Abstract
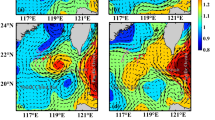
Based on experiment data of the Sino-German comprehensive investigations in the Bohai Sea in 1998 and 1999, a simple coupled pelagic-benthic ecosystem multi-box model is used to simulate the ecosystem seasonal variation. The pelagic sub-model consists of seven state variables: phytoplankton, zooplankton, TIN, TIP, DOC, POC and dissolved oxygen (DO). The benthic sub-model includes macro-benthos, meiobenthos, bacteria, detritus, TIN and TIP in the sediment. Besides the effects of solar radiation, water temperature and the nutrient from sea bottom exudation, land-based inputs are considered. The impact of the advection terms between the boxes is also considered. Meanwhile, the effects of the microbial-loop are introduced with a simple parameterization. The seasonal variations and the horizontal distributions of the ecosystem state variables of the Bohai Sea are simulated. Compared with the observations, the results of the multi-box model are reasonable. The modeled results show that about 13% of the photosynthesis primary production goes to the main food loop, 20% transfers to the benthic domain, 44% is consumed by the respiration of phytoplankton, and the rest goes to DOC. Model results also show the importance of the microbial food loop in the ecosystem of the Bohai Sea, and its contribution to the annual zooplankton production can be 60%–64%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T. R., P. J. Williams, and B. Le, 1998. Modelling the seasonal cycle of dissolved organic carbon at station E1 in English Channel.Estuar. Coast. Shelf. S.,46: 93–109.
Baretta, J., and P. Ruardij, 1988.Tidal Flat Estuaries: Simulation and Analysis of the Ems Estuary. Spring-Verlag, Berlin, 353 pp.
Ebenhoh, W., C. Kohlmeier and P. J. Radford, 1995. The benthic biological submodel in the European regional seas ecosystem model.N. J. S. R.,33 (3/4): 423–452.
Fei, Z. L., 1986. Study on the water color and transparency in the Bohai Sea.J. Oceanogr. Huanghai & Bohai Seas,4(1): 33–40 (in Chinese).
Gao, H. W., 1998. Modeling annual cycle of primary production in different regions of the Bohai Sea.Fish. Oceanogr.,7 (3/4): 258–264.
Huang, D. J., J. L. Su, and J. O. Backhaus, 1999. Modeling of the seasonal thermal stratification & baroclinic circulation in the Bohai Sea.Cont. Shelf Res.,19: 1485–1509.
Jiao, N. Z., and T. Xiao, 1995. Bacterial secondary production in Jiaozhou Bay.Chin. Sci. Bull.,40 (9): 829–832.
Kang, Y. D., 1991. The seasonal variation and biomass distribution of phytoplankton in Bohai Sea.Mar. Aquat. Res.,12: 31–54 (in Chinese).
Lin, Q. L., Y. L. Song, Q. F. Yang, Y. Cui, Z. H. Xin,et al., 1991. Chemical environments of the aquaculture area of Bohai Sea.Mar. Fish. Res.,12: 11–30 (in Chinese).
Liu, S. M., J. Zhang, Z. G. Yu, H. T. Chen, and Q. Z. Yao, 1999. Benthic fluxes of dissolved inorganic nitrogen in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea.Environ. Sci.,20(2): 12–16 (in Chinese).
Liu, S. M., J. Zhang, and S. J. Wen, 2003. Pore water nutrient regeneration in shallow coastal Bohai Sea, China.J. Oceanogr.,59: 377–385.
National Meteorological Center of China (NMC, China), 1995,Marine Climatological Atlas for Continental and Adjacent Sea Areas of China. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 600 pp.
Radach, G., and A. Moll, 1993. Estimation of the variability of production by simulating annual cycles of phytoplankton in the central North Sea.Prog. Oceanogr.,31: 339–419.
Tang, Q. S., and T. X. Meng, 1997.Atlas of the Ecological Environment and Living Resources in the Bohai Sea. Qingdao Press, Qingdao, 242 pp (in Chinese).
Wang, H., and W. M. Wang, 1994. A three-dimensional numerical simulation of the winter-time circulation in the Bohai Sea.J. Ocean Univ. Chin.,24(4): 463–470 (in Chinese).
Wei, H., J. Sun, A. Moll, and L. Zhao, 2004. Phytoplankton dynamics in the Bohai Sea—observation and modeling.J. Mar. Syst.,44: 233–251.
Wu, Z. M., G. Y. Yu, Z. N. Zhang, X. K. Lu, S. H. Gao,et al., 1999. A pelagic ecosystem model and simulation of the northern part of Jiaozhou Bay (II) A simulation study on the pelagic ecosystem seasonal variations.J. Ocean Univ. Chin.,29(3): 429–435 (in Chinese).
Wu, Z. M., X. M. Zhai, Z. N. Zhang, G. Y. Yu, S. H. Gao,et al., 2001. A simulation analysis on the pelagicbenthic coupling ecosystem of northern Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China.Acta Oceano. Sinica,20(3): 443–453.
Xiao, T., 2000. The roles of marine bacteria in macrobial food loop.Mar. Sci.,24(7): 4–6.
Yu, G. Y., Z. M. Wu, Z. N. Zhang, X. K. Lu, P. G. Xi,et al., 1999. A pelagic ecosystem model and simulation of the northern part of Jiaozhou Bay (I) Introduction to pelagic ecosystem model.J. Ocean Univ. Chin.,29 (3): 421–428 (in Chinese).
Yu, Z. G., T. Z. Mi, B. D. Xie, Q. Z. Yao, and J. Zhang, 2000. Changes of the environmental parameters and their relationship in recent twenty years in the Bohai Sea.Mar. Environ. Sci.,19(1): 15–19 (in Chinese).
Zhang, J., 1996. Nutrient elements in large Chinese estuaries.Cont. Shelf. Res.,16(8): 1023–1045.
Zhang, X. L., X. S. Guo, Z. M. Wu, J. H. You, and L. F. Yan, 2001. The observation analysis and calculation method studies of solar irradiation at sea surface for the Bohai Sea.Acta Oceano. Sinica,23(2): 46–51 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xinling, Z., Zengmao, W., Jie, L. et al. Modeling study of seasonal variation of the pelagic-benthic ecosystem characteristics of the Bohai Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 5, 21–28 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919368
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919368