Abstract
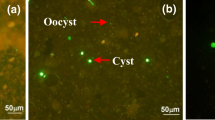
Giardia lamblia is a parasitic protozoa which is transmitted in the form of a cyst through untreated water and also treated drinking water. Since its presence in water has led to frequent outbreaks of giardiasis and death in many countries, the removal and disinfection of this protozoan cyst from the water supply are of great concern for public health. This study examined the disinfection characteristics ofG. lamblia cysts isolated from a Korean patient with giardiasis. When using sodium hypochlorite includdig 5 or 10 ppm chlorine, the killing rate was initially rapid however, the disinfection slowed down and a Blog reduction could not be achieved even after 2 h. The disinfection effectiveness was also reduced at a lower temperature, thereby implying that the risk of a giardiasis outbreak will be higher in the winter season. A CT (concentration time) curve was constructed based on the results with sodium hypochlorite for use in designing and predicting disinfection performance. The organic chlorination disinfectant SDIC (sodium dichloroisocyanurate) produced a lower pH and a much higher residual effect than sodium hypochlorote. The disinfection of cysts by SDIC continued steadily throughout 2 h of contact, although the initial killing rate was lower than that with sodium hypochlorite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Despommier, D. D., R. W. Gwadz, and P. J. Hotez (1995)Parasitic Diseases. 3rd ed., pp. 144–150. Springer-Verlag, NY, USA.
Kulda, J. and E. Nohynkova (1995)Giardia in humans and animals. In: J. P. Kreier (ed.).Parasitic Protozoa. Vol. 10, pp. 258–324. Academic Press, San Diego, USA.
Lujan, H. D., M. R. Mowatt, and T. E. Nash (1997) Mechanisms ofGiardia lamblia differentiation into cysts.Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61: 294–304.
Galal-Gorchev, H. (1996) Chlorine in water disinfection.Pure Appl. Chem. 68: 1731–1735.
LeChevallier, M. W., W. D. Norton, and R. G. Lee (1991)Giardia andCryptosposidium spp. in filtered drinking water supplies.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 2617–2621.
Keister, D. B. (1983) Axenic cultivation ofGiardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile.Trans. Royal. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 77: 487–488.
Hong, W. S., K. J. Kim, and K. Lee (2000) Optimized conditions forin vitro high density encystation ofGiardia lamblia.J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 10: 529–531.
Gillin, F. D., S. E. Boucher, S. S. Rossi, and D. S. Reiner (1989)Giardia lamblia: The roles of bile, lactic acid, and pH in the composition of the life cyclein vitro.Exp. Parasitol. 69: 164–174.
Schupp, D. G. and S. L. Erlandsen (1987) A new method to determineGiardia cyst viability: Correlation of fluorescein diacetate and propidium iodide staining with animal infectivity.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 704–707.
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (1995)Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 19th ed., Section 4500.
Office of Water (1999)Alternative Disinfectants and Oxidants Guideline Manual. Chapter 2. US EPA 815-R-99-014.
AWWA (1999)Water Quality and Treatment. 5th ed., Chapter 14 McGraw-Hill, NY, USA.
Stumm, W. and J. J. Morgan (1981)Aquatic Chemistry. 2nd ed., Chapter 7. John Wiley & Sons, NY, USA.
Oie, S. and A. Kamiya (1995) Disinfection of feeding bottles by sodium hypochlorite or sodium dichloroisocyanurate.Biomed. Lett. 51: 57–62.
Nicholl, P. and M. Prendergast (1998) Disinfection of shredded salad ingredients with sodium dichloroisocyanurate.J. Food. Process. Preserv. 22: 67–68.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K., Hong, W. & Lee, K. Disinfection characteristics of waterborne pathogenic protozoaGiardia lamblia . Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 6, 95–99 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931953
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931953