Abstract
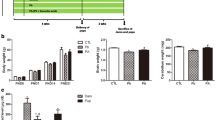
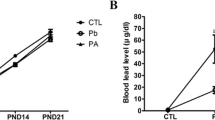
Changes in the release and uptake of glutamate in cerebellar granule and glial cells of offspring of lead-exposed mothers were determined. In cultured cerebellar granule cells exposed to lead for 5 days, glutamate release was less influenced upon N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) stimulation than that in the control. Although the NMDA-stimulated release of glutamate in cerebellar granule cells prepared from lead-exposed first generation pups was not different from that of the control group, the S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP)-stimulated release of glutamate in cerebellar granule cells obtained from lead-treated pups was less elevated than that in the control. Furthermore, in cerebellar granule cells obtained from lead-exposed second generations pups, glutamate release did not respond to both NMDA and SNAP stimulation. In cerebellar glial cells exposed to lead, the basal glutamate uptake was not changed. However, the L-trans-pyrollidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid (PDC)-blocking effects was significantly reduced. In glial cells obtained from lead-exposed pups, the glutamate uptake was also less blocked by PDC than that in the control. Further decreases in PDC-blocking effects were observed in cerebellar glial cells obtained from lead-treated second generation pups compared to those from the control group. These results indicate that lead exposure induces the changes in the sensitivities of the glutamate release and uptake transporter. In addition these results suggest that lead exposure might affect the intracellular signalling pathway and transmission in glutamatergic nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Adler, M. W. and Adler, C. H., Toxicity to heavy metals and relationship to seizure thresholds.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 22, 774–779 (1977).
Alkondon, M., Costa, A. C. S., Radhakrishnan, V., Aronstam, R. S. and Albuquerque, E. X., Selective blockade of NMDA-activated channel currents may be implicated in learning deficits caused by lead.FEBS Lett., 261, 123–130 (1990).
Arriza, J. L., Fairman, W. A., Wadiche, J. I., Murdoch, G. H., Kavanaugh, M. P. and Amara, S. G., Functional comparisons of three glutamate transporter subtypes cloned from human motor cortex.J. Neurosci., 14, 5559–5569 (1994).
Aschner, M., Gannon, M. and Kimelberg, H. M.. Interaction of trimethyltin with at primary astrocyte cultures: altered uptake and efflux of rubidium, L-glutamate and D-aspartate.Brain Res., 582, 181–185 (1992).
Bloc, A., Samuel, D., Forni, C., Dusticier, N. and Kerkerian Le Goff, L., Effects of ionotropic excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists on glutamate transport and transport-mediated changes in extracellular excitatory amino acids in the rat striatum.J. Neurochem., 64, 1598–1604 (1995).
Booze, R. M. and Mactutus, C. F., Developmental exposure to organic lead causes permanent hippocampal damage in Fisher-344 rats.Experientia, 46, 292–295 (1990).
Blazka, M. E., Harry, G. J. and Luster, M. I., Effects of lead acetate on nitrite production by murine brain endothelial cell cultures.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 126, 191–194 (1994).
Bredt, D. S. and Snyder, S. H., Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-linked enhancement of cGMP levels in the cerebellum.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 86, 9030–9033 (1989).
Bruhwyler, J., Chleide, E., Liegeois, J. F. and Carreer, F., Nitric Oxide: A new messenger in the brain.Neurosci. Biobehavior. Rev., 17, 373–384 (1993).
Busselberg, D., Evance, M. L., Haas, H. L. and Carpenter, D. O. Blockade of mammalian and invertebrate calcium channels by lead.Neurotoxicology, 14, 249–258 (1993).
Cookson, M. R., Mead, C., Austwick, S. M. and Pentreath, V. W., Use of the MTT assay for estimating toxicity in primary astrocyte and C6 glioma cell cultures.Toxicology In Vitro., 9, 39–48 (1995).
Dawson, V. L., Dawson, T. M., London, E. D., Bredt, D. S. and Snyder, S. H., Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 88, 6368–6371 (1991).
Fox, D. A., Srivastava, D. and Hurwitz, R. L., Lead-induced alteration in rod-mediated visual function and cGMP metabolism: new insights.Neurotoxicology, 15, 503–512 (1994).
Garthwaite, J., Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell-cell signalling in the nervous system.Trends in Neuroscience, 14, 60–67 (1991).
Gilad G. M., Gilad, V. H., Wyatt, R. J. and Tizabi, Y., Region-selective stress-induced increase of glutamate uptake and release in rat forebrain.Brain Res., 525, 335–338 (1990).
Goldstein, G. W., Evidence that lead acts as a calcium substitute in second messenger metabolism.Neurotoxicology, 14, 97–102, (1993).
Guilarte, T. R. and Miceli, R. C., Age-dependent effects of lead on [3H]MK-801 binding to the NMDA receptor-gated ionophore:in vitro andin vivo studies.Neurosci. Lett., 148, 27–30 (1992).
