Abstract
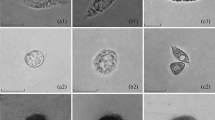
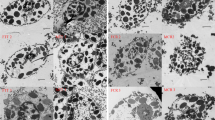
Light and electron microscopic studies were carried out in order to characterize haemocytes in the bivalve molluseMeretrix meretrix. According to nucleus and cytoplasm characters, four types of haemocytes were recognized: agranular haemocytes, lymphoid haemocyte, large granular and small granular haemocytes. Agranular hamocyte is the main cell type, accounting for 75%. It is agranular with rich organelles in cytoplasm, including mitochondria, golgi body and endoplasmic reticulum. Glycogen deposits were usually found in this cell type. The number of lymphoid haemocyte accounts for 1%–2%. This cell type is agranular and shows a high ratio of nucleus to cytoplasm. A few organelles were found. High electrondense granules with diameters of 0.2–0.5 μm and rich organelles were found in small granular haemocyte. The proportion of this cell type is about 15%. Rich granules of high electron-dense with diameters of 0.8–2.4 μm were found in large granular haemocyte. The proportion of this cell type is about 10%, and the quantity of organelles is the least.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auffret, M. 1989. Comparative study of the hemocytes of two cyster species: the European flat oyster,Ostrea edulis Linnaeus, and the Pacific oyster,Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg, 1793).J. Shellfish. Res.,8: 367–373.
Carballal, M. J., A. Villalba, and C. Lopez, 1998. Seasonal variation and effects of age, food availability, size, gonadal development, and parasitism on the hemogram ofMytilus galloprovincialis.J. Invertebr. Pathol.,72: 304–312.
Chen, Q., J. Yang, X. Wang, and A. Gao, 2001. Ultrastructure and classification of blood cells ofHaliotis discus hannai.J. Fish. Chin.,25: 492–495.
Cheng T. C., 1981. Bivalves. In:Inverbertebrate Bloods Cell. Ratcliffe, N. A., and A. F. Rowley, eds., Acdemic Press, London, 233–300.
Cheng, T. C., 1984. A classification of molluscan hemocytes based on functional evidences. In:Comparative Pathobiology, 6: Inverbrate Blood Cells and Serum Factors. Cheng, T. C., ed.: Plenum, New York, 111–146.
Friebel, B., and L. Renwrantz, 1995. Application of density gradient centrifugation for separation of eosinophilic and basophilic hemocytes fromMytilus edulis and characterization of both cell groups.Comp. Physiol. B.,112: 81–90.
Gary, W. W., N. M. Michael, A. K. Miles, and S. Claudia, 1996. Production of reactive oxygen species by hemocytes from the marine mussel,Mytilus edulis: lysosomal localization and effect of xenobiotics.Comp. Physiol. B.,113: 211–229.
Gray, D., 1993. Immunological memory.Ann. Rev. Immunol.,11: 49–77.
Hanton, C., L. E. Hawkins, and S. Hutchinson, 1998. The use of neutral retention assay to examine the effects of temperature and salinity on haemocytes of European flat oysterOstrea edulis (L).Comp. Physiol. B.,119: 619–623.
Leah, M. O., S. F. William, K. V. Aswani, and M. Ziad, 2003. Greater hemocyte bactericidal activity in oysters (Crassostrea virginica) from a relatively contaminated site in Pensacola Bay, Florida.Aquat. Toxicol.,64: 363–373.
Li, J., A. Shi, and Q. Li, 2000. Phagocytic activity of hemocytes from injuredAnodonta woodiana pacifica.J. Fish. Chin.,24: 399–402.
Liu, Z., S. Zhang, A. Yang, F. Du, L. Zhou,et al., 2003. Morphologic observation and phagocytosis property of the haemocytes of blood elamScipharca subrenata.High Technol. Lett.,10: 94–96.
Lopez, C., M. J. Carballal, C. Azebedo, and A. Villalba, 1997. Morphological charaction of the hemocyter of clam,Ruditapes decussatus (Molluses: Bivalvia).J. Invertebr. Pathol.,69: 51–57.
Marvin, R. A., E. F. Frank, and R. R. Francisco, 1995. In vivo chemoactivation of oyster hemocytes induced by bacteria seretion products.J. Invertebr. Pathol.,66: 287–292.
Nakayama, K., A. M. Nomoto, M. Nishijima, and T. Maruyama, 1997. Morphological and functional characterization of hemocytes in giant clamTridacna crocea.J. Invertebr. Pathol.,69: 105–111.
Patricia, M., S. Da, R. M. M. Aime, and A. B. Margherita, 2002. Effects ofBucephalus sp. (Trematoda: Bucephialidae) onPerna perna mussels from a culture station in Ratomes Grande Island, Brazil.J. Invertebr. Pathol.,79: 154–162.
Reade, P., and E. Reade, 1976. Phagocytosis in invertebrates: Studies on the hemocytes of the clamTridacna maxima.J. Invertebr. Pathol.,28: 281–290.
Robert, S. A., and E. B. Amy, 2001. Antibacterial activities of oyster (Crassostrea virginica) and mussel (Mytilus eduils andGeukensia demissa) plasma.Aquat. Living Resour.,14: 343–349.
Shen, Y., and L. Ma, 1993. Preliminary observation on haemocytes of freshwater peral oysterCristaria plicata Leach.Acta Hydrobiol. Sin.,17: 190–192.
Shi, A., A. Qiu, M. Tang, Y. Yu, H. Zhang,et al., 2001. Hemoculture ofAnodonta woodiana pacifica.Acta Hydrobiol. Sin.,25: 116–122.
Sun, H., and G. Li, 2001. Phagocytosis and scanning electron microscopy study ofChlamys farrsri Haemocytes.High Technol. Lett.,4: 16–19.
Wootton, E. C., E. A. Dyrynda, and N. A. Ratclife, 2003. Bivalve immunity: comparisons between the marine mussel (Mytilus edulis), the edible cockle (Cerastoderma edule) and the razor-shell (Ensis siliqua).Fish Shellfish Immunol.,15: 195–210.
Wootton, E. C., and R. K. Pipe, 2003. Structural and functional characterization of the blood cells of the bivalve mollusc,Scrobicularia plana.Fish Shellfish Immunol.,15: 249–262.
Xing, J., W. Zhang, and L. Zhou, 2003. Hemocyte types and antibacteia research ofChlamys farrsri.J. Ocean Univ. Chin.,33: 41–46 (in Chinese).
Zhang, F., and G. Li, 1999. Study on the generation of reactive oxygen species by hemocytes inHaliotis discus hannai.J. Fish. Chin.,6: 36–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanyan, Z., Sulian, R., Dexiu, W. et al. Structure and classification of haemocytes in the bivalve molluscMeretrix meretrix . J. Ocean Univ. China 5, 132–136 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919211
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919211