal. It has been demonstrated that the TMPD fluorescence intensity was directly proportional to concentration, was independent of the chamber pressure, and was not sensitive to quenching by either water vapor or carbon dioxide. Using a dual heated-jet experiment, the temperature dependence of TMPD fluorescence up to 1000 K was measured. The temperature field in the spray images was determined using a simple mixing model, and an iterative solution method was used to determine the concentration and temperature field including the additional effects of the laser sheet extinction. The integrated fuel vapor concentration compared favorably with the measured amount of injected fuel when all of the liquid fuel had evaporated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cp :
-
Specific heat
- Cgas :
-
TMPD concentration [mol/l]
- f:
-
Photophysical function defined as Eq.(3)
- hc/λ:
-
Energy of the fluorescence photon
- hu :
-
latent heat of vaporization
- l0 :
-
Incident intensity of the laser sheet [W/cm2]
- K:
-
Absolute calibration constant
- L:
-
Distance that the laser sheet has traveled [cm]
- MW:
-
Molecular weight
- N:
-
Number density [cm-3]
- P:
-
Pressure
- R:
-
Gas constant
- S:
-
Spray tip penetration or pixel intensity on the camera [pixel count]
- T:
-
Temperature
- t:
-
Time
- V:
-
Measurement volume
- x:
-
Spray axial position or mole fraction
- y:
-
Spray radial position
- ε:
-
Molar extinction coefficient [(l/molcm]
- φ:
-
Local equivalence ratio within the fuel vapor field
- ηc :
-
Fluorescence efficiency (Stern-Vollmer factor)
- η:
-
Detection effincy
- λ:
-
Wavelength
- θ:
-
Spray spreading angle
- p:
-
Ratio of the fuel to the ambient density
- σ:
-
Absorption coefficient [cm2] or unit standard deviation
- Ω :
-
Collection solid angle
- a or amb:
-
Ambient
- cal:
-
Calibration reference condition
- f:
-
Fuel
- i:
-
Initial state
- int:
-
Intermediate state at which the fuel vaporized
- LIF :
-
laser induced fluorescence
- l or liquid:
-
liquid
- mix :
-
Adiabatic (final) mixture state
- st :
-
Stoichiometric condition
- v orvapor :
-
Vapor
References
Berlman, I. B., 1971,Handbook of Fluorescence Spectra of Aromatic Molecules, 2nd edition, Academic Press.
Browne, K., Partridge, I., and Greeves, G., 1986, “Fuel Property Effects on Fuel/Air Mixing in an Experimental Diesel Engine,” SAE 860223.
Bruneaux, G., 200I, “Liquid and Vapor Spray Structure in High Pressure Common Rail Diesel Injection,”Atomization and Sprays, Vol. 11.
El-Wakil, M., Myers P. and Uyehara, O., 1956. “Fuel Vaporization and Ignition Lag in Diesel Combustion,” SAE Paper 560063.
Espey, C. and Dec, J., 1995, “The Effect of TDC Temperature and Density on the Liquid-Phase Fuel Penetration in a D. I. Diesel Engine, ”SAE Paper 952456.
Espey, C, Dec, J., Litzinger T. and Santavicca, D., 1997, “Planar Laser Rayleigh Scattering for Quantitative Vapor-Fuel Imaging in a Diesel Jet,”Combustion and Flame, Vol. 109, pp. 65–86.
Felton, P., Bracco F. and Bardsley. M.. 1993. “On the Quantitative Application of Exciplex Fluorescence to Engine Sprays,”SAE Paper 930870.
Kim, T and Ghandhi, J. B. 2001, “Quantitative 2-D Fuel Vapor Concentration Measurements in an Evaporating Diesel Spray using the Exciplex Fluorescence Method,”SAE Paper 2001-01-3495.
Kim, T., 2001, Quantitative 2-D Fuel Vapor Concentration Measurements in an Evaporating Diesel Spray using the Exciplex Fluorescence Method, Ph. D. diss., Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin.
Kosaka, H. and Kamimoto, T., 1993, “Quantitative Measurement of Fuel Vapor Concentration in an Unsteady Evaporating Spray via a 2-D Miescattering Imaging Technique,”SAE paper 932653.
Melton, L., 1983, “Spectrally Separated Fluorescence Emissions for Diesel Fuel Droplets and Vapor,”Applied Optics, Vol. 22, No. 14, pp. 2224–2226.
Naber, J. and Siebers, D., 1996, “Effects of Gas Density and Vaporization on Penetration and Dispersion of Diesel Sprays,”SAE Paper 960034.
Oren, D., Wahiduzzaman, S. and Ferguson, C, 1984, “A Diesel Combustion Bomb : Proof of Concept,”SAE Paper 841358.
Rabenstein, F., Egermann, J,, Leipertz A. and D’Alfonso, N., 1998, “Vapor-Phase Structures of Diesel-Type Fuel Sprays : An Experimental Analysis,”SAE Paper 982543.
Rotunno, A., Winter, M., Dobbs G., and Melton, L., 1990, “Direct Calibration Procedures for Exciplex-Based Vapor/Liquid Visualization of Fuel Sprays,”Combust. Sci. and Tech., Vol. 71, pp. 247–261.
Scheid, E., Pischinger, F., Knoche, K., Daams, H., Hassel E. and Ruter, U., 1986, “Spray Combustion Chamber with Optical Access, Ignition Zone Visualization and First Raman Measurements of Local Air-Fuel Ratio,”SAE Paper 861121.
Senda J. and Kanda, T., 1997, “Quantitative Analysis of Fuel Vapor Concentration in Diesel Spray by Exciplex Fluorescence Method,”SAE paper 970796.
Siebers, D., 1999, “Scaling Liquid-Phase Fuel Penetration in Diesel Sprays Based on Mixing-Limited Vaporization,”SAE Paper 1999-01-0528.
Vargaftik, N.B., 1983,Handbook of Physical Properties of Liquid and Gas, Hemisphere, Washington.
Yaws, C. L., 1992,Thermodynamic and Physical Property Data, Gulf Publishing Company.
Yeh, C, Kamimoto, T., Kosaka H. and Ko-bori, S., 1994, “Quantitative Measurement of 2-D Fuel Vapor Concentration in a Transient Spray via Laser-Induced Fluorescence Technique,”SAE paper 941953.
Zhao, H. and Ladommatos, N., 1998, “Optical Diagnostics for In-cylinder Mixture Formation Measurements in IC Engines,”Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., Vol. 24, pp. 297–336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, T., Ghandhi, J.B. Quantitative vapor phase exciplex fluorescence measurements at high ambient temperature and pressure. KSME International Journal 17, 157–167 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984297
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984297