Abstract
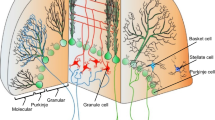
Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are a family of proteins that have seven transmembrane segments and that couple to G proteins. They differ from ionotropic glutamate receptors in that they do not form ion channels but instead affect intracellular chemical messenger systems. Eight genes coding for different subtypes of mGluRs have been identified to date and numbered accordingly in the order in which the cDNAs were cloned. Based on their principal signal-transduction capabilities in recombinant expression systems and sequence similarities, the family of mGluR subtypes is subdivided into three groups. Group 1 mGluRs (consisting of mGluR1 and 5) functionally couple to phos-pholipase C and affect the IP3/Ca2+ signaling pathway. The subtypes of group 2 (mGluR2 and 3) and group 3 (mGluR4, 6 7 and 8) inhibit adenylate cyclase and, thereby, mediate a decrease in cAMP concentration. All mGluR subtypes are found in the cerebellar cortex with the exception of mGluR6 which is exclusively expressed in the retina. At the parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses mGluR1 is localized in the peri- and extra-synaptic membrane of Purkinje cells. The main focus of this review deals with the functions of this postsynaptically localized mGluR1. These functions include (i) mediation of an inward current and a slow excitatory postsynaptic potential, and (ii) a role in induction of parallel fiber-Purkinje cell long-term depression. We discuss the mechanism underlying the mGluR1-mediated postsynaptic current as well as current theories on the role of mGluR1 in parallel fiber-Purkinje cell long-term depression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sladeczek F, Pin JP, Recasens M, Bockaert J, Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature 1985; 317: 717–719.
Nicoletti F, Wroblewski JT, Novelli A, Alho H, Guidotti A, Costa E. The activation of inositol phospholipid metabolism as a signal-transducing system for excitatory amino acids in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci 1986; 6: 1905–1911.
Masu M, Tanabe Y, Tsuchida K, Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S. Sequence and expression of a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature 1991; 349: 760–765.
Nicoletti F, Bruno V, Copani A, Casabona G, Knöpfel T. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: a new target for the therapy of neurodegenerative disorders? Trends Neurosci 1996; 19: 267–271.
Tanabe Y, Masu M, Ishii T, Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S. A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuron 1992; 8: 169–179.
Hayashi Y, Momiyama A, Takahashi T., et al. Role of a metabotropic glutamate receptor in synaptic modulation in the accessory olfactory bulb. Nature 1993; 366: 687–690.
Saugstad JA, Kinzie JM, Mulvihill ER, Segerson TP, Westbrook GL. Cloning and expression of a new member of the L-2-amino- 4-phosphonobutyric acid-sensitive class of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Mol Pharmacol 1994; 45: 367–372.
Duvoisin RM, Zhang C, Ramonell K. A novel metabotropic glutamate receptor expressed in the retina and olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 1995; 15: 3075–3083.
Pin JP, Waeber C, Prezeau L, Bockaert J, Heinemann SF. Alternative splicing generates metabotropic glutamate receptors inducing different patterns of calcium release in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 10331–10335.
Grandes P, Mateos JM, Ruegg D, Kuhn R, Knöpfel T. Differential cellular localization of three splice variants of the mGluR1 metabotropic glutamate receptor in rat cerebellum. Neuroreport 1994; 5: 2249–2252.
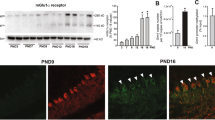
Mateos JM, Benitez R, Elezgarai I, et al. Immunolocalization of the mGluR1b splice variant of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 at parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses in the rat cerebellar cortex. J Neurochem 2000; 74: 1301–1309.
Mateos JM, Osorio A, Azkue JJ, et al. Parasagittal compartmentalization of the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR1b in the cerebellar cortex. Eur J Anatomy 2001 (in press).
Phillips T, Makoff A, Murrison E, et al. Immunohistochemical localisation of mGluR7 protein in the rodent and human cerebellar cortex using subtype specific antibodies. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1998; 57: 132–141.