Guilarte, T. R., Miceli, R. C., Altmann, L., Weinberg, F., Winneke, G. and Wiegand, H., Chronic prenatal and postnatal Pb+2 exposure increases [3H]MK-801 binding sites in adult rat forebrain.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 248, 273–275 (1993).
Guilarte, T. R., Miceli, R. C. and Jett, D. A., Neurochemical aspects of hippocampal and cortical Pb+ neurotoxicity.Neurotoxicology, 15, 459–466 (1994).
Judd, M. G., Nagaraja, T. N. and Brookes, N., Potassium-induced stimulation of glutamate uptake in mouse cerebral astrocytes.J. Neurochem., 66, 169–176 (1996).
Lawrence, A. J. and Jarrott, B., Nitric oxide increases interstitial excitatory amino acid release in the rat dorsomedial medulla oblongata.Neurosci. Lett., 151, 126–129 (1993).
Legare, M. E., Castiglioni, A. J., Rowles, T. K., Calvin, J. A., Snyder-Armstead, C. and Tiffsny-Castiglioni, E., Morphological alterations of neurons and astrocytes in guinea pigs exposed to low levels of inorganic lead.Neurotoxicology, 14, 77–80 (1993).
Lim, D. K. and Ho, I. K., Different response to N-methyl-D-aspartate and Kainic acid in cerebellar granule cells of lead-exposed pups.Neurotoxicology, 19, 49–56 (1998).
Lorton, D. and Anderson, W. J., The effects of postnatal lead toxicity on the development of cerebellum in rats.Neurobehav. Toxicol. Teratol., 8, 51–59 (1986).
McCaslin, P. P. and Ho, I. K., Cell culture in neurotoxicology, In Hayers, A. W. (Eds.).Principles and Methods of Toxicology. Raven Press, Ltd., New York, pp. 1315–1334, 1994.
McCaslin, P. P. and Morgan, W. W., Culture cerebellar cells as anin vitro model of excitatory amino acid receptor function.Brain Res., 417, 380–384 (1987).
Nicholls, D. and Attwell, D., The release and uptake of excitatory amino acids.Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 11, 462–468 (1990).
Petit, T. L., LeBoutillier, J. C. and Brooks, W. J., Altered sensitivity to NMDA following developmental lead exposure in rats.Physiol. Behavior, 52, 687–693 (1992).
Roettger, V. R. and Goldfinger, M. D., HPLC-EC detection of free primary amino acid concentrations in cat csternal cerebrospinal fluid.J. Neurosci. Methods, 39, 263–270 (1991).
Rice, D. C., Lead-induced changes in learning Evidence for behavioral mechanisms from experimental animal studies.Neurotoxicology, 14, 167–178 (1993).
Rothstein, J. D., Dykes-Hoberg, M., Pardo, C. A., Bristol, L. A., Jin, L., Kuncl, R. W., Kanai, Y., Hediger, M., Wang, Y., Schielke, J. P. and Welty, D. F., Knockout of glutamate transporters reveals a major role for astroglial transport in excitotoxicity and clearance of glutamate.Neuron, 16, 675–686 (1996).
Singh, A. K., Age-dependent neurotoxicity in rats chronically exposed to low levels of lead: Calcium homeostasis in central neurons.Neurotoxicology, 14, 417–428 (1993).
Southam, E. and Gathwaite, J., Comparative effects of some nitric oxide donors on cyclic GMP levels in rat cerebellar slices.Neurosci. Lett., 130, 107–111 (1991).
Sutherland, M. L., Delaney, T. A. and Noebels, J. L., Glutamate transporter mRNA expression in proliferative zones of the developing and adult murine CNS.J. Neurosci., 16, 2191–2207 (1996).
Swanson, R. A., Liu, J., Miller, J. W., Rothstein, J. D., Farrell, K., Stein, B. A. and Longuemare, M. C., Neuronal regulation of glutamate transporter subtype expresion in astrocytes.J. Neurosci., 17, 932–940 (1997).
Tiffany-Castiglioni, E., Sierra, E. M., Wu, J. and Rowles, T. K., Lead Toxicity in neuroglia.Neurotoxicology, 10, 417–444 (1989).
Tiffany-Castiglioni, E., Cell culture models for lead toxicity in neuronal and glial cells.Neurotoxicology, 14, 513–536 (1993).
Uteshev, V., Busselberg, D. and Haas, H. L., Pb2+ modulates the NMDA-receptor-channel complex.Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol., 347, 209–213, (1993).
Widmer, H. R., Vedder, H., Schlumpf, M. and Lichtensteiger, W., Concurrent changes in regional cholinergic parameters and nest odor preference in the early postnatal rat after lead exposure.Neurotoxicology, 13, 615–624 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, E.Y., Lim, D.K. Effects of chronic lead exposure on glutamate release and uptake in cerebellar cells of rat pups. Arch. Pharm. Res. 21, 113–119 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974014
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974014