Abstract
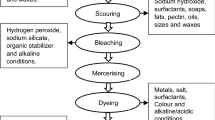
Textile wastewater from the Pusan Dyeing Industrial Complex (PDIC) was treated utilizing a two-stage continuous system, composed of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor and an activated sludge reactor. The effects of color and organic loading rates were studied by varying the hydraulic retention time and influent glucose concentration. The maximum color load to satisfy the legal discharge limit of color intensity in Korea (400 ADMI, unit of the American Dye Manufacturers Institute) was estimated to be 2,700 ADMI·L−1 day−1. This study indicates that the two-stage anaerobic/aerobic reaction system is potentially useful in the treatment of textile wastewater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banat, I. M., P. Nigam, D. Singh, and R. Marchant (1996) Microbial decolorization of textile-dye-containing effluents: a review.Bioresource Technol. 58: 217–227.
Shaul, G. M., T. J. Holdsworth, C. R. Dempsey, and K. A. Dostal (1991) Fate of water soluble azo dyes in the activated sludge process.Chemosphere 22: 107–119.
Seshadri, S., P. L. Bishop, and A. M. Agha (1994) Anaerobic/aerobic treatment of selected azo dyes in wastewater.Waste Manage. 14: 127–137.
FitzGerald, S. W. and P. L. Bishop (1995) Two stage anaerobic/aerobic treatment of sulfonated azo dyes.J. Environ. Sci. Health A30: 1251–1276.
Haug, W., A. Schmidt, B. Nortemann, D. C. Hempel, A. Stolz, and H. J. Knackmuss (1991) Mineralization of the sulfonated azo dye Mordant Yellow 3 by a 6-aminonaphthalene-2-sulfonate-degrading bacterial consortium.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 3144–3149.
Sponza, D. T. and M. Isik (2002) Decolorization and azo dye degradation by anaerobic/aerobic sequential process.Enzyme Microb. Technol. 31: 102–110.
Oxspring, D. A., G. McMullan, W. F. Smyth, and R. Marchant (1996) Decolourisation and metabolism of the reactive textile dye, Remazol Black B, by an immobilized microbial consortium.Biotechnol. Lett. 18: 527–530.
Panswad, T., A. Techovanich, and J. Anotai (2001) Comparison of dye wastewater treatment by normal and anoxic+anaerobic/aerobic SBR activated sludge processes.Wat. Sci. Technol. 43: 355–362.
Ganesh, R., G. D. Boardman, and D. Michelsen (1994) Fate of azo dyes in sludge.Wat. Res. 28: 1367–1376.
Li, Q., J. Wu, G. Chen, J. Yu, and P. L. Yue (1997) Anaerobic-aerobic biological treatment of textile wastewater by fluidized bed reactors.Proceedings of APBioChEC’97. October 20–23. Beijing, China.
Sen, S. and G. N. Demirer (2003) Anaerobic treatment of real textile wastewater with a fluidized bed reactor.Wat. Res. 37: 1868–1878.
Oh, Y-K, M. S. Park, E.-H. Seol, S.-J. Lee, and S. Park (2003) Isolation of hydrogen-producing bacteria from granular sludge of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor.Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 8: 54–57.
Kim, M. G., W. R. Ryu, and M. H. Cho (1997) Removal of anthraquinone dyes in dye wastewater by microbial adsorption and coagulation.Kor. J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 12: 1–7.
Ahn, Y. and S. Park (2003) Microbial and physicochemical monitoring of granular sludge during start-up of thermophilic UASB reactor.J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 13: 378–384.
Nakamura, Y. and G. Mtui (2003) Anaerobic fermentation of woody biomass treated by various methods.Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 8: 179–182.
A. P. H. A., A. W. W. A., and W. P. C. F. (1995)Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater. 19th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, USA.
Oh Y-K, S.-H. Lee, H.-S. Kim, Y.-J. Kim, S.-J. Lee, and S. Park (1999) Biodegradation of a reactive dye, Remazol Black B in a UASB reactor.Kor. J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 14: 688–695.
Donlon, B. A., E. Razo-Flores, M. Luijten, H. Swarts, G. Lettinga, and J. Field (1997) Detoxification and partial mineralization of the azo dye Mordant Orange 1 in a continuous upflow anaerobic sludge-blanket reactor.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 47: 83–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, YK., Kim, YJ., Ahn, Y. et al. Color removal of real textile wastewater by sequential anaerobic and aerobic reactors. Biotechnol Bioproc E 9, 419–422 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02933068
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02933068