Kinoshita A, Shigemoto R, Ohishi H, van der Putten H, Mizuno N. Immunohistochemical localization of metabotropic glutamate receptors, mGluR7a and mGluR7b, in the central nervous system of the adult rat and mouse: a light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 1998; 393: 332–352.
Neki A, Ohishi H, Kaneko T, Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N. Metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR2 and mGluR5 are expressed in two non-overlapping populations of Golgi cells in the rat cerebellum. Neuroscience 1996; 75: 815–826.
Negyessy L, Vidnyanszky Z, Kuhn R, Knöpfel T, Gorcs TJ, Hamori J. Light and electron microscopic demonstration of mGluR5 metabotropic glutamate receptor immunoreactive neuronal elements in the rat cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 1997; 385: 641–650.
Ohishi H, Neki A, Mizuno N. Distribution of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR2, in the central nervous system of the rat and mouse: an immunohistochemical study with a monoclonal antibody. Neurosci Res 1998; 30: 65–82.
Takacs J, Markova L, Borostyankoi Z, Gorcs TJ, Hamori J. Metabotrop glutamate receptor type 1a expressing unipolar brush cells in the cerebellar cortex of different species: a comparative quantitative study. J Neurosci Res 1999; 55: 733–748.
Kinoshita A, Ohishi H, Nomura S, Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N. Presynaptic localization of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR4a, in the cerebellar cortex: a light and electron microscope study in the rat. Neurosci Lett 1996; 207: 199–202.
Mateos JM, Azkue J, Sarria R, Kuhn R, Grandes P, Knöpfel T. Localization of the mGlu4a metabotropic glutamate receptor in rat cerebellar cortex. Histochem Cell Biol 1998; 109: 135–139.
Mateos JM, Elezgarai I, Benitez R, et al. Clustering of the group III metabotropic glutamate receptor 4a at parallel fiber synaptic terminals in the rat cerebellar molecular layer. Neurosci Res 1999; 35: 71–74.
Makoff AJ, Phillips T, Pilling C, Emson P. Expression of a novel splice variant of human mGluR1 in the cerebellum. Neuroreport 1997; 8: 2943–2947.
Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N. Distribution of the mRNA for a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1) in the central nervous system: an in situ hybridization study in adult and developing rat. J Comp Neurol 1992; 322: 121–135.
Simonyi A, Miller LA, Sun GY. Region-specific decline in the expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 mRNA in rat brain during aging. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2000; 82: 101–106.
Bradley SR, Rees HD, Yi H, Levey AI, Conn PJ. Distribution and developmental regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 7a in rat brain. J Neurochem 1998; 71: 636–645.
Ichise T, Kano M, Hashimoto K, et al. mGluR1 in cerebellar Purkinje cells essential for long-term depression, synapse elimination, and motor coordination. Science 2000; 288: 1832–1835.
Hashimoto K, Watanabe M, Kurihara H, et al. Climbing fiber synapse elimination during postnatal cerebellar development requires signal transduction involving G alpha q and phospholipase C beta 4. Prog Brain Res 2000; 124: 31–48.
Kano M, Hashimoto K, Chen C, et al. Impaired synapse elimination during cerebellar development in PKC gamma mutant mice. Cell 1995; 83: 1223–1231.
Audinat E, Knöpfel T, Gahwiler BH. Responses to excitatory amino acids of Purkinje cells’ and neurones of the deep nuclei in cerebellar slice cultures. J Physiol (Lond) 1990; 430: 297–313.
Llano I, Marty A, Armstrong CM, Konnerth A. Synaptic- and agonist-induced excitatory currents of Purkinje cells in rat cerebellar slices. J Physiol 1991; 434: 183–213.
Misra C, Brickley SG, Wyllie DJ, Cull-Candy SG. Slow deactivation kinetics of NMDA receptors containing NR1 and NR2D subunits in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol 2000; 525 Pt 2: 299–305.
