Abstract
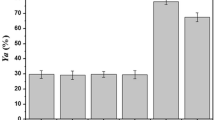
Candida cylindracea lipase was immobilized by adsorption on acid washed glass beads. It was observed that protein loading of the support depends on the size of the particle, with smaller particle containing higher amount of protein per unit weight. Initial reaction rate linearly varied up to enzyme concentration of 17.25 U/mL. Amount of free fatty acids produced was linearly proportional up to the enzyme loading of 1650 μg/g of bead. Achievement of chemical equilibrium took longer time in the case of less protein loading. Degree of hydrolysis was found to decrease in second and third consecutive batch operations on repeated use of immobilized lipase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kosugi, Y; H. Suzuki, and T. Funada (1988) Hydrolysis of beef tallow by lipase fromPseudomonas sp.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 31: 349–356.
Wang, Y. J., J. Y. Sheu, F. F. Wang, and J. F. Shaw (1988) Lipase catalyzed oil hydrolysis in the absence of added emulsifier.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 31: 628–633.
Hoq, M. M., T. Yamane, S. Shimizu, T. Funada, and S. Ishida (1985) Continuous hydrolysis of olive oil by lipase in microporous hydrophobic membrane bioreactor.J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 62: 1016–1021.
Khor, H. T., N. H. Tan, and C. L. Chua (1986) Lipase catalyzed hydrolysis of palm oil.J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 63: 538–540.
Murty, V. R. C., J. Bhat, and P. K. A. Muniswaran (2002) Hydrolysis of oils by using immobilized lipase enzyme: A review.Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 7: 57–66.
Kang, S. T. and J. S. Rhee (1989) Characteristics of immobilized lipase catalyzed hydrolysis of olive oil of high concentration in reverse phase system.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 33: 1469–1476.
Tsai, S. W. and C. L. Chiang (1991) Kinetics, Mechanism, and time course analysis of lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of high concentration of olive oil in AOT-isooctane reversed micelles.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 38: 206–211.
Prazeres, D. M. F., F. A. P. Garcia, and J. M. S. Cabral (1993) An ultrafiltration membrane bioreactor for the lipolysis of olive oil in reversed micellar media.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 41: 761–770.
Yang, D. and J. S. Rhee (1992) Continuous hydrolysis of olive oil by immobilized lipase in organic solvent.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 40: 748–752.
Yamane, T., M. M. Hoq, and S. Shimizu (1986) Kinetics of continuous hydrolysis of olive oil by lipase in microporous hydrophobic membrane bioreactor.J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 35: 10–17.
Kosugu, Y., H. Tanaka, and N. Tomizuka (1990) Continuous hydrolysis of oil by immobilized lipase in a counter-current reactor.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 36: 617–622.
Padmini, P., S. K. Rakshit, and A. Baradarajan (1993) Lipase catalyzed hydrolysis of Rice bran oil by free and immobilized enzyme system in batch stirred reactor.Bioprocess Eng. 9: 103–106.
Wu, J.-Y. and H.-S. Weng (1991) Transient response method for evaluating the rate constants of reactions over immobilized enzymes.Biotechnol. Bioeng. 37: 922–926.
Kwon, D. Y. and J. S. Rhee (1986) A simple and rapid colorimetric method for determination of free fatty acid for lipase assay.J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 63: 89–92.
Mary Aann, K. M., M. H. Suzanne, L. L. Bieber, and N. E. Tolbert (1978) A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples.Anal. Biochem. 87: 206–210.
Lowry, O. H., N. J. Rosenbrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265.
Bailey, J. E. and D. F. Ollis (1986)Biochemical Engineering Fundamentals, 2nd ed., Mc. Graw-Hill, New York, USA.
Murty, V. R. C., J. Bhat, and P. K. A. Muniswaran (2002) Prediction of continuous rectors performance based on batch reactor deactivation data of immobilized lipase.Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 7: 225–230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murty, V.R., Bhat, J. & Muniswaran, P.A. Hydrolysis of rice bran oil using immobilized lipase in a stirred batch reactor. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 7, 367–370 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02933523
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02933523