Abstract
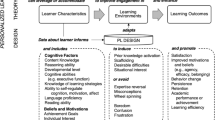
CHARACTERISTICS OF LEARNERS interact with instruction to influence its effectiveness. These characteristics include not only subject-specific prerequisite knowledge and motivation but also prior knowledge, metacognitive skills, learning strategies, and expectations. This article shows how these characteristics affect learning and discusses the implications for designing and evaluating computer-assisted instruction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avner, R.A., Moore, C., & Smith, S. (1980). Active external control: A basis for superiority of CBI.Journal of Computer-based Instruction, 6 (4), 115–118.
Bransford, J.D. (1982). Comparisons of successful and unsuccessful learners. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York.
Brown, A.L. (1978). Knowing when, where, and how to remember: A problem of metacognition. In R. Glaser (Ed.),Advances in instructional psychology, 1, 77–165. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Jaeger, M. (1988, March). Zaps, booms, & whistles.The Computing Teacher, pp. 20–22.
Miller, G.A. (1956). The magical number seven, plus or minus two: Some limits on our capacity for processing information.Psychological Review, 63, 81–97.
Ross, S.M. & Rakow, E.A. (1981). Learner control versus program control as adaptive strategies for selection of instructional support on math rules.Journal of Educational Psychology, 73 (5), 745–753.
Sherwood, G.E.F. & Taylor, A.E. (1946).Calculus. New York: Prentice-Hall.
Steinberg, E.R. (1977). Review of student control in computer-assisted instruction.Journal of Computer-Based Instruction, 3 (3), 84–90.
Steinberg, E.R. (1983, January). Reviewing the instructional effectiveness of computer courseware.Educational Technology, 23, 17–19.
Steinberg, E.R. (1984).Teaching computers to teach. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Steinberg, E.R. (1989). Cognition and learner control: A literature review 1977–1988.Journal of Computer-Based Instruction, 16 (4), 117–121
Sternberg, R.J. (1986, March–April). Inside intelligence.American Scientist, 74, 137–143.
Tennyson, C.L., Tennyson, R.D., & Rothen, W. (1980). Content structure and instructional control strategies as design variables in concept acquisition.Journal of Educational Psychology, 72 (4), 499–505.
Tennyson, R.D. & Buttrey, T. (1980). Advisement and management strategies as design variables in computer-assisted instruction.Educational Communication and Technology Journal, 28, 169–176. Reprinted in D.F. Walker & R.D. Hess (Eds.), (1984).Instructional software: Principles and perspectives for design and use. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinberg, E.R. The centrality of learner characteristics in computer-assisted instruction. J. Comput. High. Educ. 1, 49–58 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02941634
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02941634