Vranesic I, Batchelor A, Gahwiler BH, Garthwaite J, Staub C, Knöpfel T. Trans-ACPD-induced Ca2 signals in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuroreport 1991; 2: 759–762.
Staub C, Vranesic I, Knöpfel T. Responses to metabotropic glutamate receptor activation of cerebellar Purkinje cells: Induction of an inward current. Eur J Neurosci 1992; 4: 832–839.
Lingenhöhl K, Knöpfel T, Olpe H-R. Multiphasic responses of cerebellar Purkinje cells to 1S, 3R-ACPD: An in vivo study. Neurosci Res 1993; 18: 223–228.
Lingenhöhl K, Olpe H-R, Bendali N, Knöpfel T. Phenylglycine derivatives antagonize the excitatory response of Purkinje cells to (1S,3R)-ACPD: An in vivo and in vitro study. Neurosci Res 1993; 18: 229–234.
Linden DJ, Smeyne M, Connor JA. Trans-ACPD, a metabotropic receptor agonist, produces calcium mobilization and an inward current in cultured cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurophysiol 1994; 71: 1992–1998.
Vranesic I, Staub C, Knöpfel T. Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors induces an outward current which is potentiated by methylxanthines in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neurosci Res 1993; 16: 209–215.
Llano I, Dreessen J, Kano M, Konnerth A. Intradendritic release of calcium induced by glutamate in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron 1991; 7: 577–583.
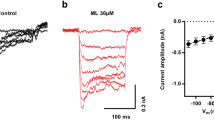
Tempia F, Alojado ME, Strata P, Knöpfel T. Characterization of the mGluR1-mediated electrical and calcium signaling in Purkinje cells of mouse cerebellar slices. J Neurophysiol 2001; 86: 1389–1397.
Hirono M, Konishi S, Yoshioka T. Phospholipase C-independent group I metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated inward current in mouse Purkinje cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998; 251: 753–758.
Tempia F, Miniaci MC, Anchisi D, Strata P. Postsynaptic current mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptors in cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Neurophysiol 1998; 80: 520–528.
Netzeband JG, Parsons KL, Sweeney DD, Gruol DL. Metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists alter neuronal excitability and Ca2+ levels via the phospholipase C transduction pathway in cultured Purkinje neurons. J Neurophysiol 1997; 78: 63–75.
Knöpfel T, Anchisi D, Alojado ME, Tempia F, Strata P. Elevation of intradendritic sodium concentration mediated by synaptic activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Eur J Neurosci 2000; 12: 2199–2204.
Batchelor AM, Madge DJ, Garthwaite J. Synaptic activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the parallel fibre-Purkinje cell pathway in rat cerebellar slices. Neuroscience 1994; 63: 911–915.
Batchelor AM, Knöpfel T, Gasparini F, Garthwaite J. Pharmacological characterization of synaptic transmission through mGluRs in rat cerebellar slices. Neuropharmacology 1997; 36: 401–403.
Finch EA, Augustine GJ. Local calcium signalling by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate in Purkinje cell dendrites. Nature 1998; 396: 753–756.
Takechi H, Eilers J, Konnerth A. A new class of synaptic response involving calcium release in dendritic spines. Nature 1998; 396: 757–760.
Wang SS, Denk W, Hausser M. Coincidence detection in single dendritic spines mediated by calcium release. Nat Neurosci 2000; 3: 1266–1273.
Batchelor AM, Vranesic I, Del Principe F, Garthwaite J, Knöpfel T. The synaptic potential mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptors is not associated with a substantial elevation of cytosolic free calcium concentration in Purkinje cells. Neuroreport 1996; 7: 1949–1952.
Reichelt W and Knöpfel T. Metabotropic glutamate receptors probe slow clearance of synaptically released glutamate in the cerebellar molecular layer. Soc Neurosci Abstr 1999; 25: 992.
Kase M, Miller DC, Noda H. Discharges of Purkinje cells and mossy fibres in the cerebellar vermis of the monkey during saccadic eye movements and fixation. J Physiol 1980; 300: 539–555.
