Abstract
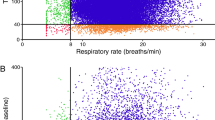
A respiratory inductance plethysmograph, Respitrace, was used to assess the respiratory effects of narcotic analgesia for the first 24 hours after surgery. Data were collected on-line from the plethysmograph with an Apple ][+ microcomputer and stored on disc for later analysis of respiratory rates and tidal volumes, and also periods of central or obstructive apnoea using the difference in phase angle between the abdominal and respiratory components. This involved the measurement of, on average, more than 20,000 breaths per patient and techniques of data compression were required to store this amount of information on a single floppy disc. Frequent nursing interventions reduced the accuracy of tidal volume and phase angle measurements, but respiratory rates were obtained accurately breath by breath.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashutosh K, Gilbert R, Auchincloss JH, Erlebacher J, Peppi D: Impedance pneumograph and magnetometer methods for monitoring tidal volume. J Appl Physiol 37: 964–966, 1974.
Catling JA, Pinto DM, Jordan C, Jones JG: Respiratory effects of analgesia after cholecystectomy: comparison of continuous and intermittent papaveretum. Br Med J 281: 478–480, 1980.
Chadha TS, Watson H, Birch S, Jenouri GA, Schneider AW, Cohn MA, Sackner MA: Validation of respiratory inductive plethysmography using different calibration techniques. Am Rev Respir Dis 125: 644–649, 1982.
Cohn MA, Rao BVA, Davis B, Watson H, Broundy MJ, Sackner JD, Sackner MA: Measurement of tidal ventilation and forced vital capacity in normals and patients with obstructive lung disease with a respiratory inductance plethysmograph. In: Stott FD, Raferty EB, Goulding L (eds) ISAM 1979: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Ambulatory Monitoring. Academic Press, London, 1980, pp 355–365.
Ford GT, Whitelaw WA, Cruse PJ, Rosenal T, Bosdech L: Diaphragm function after upper abdominal surgery. Am Rev Respir Dis 123: 186, 1981.
Gilbert R, Auchincloss JH, Brodsky J, Boden W: Changes in tidal volume, frequency, and ventilation induced by their measurement. J Appl Physiol 33: 252–254, 1972.
Hanning CD, Spence AA: Measurement of lung volumes and respiratory frequency. In: Spence AA (ed) Respiratory Monitoring in Intensive Care. Churchill Livingstone, London, 1982, pp 1–21.
Jordan C: Assessment of effects of drugs on respiration. Br J Anaesth 54: 763–781, 1982.
Konno K, Mead J: Measurement of the separate volume change of ribcage and abdomen during breathing. J Appl Physiol 22: 407–422, 1967.
Sackner JD, Nixon AJ, Davies B, Atkins N, Sackner MA: Non-invasive measurement of ventilation during exercise using a respiratory induction plethysmograph. Am Rev Respir Dis 122: 867–871, 1980.
Tusiewicz K, Bryan AC, Froese AB: Contribution of changing ribcage-diaphragm interactions to the ventilatory depression of halothane anesthesia. Anesthesiology 47: 327–337, 1977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodsman, N.B.A., Kenny, G.N.C., Rennie, R. et al. Data collection and analysis from a respiratory inductance plethysmograph. J Clin Monit Comput 4, 237–241 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915864
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915864