Abstract
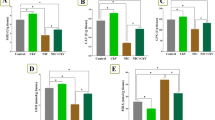
The suppressive effects of Platycodi Radix (Changkil: CK), the root ofPlatycodon grandiflorum A. DC (Campanulaceae), on the progress of acute carbon tetrachloride (CCI4)-induced hepatic fibrosis were investigated in the rat. CK significantly suppressed CCI4-induced hepatic necrosis and inflammation, as determined by the serum enzymatic activities of alanine and aspartate aminotransferase and serum tumor necrosis factor-α levels, in dose-dependent manners. In addition, the increased hepatic fibrosis after acute CCI4 treatment was suppressed by the administration of CK. CK also significantly prevented the elevation of hepatic α1(l) procollagen (type I collagen) mRNA and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expressions in the liver of CCI4-intoxicated rats and also suppressed the induction of α-SMA and type l collagen in cultured hepatic stellate cells, in dose-dependent manners. These results suggest that the suppressive effects of CK against the progress of acute CCI4-induced hepatic fibrosis possibly involve mechanisms related to its ability to block both hepatic inflammation and the activation of hepatic stellate cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beutler, B. and Kruys, V., Lipopolysaccharide signal transduction, regulation of tumor necrosis factor biosynthesis, and signaling by tumor necrosis factor itself.J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 25, S1-S8 (1995).
Bradford, M. M., A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem., 72, 248–254 (1976).
Brandsten, C., Lundmark, C., Christersson, C., Hammarstrom, L., and Wurtz, T., Expression of collagen alphal(l) mRNA variants during tooth and bone formation in the rat.J. Dent. Res., 78, 11–19 (1999).
Brattin, W. J., Glende, E. A. Jr., and Recknagel, R. O., Pathological mechanisms in carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity.J. Free Radio. Biol. Med., 1, 27–38 (1985).
Brenner, D. A., Waterboer, T., Choi, S. K., Lindquist, J. N., Stefanovic, B., Burchardt, E., Yamauchi, M., Gillan, A., and Rippe, R. A., New aspects of hepatic fibrosis.J. Hepatol., 32, 32–38 (2000).
Casini, A., Cunningham, M., Rojkind, M., and Lieber, C. S., Acetaldehyde increases procollagen type I and fibronectin gene transcription in cultured rat fat-storing cells through a protein synthesis-dependent mechanism.Hepatology, 13, 758–765 (1991).
Castro, J. A., Ferreyra, E. C., Casro, C. R., Sasame, H., Fenos, O. M., and Gillette, J. R., Prevention of carbon tetrachloride-induced necrosis by inhibitors of drug metabolism. Further studies on the metabolism of their action.Biochem. Pharmacol., 23, 295–302 (1974).
Choi, C. Y., Kim, J. Y., Kim, Y. S., Chung, Y. C., Hahm, K. S., and Jeong, H. G., Augmentation of macrophage functions by an aqueous extract isolated from Platycodon grandiflorum.Cancer Lett., 166, 17–25 (2001).
Chomczynski, P. and Sacchi, N., Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol chloroform extraction.Anal. Biochem., 162, 156–159 (1987).
Davis, B. H. and Madri, J. A., Type I and type III procollagen peptides during hepatic fibrogenesis: an immunohisto-chemical and ELISA serum study in the CCI4 rat model.Am. J. Pathol., 26, 119–129 (1987).
Friedman, S. L., The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis: Mechanism and treatment strategies.N. Engl. J. Med., 328, 1828–1835 (1993).
Friedman, S. L., Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis. An integrated cellular response to tissue injury.J. Biol. Chem., 275, 2247–2250 (2000).
George, J., Roulot, D., Koteliansky, V. E., and Bissell, D. M.,In vivo inhibition of rat stellate cell activation by soluble transforming growth factor beta type II receptor: a potential new therapy for hepatic fibrosis.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 96, 12719–12724 (1999).
Iredale, J. P., Benyon, R. C., Arthur, M. J., Ferris, W. F., Alcolado, R., and Winwood, P. J., Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 messenger RNA expression is enhanced relative to interstitial collagenase messenger RNA in experimental liver injury and fibrosis.Hepatology, 24, 176–184 (1996).