Gabbiani F, Midtgaard J, Knöpfel T. Synaptic integration in a model of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurophysiol 1994; 72: 999–1009.
Mitchell SJ, Silver RA. GABA spillover from single inhibitory axons suppresses low-frequency excitatory transmission at the cerebellar glomerulus. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 8651–8658.
Batchelor AM, Garthwaite J. Frequency detection and temporally dispersed synaptic signal association through a metabotropic glutamate receptor pathway. Nature 1997; 385: 74–77.
Boxall AR. GABAergic mIPSCs in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells are modulated by TrkB and mGluR1-mediated stimulation of Src. J Physiol 2000; 524 Pt 3: 677–684.
Pekhletski R, Gerlai R, Overstreet LS, et al. Impaired cerebellar synaptic plasticity and motor performance in mice lacking the mGluR4 subtype of metabotropic glutamate receptor. J Neurosci 1996; 16: 6364–6373.
Lu YM, Knöpfel T. Up- and down regulation of P-type CA-2+channels by two different metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes. Soc Neurosci Abstr 1994; 20: 1468.
Perroy J, Prezeau L, De Waard M, Shigemoto R, Bockaert J, Fagni L. Selective blockade of P/Q-type calcium channels by the metabotropic glutamate receptor type 7 involves a phospholipase C pathway in neurons. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 7896–7904.
Ito M, Kano M. Long-lasting depression of parallel fiber Purkinje cell transmission induced by conjunctive stimulation of parallel fibers and climbing fibers in the cerebellar cortex. Neurosci Letters 1982; 33: 253–256.
Ito M, Sakurai M, Tongroach P. Climbing fibre induced depression of both mossy fibre responsiveness and glutamate sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol (Lond) 1982; 324: 113–134.
Ekerot CF, Kano M. Long-term depression of parallel fibre synapses following stimulation of climbing fibres. Brain Res 1985; 342: 357–360.
Ito M. Long-term depression. Ann Rev Neurosci 1989; 12: 85–102.
Ito M, Karachot L. Long-term desensitization of quisqualatespecific glutamate receptors in Purkinje cells investigated with wedge recording from rat cerebellar slices. Neurosci Res 1989; 7: 168–171.
Linden DJ, Connor JA. Participation of postsynaptic PKC in cerebellar long-term depression in culture. Science 1991; 254: 1656–1659.
Crepel F, Jaillard D. Pairing of pre- and postsynaptic activities in cerebellar Purkinje cells induces long-term changes in synaptic efficacy in vitro. J Physiol 1991; 432: 123–141.
Linden DJ, Dickinson MH, Smeyne M, Connor JA. A long-term depression of AMPA currents in cultured cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Neuron 1991; 7: 81–89.
Miyata M, Finch EA, Khiroug L, et al. Local calcium release in dendritic spines required for long-term synaptic depression. Neuron 2000; 28: 233–244.
Bezprozvanny I, Watras J, Ehrlich BE. Bell-shaped calciumresponse curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature 1991; 351: 751–754.
Lev-Ram V, Jiang T, Wood J, Lawrence DS, Tsien RY. Synergies and coincidence requirements between NO, cGMP, and Ca2+ in the induction of cerebellar long-term depression. Neuron 1997; 18: 1025–1038.
Wang YT, Linden DJ. Expression of cerebellar long-term depression requires postsynaptic clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Neuron 2000; 25: 635–647.
Ito M. Mechanisms of motor learning in the cerebellum. Brain Res 2000; 886: 237–245.
Hansel C, Linden DJ. Long-term depression of the cerebellar climbing fiber-Purkinje neuron synapse. Neuron 2000; 26: 473–482.
Callaway JC, Lasser-Ross N, Ross WN. IPSPs strongly inhibit climbing fiber-activated [Ca2+]i increases in the dendrites of cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurosci 1995; 15: 2777–2787.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knöpfel, T., Grandes, P. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in the cerebellum with a focus on their function in Purkinje cells. Cerebellum 1, 19–26 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02941886
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02941886