Abstract
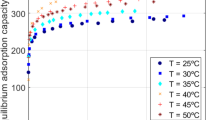
This paper compares regression and neural network modeling approaches to predict competitive biosorption equilibrium data. The regression approach is based on the fitting of modified Langmuir-type isotherm models to experimental data. Neural networks, on the other hand, are non-parametric statistical estimators capable of identifying patterns in data and correlations between input and output. Our results show that the neural network approach outperforms traditional regression-based modeling in correlating and predicting the simultaneous uptake of copper and cadmium by a microbial biosorbent. The neural network is capable of accurately predicting unseen data when provided with limited amounts of data for training. Because neural networks are purely data-driven models, they are more suitable for obtaining accurate predictions than for probing the physical nature of the biosorption process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sag, Y. and T. Kutsal (2001) Recent trends in the biosorption of heavy metals: a review.Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 6: 376–385.
Pagnanelli, F., M. Trifoni, F. Beolchini, A. Exposito, L. Toro, and F. Veglio (2001) Equilibrium biosorption studies in single and multi-metal systems.Process Biochem. 37: 115–124.
Klimmer, S., H.-J. Stan, A. Wilke, G. Bunke, and R. Buchholz (2001) Comparative analysis of the biosorption of cadmium, lead, nickel, and zinc by algae.Environ. Sci. Technol. 35: 4283–4288.
Lee, M.-G., J.-H. Lim, and S.-K. Kam (2002) Biosorption characteristics in the mixed heavy metal solution by biosorbents of marine brown algae.Kor. J. Chem. Eng. 19: 277–284.
Li, Q., S. Wu, G. Liu, X. Liao, X. Deng, D. Sun, Y. Hu, and Y. Huang (2004) Simultaneous biosorption of cad mium (II) and lead (II) ions by pretreated biomass ofPhanerochaete chrysosporium.Sep. Purif. Technol. 34: 135–142.
Kang, S. Y., J. U. Lee, and K. W. Kim (2005) Metal removal from wastewater by bacterial sorption: kinetics and competition studies.Environ. Technol. 26: 615–624.
Pagnanelli, F., S. Mainelli, S. De Angelis, and L. Toro (2005) Biosorption of protons and heavy metals onto olive pomace: modeling of competition effects.Water Res. 39: 1639–1651.
Sag, Y. (2001) Biosorption of heavy metals by fungal biomass and modeling of fungal biosorption: a review.Sep. Purif. Methods 30: 1–48.
Pagnanelli, F., A. Esposito, and F. Veglio (2002) Multimetallic modeling for biosorption of binary systems.Water Res. 36: 4095–4105.
Aksu, Z., U. Acikel, E. Kabasakal, and S. Tezer (2002) Equilibrium modeling of individual and simultaneous biosorption of chromium (VI) and nickel (II) onto dried activated sludge.Water Res. 36: 3063–3073.
Ma, W. and J. M. Tobin (2003) Development of multimetal binding model and application to binary metal biosorption onto peat biomass.Water Res. 37: 3967–3977.
Chang, J.-S. and J.-C. Huang (1998) Selective adsorption/recovery of Pb, Cu, and Cd with multiple fixed beds containing immobilized bacterial biomass.Biotechnol. Prog. 14: 735–741.
Texier, A. C., Y. Andres, C. Faur-Brasquet, and P. Le Cloirec (2002) Fixed-bed study for lanthanide (La, Eu, Yb) ions removal from aqueous solutions by immobilizedPseudomonas aeruginosa: experimental data and modelization.Chemosphere 47: 333–342.
Chu, K. H. (2004) Prediction of two-metal biosorption equilibria using a neural network.Eur. J. Mineral Proc. Environ. Protect. 3: 119–127.
Hornik, K., M. Stinchcombe, and H. White (1989) Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators.Neural Netw. 2: 359–366.
Hornik, K. (1991) Approximation capabilities of multilayer feedforward networks.Neural Netw. 4: 251–257.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, K.H., Kim, E.Y. Predictive modeling of competitive biosorption equilibrium data. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 11, 67–71 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931871
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931871