Kim, K. S., Ezaki, O., Ikemoto, S., and Itakura, H., Effects of Platycodon grandiflorum feeding on serum and liver lipid concentrations in rats with diet-induced hyperlipidemia.J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 41, 485–491 (1995).
Knittel, T., Schuppan, D., Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K. H., and Ramadori, G., Differential expression of collagen types I, III, and IV by fat-storing (Ito) cellsin vivo.Gastroenterology, 102, 1724–1735 (1992).
Kristensen, D. B., Kawada, N., Imamura, K., Miyamoto, Y., Tateno, C., Seki, S., Kuroki, T., and Yoshizato, K., Proteome analysis of rat hepatic stellate cells.Hepatology, 32, 268–277 (2000).
Kunstle, G., Hentze, H., Germann, P. G., Tiegs, G., Meergans, T., and Wendel. A., Concanavalin A hepatotoxicity in mice: Tumor necrosis factor-mediated organ failure independent of caspase-3-like protease activation.Hepatology, 30, 1241–1251 (1999).
Lee, K. J., Choi, C. Y., Chung, Y. C., Kim, Y. S., Ryu, S. Y., Roh, S. H., and Jeong, H. G., Protective effect of saponins derived from roots of Platycodon grandiflorum onterf-butylhydro-peroxide-induced oxidative hepatotoxicity.Toxicol. Lett., 147, 271–282 (2004).
Lee, K. J. and Jeong, H. G., Protective effect of Platycodi radix on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity.Food Chem. Toxicol., 40, 517–525 (2002).
Lee, K. J., You, H. J., Park, S. J., Kim, Y. S., Chung, Y. C., Jeong, T. C., and Jeong, H. G., Hepatoprotective effects of Platycodon grandiflorum on acetaminophen-induced liver damage in mice.Cancer Lett., 174, 73–81 (2001).
Li, D. and Friedman, S. L., Liver fibrosis and the role of hepatic stellate cells: new insights and prospects for therapy.J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 14, 618–633 (1999).
Maher, J. J. and McGuire, R. F., Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosisin vivo.J. Clin. Inves., 86, 1641–1648 (1990).
Milani, S., Herbst, H., Schuppan, D., Surrenti, C., Riecken, E. O., and Stein, H., Cellular localization of type I, III, and IV procollagen gene transcripts in normal and fibrotic human liver.Am. J. Pathol., 137, 59–70 (1990).
Nakatsukasa, H., Nagy, P., Evarts, R. P., Hsia, C. C., Marsden, E., and Thorgeirsson, S. S., Cellular distribution of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and procollagen types I, III, and IV transcripts in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver fibrosis.J. Clin. Invest., 85, 1833–1843 (1990).
Pinzani, M. and Gentilini, P., Biology of hepatic stellate cells and their possible relevance in the pathogenesis of portal hypertension in cirrhosis.Semin. Liver Dis., 19, 397–410 (1999).
Ramadori, G., Veit, T., Schwogler, S., Dienes, H. P., Knittel, T., Rieder, H., and Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K. H., Expression of the gene of the alpha-smooth muscle actin isoform in rat liver and in rat fat-storing (ITO) cells.Virchows. Arch. B Cell Pathol. Incl. Mol. Pathol., 59, 349–357 (1990).
Sakaida, I., Matsumura, Y., Akiyama, S., Hayashi, K., Ishige, A., and Okita, K., Herbal medicine Sho-saiko-to (TJ-9) prevents liver fibrosis and enzyme-altered lesions in rat liver cirrhosis induced by a choline-deficient L-amino acid-defined diet.J. Hepatol., 28, 298–306 (1998).
Svegliati Baroni, G., D’Ambrosio, L., Ferretti, G., Casini, A., Di Sario, A., Salzano, R., Ridolfi, F., Saccomanno, S., Jezequel, A., and Benedetti, A., Fibrogenic effect of oxidative stress on rat hepatic stellate cells.Hepatol., 27, 720–726 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K.J., Kim, J.Y., Jung, K.S. et al. Suppressive effects ofPlatycodon grandiflorum on the progress of carbon tetrachloride-lnduced hepatic fibrosis. Arch Pharm Res 27, 1238–1244 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975888
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975888